Abstract
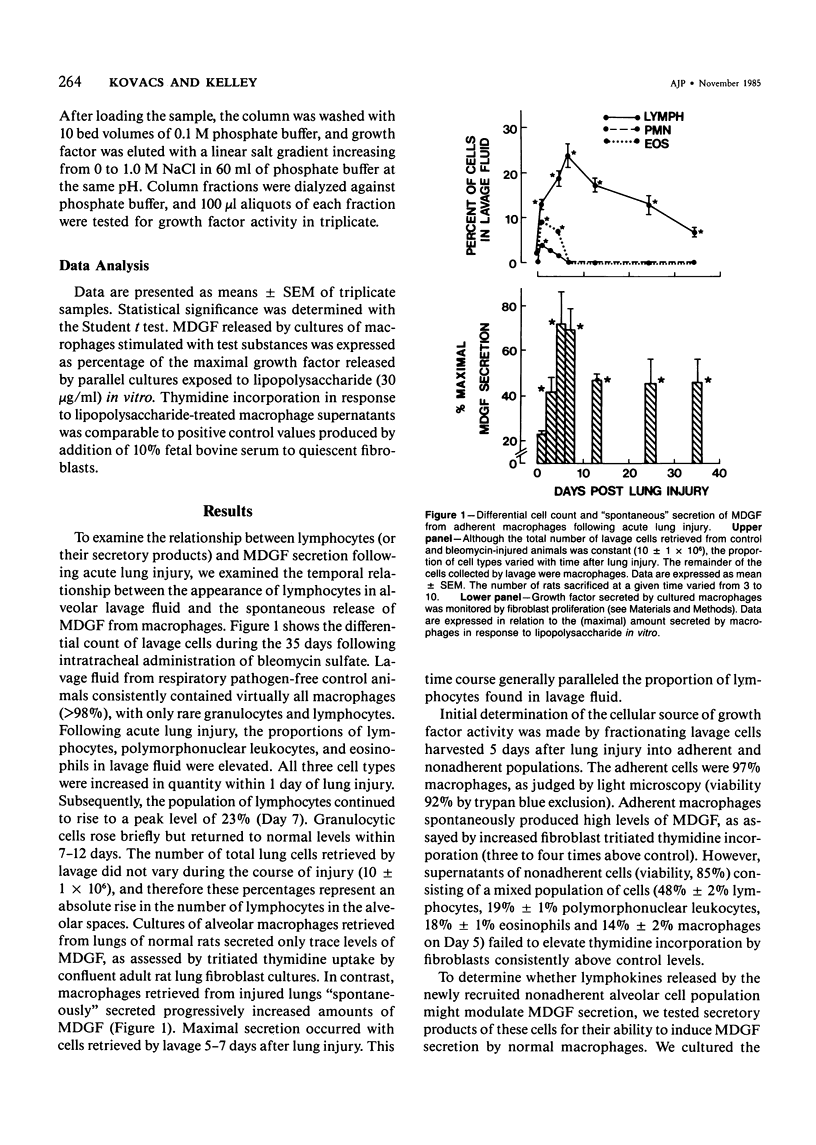
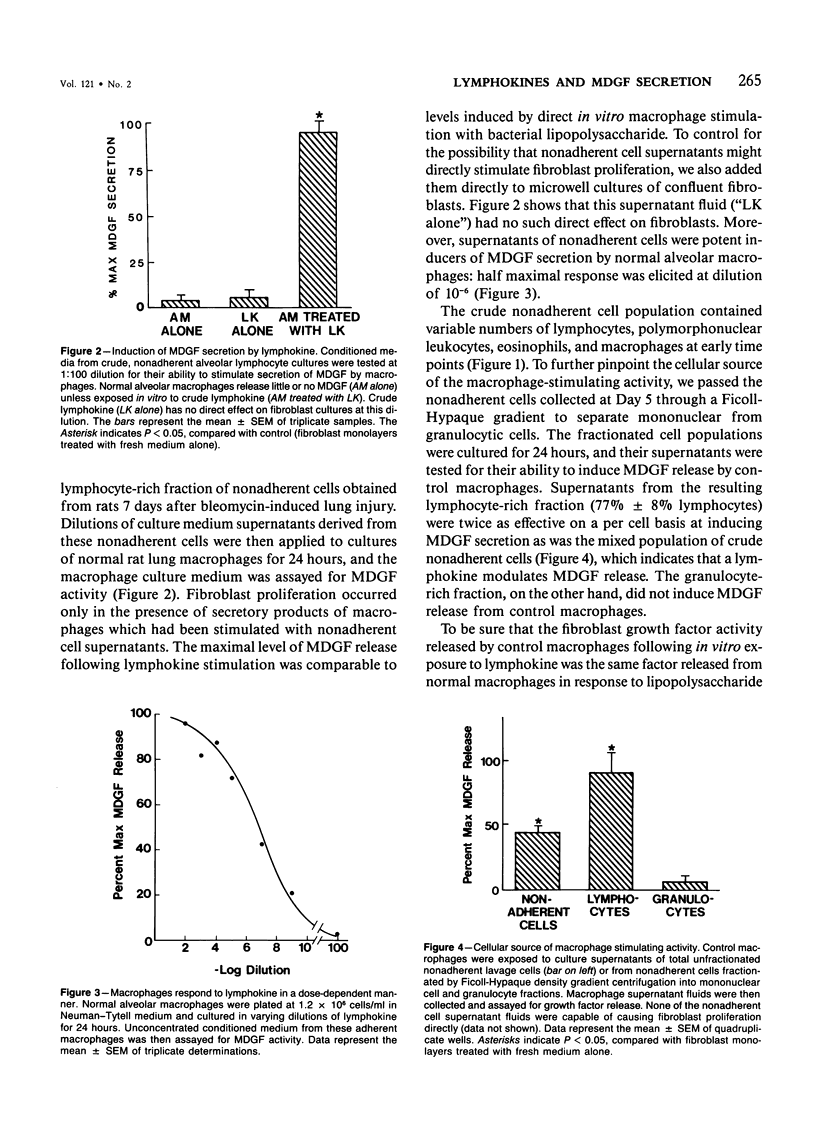
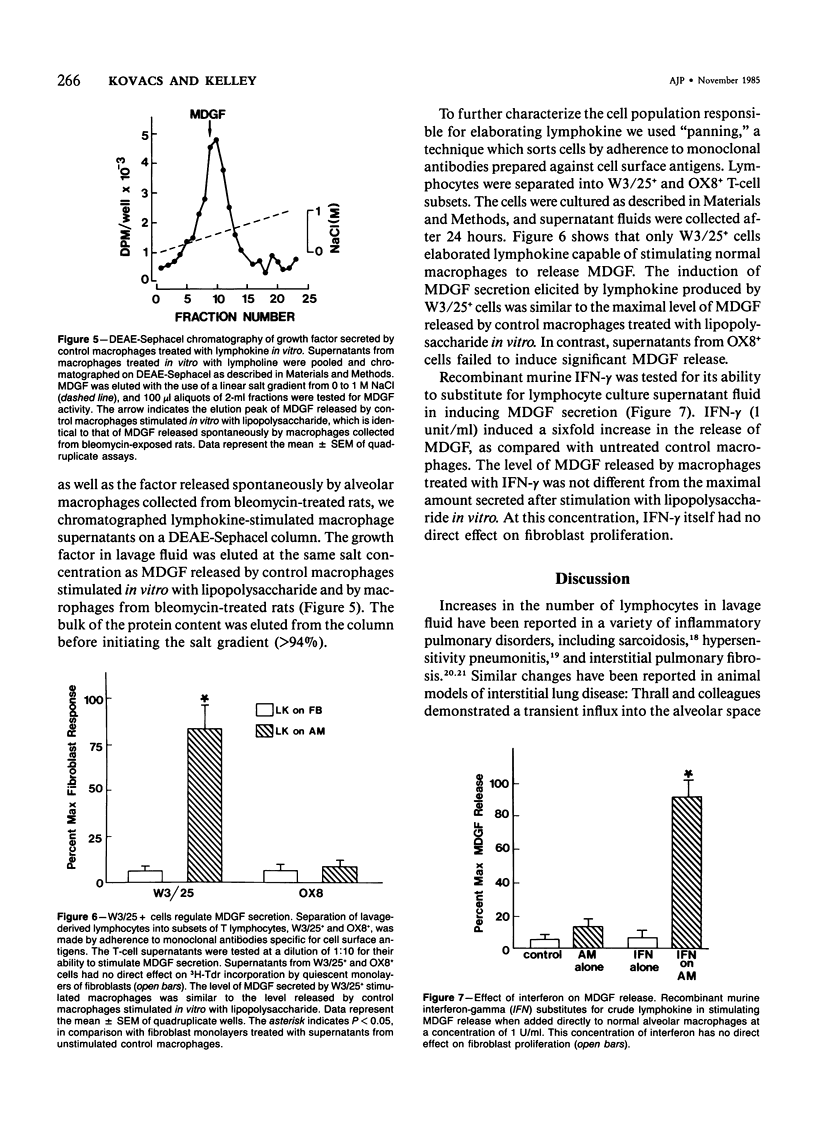
Rat alveolar macrophages secrete enhanced levels of a growth factor for fibroblasts following acute lung injury. The authors have previously identified this anionic, heat-labile substance as macrophage-derived growth factor (MDGF) and have now focused on how its release by alveolar macrophages is controlled following lung damage. In response to pulmonary injury induced with a single intratracheal instillation of bleomycin sulfate, the lymphocyte count rose from undetectable to 23% of the cells retrieved in lavage fluid. Spontaneous MDGF secretion by macrophages cultured from the same lungs generally paralleled the changes in lymphocyte counts over time. To test whether lymphokine(s) secreted by alveolar lymphocytes regulated MDGF secretion by macrophages in this model, the authors exposed normal macrophages harvested from control rat lungs to lymphokine preparations in vitro. Lymphokines provided a powerful stimulus to normal macrophages, inducing MDGF secretion at dilutions as low as 10(-6). Fractionating T-lymphocyte subsets by adherence to monoclonal antibodies indicated that the W3/25+ cells elaborated the macrophage-stimulating lymphokine, but that OX8+ cells did not. Furthermore, recombinant murine gamma interferon was capable of substituting for native lymphokine in activating MDGF secretion by normal macrophages. It is concluded that immune stimulation of fibroblast proliferation requires cooperative interaction of both lymphocytes and macrophages in this model of acute lung injury.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage growth factor for fibroblasts. Regulation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):806–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI110677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Analysis of airspace and interstitial mononuclear cell populations in human diffuse interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):7–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes J. E., Pledger W. J., Gillespie G. Y. Macrophage-derived growth factor for fibroblasts and Interleukin-1 are distinct entities. