Abstract
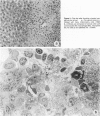
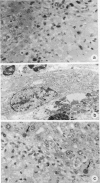
The healing process of focal hepatic injury produced by thrusting a liquid nitrogen-cooled or fire-heated needle in rat liver was investigated by light and electron microscopy and autoradiography. Twenty-four hours after the injury, necrotic areas were sharply demarcated from the surrounding normal hepatic tissue, and their margin was infiltrated with monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and platelets. Following the inflammatory infiltration, Ito cells, cholangiolar cells, and capillary endothelial cells proliferated in the peripheral areas of the necrosis. In accordance with the proliferation of Ito cells, collagen fibers markedly increased. Autoradiography demonstrated that cells proliferating in necrotic areas were predominantly Ito cells, and that hepatocytes adjacent to the damaged sites showed DNA synthesis. Necrotic and fibrotic areas were gradually decreased in size; and by 2 weeks, damaged sites were restored to almost normal histologic appearance, occasional scars remaining. The results of this study indicate that small focal hepatic injury is repaired locally by a mechanism resembling that of wound healing, and that Ito cells play an important role in that process.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Hovi T., Vaheri A. Fibronectin is produced by human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):602–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHER N. L. REGENERATION OF MAMMALIAN LIVER. Int Rev Cytol. 1963;15:245–300. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCHER N. L., SWAFFIELD M. N. THE RATE OF INCORPORATION OF LABELED THYMIDINE INTO THE DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID OF REGENERATING RAT LIVER IN RELATION TO THE AMOUNT OF LIVER EXCISED. Cancer Res. 1964 Oct;24:1611–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathal P. S. Presence of modified fibroblasts in cirrhotic livers in man. Pathology. 1972 Apr;4(2):139–144. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher N. L., Patel U., Cohen S. Hormonal factors concerned with liver regeneration. Ciba Found Symp. 1977;(55):95–107. doi: 10.1002/9780470720363.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Cunningham D. D. Initiation of check cell division by trypsin action at the cell surface. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):602–606. doi: 10.1038/268602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deimann W., Fahimi H. D. Hepatic granulomas induced by glucan. An ultrastructural and peroxidase-cytochemical study. Lab Invest. 1980 Aug;43(2):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrikant J. I. The kinetics of cellular proliferation in regenerating liver. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):551–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Hirschel B. J., Ryan G. B., Statkov P. R., Majno G. Granulation tissue as a contractile organ. A study of structure and function. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):719–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G. Reparative processes in mammalian wound healing: the role of contractile phenomena. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;48:187–219. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61745-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D., Nyfors A. Effect of methotrexate therapy in psoriatics on the Ito cells in liver biopsies, assessed by point-counting. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Aug;29(8):698–703. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.8.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Russell R. M., Boyer J. L., Glagov S., Bagheri S. A. Ultrastructural changes in livers of two patients with hypervitaminosis A. Am J Pathol. 1974 Sep;76(3):451–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries M. J., Ayad S. R. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by cathepsin D digests of fibronectin. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):811–813. doi: 10.1038/305811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO T., NEMOTO M. Uber die Kupfferschen Sternzellen und die Fettspeicherungszellen (fat storing cells) in der Blutkapillarenwand der memschlichen Leber. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1952 Oct;24(4):243–258. doi: 10.2535/ofaj1936.24.4_243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent G., Gay S., Inouye T., Bahu R., Minick O. T., Popper H. Vitamin A-containing lipocytes and formation of type III collagen in liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3719–3722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Takahashi Y., Shibasaki S. Cytological studies of fat-storing cells in the liver of rats given large doses of vitamin A. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 6;243(127):186–188. doi: 10.1038/newbio243186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J. Production of macrophage-dependent fibroblast-stimulating activity (M-FSA) by murine macrophages. Effects on BALBc 3T3 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Apr;113(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. A macrophage-dependent factor that stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):501–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Gabbiani G., Hirschel B. J., Ryan G. B., Statkov P. R. Contraction of granulation tissue in vitro: similarity to smooth muscle. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):548–550. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Feinman L., Fainsilber Z., Nakano M., Okazaki I., Lieber C. S. Mammalian collagenase increases in early alcoholic liver disease and decreases with cirrhosis. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 19;30(16):1379–1384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Patrick R. S. The role of perisinusoidal cells in hepatic fibrogenesis. An electron microscopic study of acute carbon tetrachloride liver injury. Lab Invest. 1972 Apr;26(4):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka M., Terayama H. Cathepsin D stimulates DNA synthesis and mitosis in mouse liver in vivo. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Mar;151(1):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okanoue T., Burbige E. J., French S. W. The role of the Ito cell in perivenular and intralobular fibrosis in alcoholic hepatitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1983 Sep;107(9):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST J., KLEIN A., HOFFMAN J. Responses of the liver to injury. Effects of age upon the healing pattern after acute carbon tetrachloride poisoning. Arch Pathol. 1960 Sep;70:314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran P. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Unanue E. R. Activated macrophages induce vascular proliferation. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):804–806. doi: 10.1038/269804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Uenfriend S. Hepatic fibrosis. Correlation of biochemical and morphologic investigations. Am J Med. 1970 Nov;49:707–721. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Balian G., Kang A. H. Induction of fibroblast chemotaxis by fibronectin. Localization of the chemotactic region to a 140,000-molecular weight non-gelatin-binding fragment. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):494–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauterberg J., Voss B., Pott G., Gerlach U. Connective tissue components of the normal and fibrotic liver. I. Structure, local distribution and metabolism of connective tissue components in the normal liver and changes in chronic liver diseases. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Jul 15;59(14):767–779. doi: 10.1007/BF01724682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Pérez-Tamayo R. Liver fibrosis. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1983;10:333–393. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363710-9.50012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The fibroblast and wound repair. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Feb;43(1):51–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb01109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph R., McClure W. J., Woodward M. Contractile fibroblasts in chronic alcoholic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1979 Apr;76(4):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Spector W. G. Macrophage turnover in inflamed connective tissue. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Aug 4;174(1040):269–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1970.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoshan S. Wound healing. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1981;9:1–26. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363709-3.50007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D. The molecular biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):653–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain A. J., McGowan J. A., Bucher N. L. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes by rat platelet-associated substance(s). In Vitro. 1982 Feb;18(2):108–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02796402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcker E., Schultze B., Heine W. D., Liebscher H. Wachstum und Regeneration in parenchymatösen Organen der Ratte. Autoradiographische Untersuchungen mit 3 H-Thymidin. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;125(3):306–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto Y., Helsel W. E., Wahl S. M. Macrophage production of fibronectin, a chemoattractant for fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake K. "Sternzellen" in the liver: perisinusoidal cells with special reference to storage of vitamin A. Am J Anat. 1971 Dec;132(4):429–462. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001320404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A., Hirsch J. G., Humphrey J. H., Spector W. G., Langevoort H. L. The mononuclear phagocyte system: a new classification of macrophages, monocytes, and their precursor cells. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(6):845–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]