Abstract
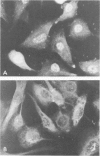
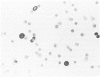
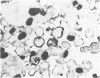
The isolation and characterization of a monoclonal antibody (C5F10) which identifies dividing cells in normal and neoplastic tissues (carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphoreticular malignancies) in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections is described. The antibody also recognizes rapidly dividing cells in normal and transformed cells in culture. A combination of autoradiography with 3H-thymidine and immunochemical localization of C5F10 showed that cells in S-phase of the cell cycle were weakly stained for C5F10, while dividing cells stained intensely with this antibody. The target structure of C5F10 appears to be different from the commonly recognized microtubule, intermediate filament and microfilament proteins and from the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (cyclin). This antibody may be a useful tool for readily detecting dividing cells in cell cultures and in tissue sections and may prove useful in studies to analyze the molecular basis of cell growth.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. A search for differential polypeptide synthesis throughout the cell cycle of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. Human proteins sensitive to neoplastic transformation in cultured epithelial and fibroblast cells. Clin Chem. 1982 Apr;28(4 Pt 2):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Fey S. J., Bellatin J., Larsen P. M., Arevalo J., Celis J. E. Identification of a nuclear and of a cytoplasmic polypeptide whose relative proportions are sensitive to changes in the rate of cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Binder L. I., Payne M. R., Bender P., Rebhun L., Steward O. Differential subcellular localization of tubulin and the microtubule-associated protein MAP2 in brain tissue as revealed by immunocytochemistry with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):394–410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00394.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Fey S. J., Larsen P. M., Celis A. Expression of the transformation-sensitive protein "cyclin" in normal human epidermal basal cells and simian virus 40-transformed keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3128–3132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S., Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Infection with vaccinia favors the selection of hybridomas synthesizing autoantibodies against intermediate filaments, one of them cross-reacting with the virus hemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1546–1553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M., De Mey J., Joniau M., Geuens S. Immunocytochemical visualization of microtubules and tubulin at the light- and electron-microscopic level. J Cell Sci. 1977 Dec;28:283–301. doi: 10.1242/jcs.28.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Mazié J. C., Rouyre S., Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G., Avrameas S. Murine hybridomas secreting natural monoclonal antibodies reacting with self antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2267–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKARI J. G. The polysaccharide behaviour of cancer antigens. Br Med J. 1958 Aug 9;2(5092):355–358. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5092.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Wallis K. T. Isolation of microtubule protein from chicken erythrocytes and determination of the critical concentration for tubulin polymerization in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8357–8364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper D. A., Kim H. Y., Berns M. W. Studies of a microtubule-associated protein using a monoclonal antibody elicited against mammalian mitotic spindles. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):503–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Saegusa J., Onodera T., Notkins A. L. Lymphocytes capable of making monoclonal autoantibodies that react with multiple organs are a common feature of the normal B cell repertoire. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2815–2817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki Y., Deng J. S., Tan E. M. A nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation and blast transformation. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1899–1909. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]