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Jan;35(1):115–129. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. G., Golightly M. G., Koren H. S. Potentiation of the cytolytic activity of peripheral blood monocytes by lymphokines and interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1220–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., Seager J., Groopman J. E., Berliner J. A., Haberland M. E., Edwards P. A., Golde D. W. Lymphokines secreted by an established lymphocyte line modulate receptor-mediated endocytosis in macrophages derived from human monocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2368–2373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K. C., Ross R. Human monocyte-derived growth factor(s) for mesenchymal cells: activation of secretion by endotoxin and concanavalin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Crabtree G. R., Bodwell J. E., Munck A. MLC-conditioned media stimulate an increase in Fc receptors on human macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):666–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Turton C. W., Heard B., Lukoszek A., Collins J. V., Salsbury A. J., Turner-Warwick M. Bronchoalveolar lavage in pulmonary fibrosis: comparison of cells obtained with lung biopsy and clinical features. Thorax. 1980 Jan;35(1):9–18. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J., Newman R. A., Evans J. N. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the rat. Prevention with an inhibitor of collagen synthesis. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Dec;96(6):954–964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs E. J., Kelley J. Secretion of macrophage-derived growth factor during acute lung injury induced by bleomycin. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Jan;37(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. Resistance to intracellular infection. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):439–445. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Karnovsky M. L., David J. R. Alterations of macrophage functions by mediators from lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1356–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Sharrow S. O., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Natural killer activity in the rat. II. Analysis of surface antigens on LGL by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2204–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Kazmierowski J. A., Roberts W. C., Frank M. M., Crystal R. G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon P. L., Farrar J. J., Dind P. D. Biochemical relationship between murine immune interferon and a killer cell helper factor. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrall R. S., Barton R. W., D'Amato D. A., Sulavik S. B. Differential cellular analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid obtained at various stages during the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Sep;126(3):488–492. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.3.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Martin G. R. Collagenase production by lymphokine-activated macrophages. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):261–263. doi: 10.1126/science.163038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Gately C. L. Modulation of fibroblast growth by a lymphokine of human T cell continuous T cell line origin. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1226–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Gillespie G. Y., Russell S. W., Pledger W. J. Mitogenic activity elaborated by macrophage-like cell lines acts as competence factor(s) for BALB/c 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jan;110(1):93–100. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W. Human macrophage-like cell line U937-1 elaborates mitogenic activity for fibroblasts. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Feb;33(2):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


