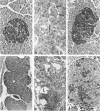
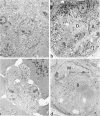
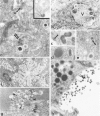
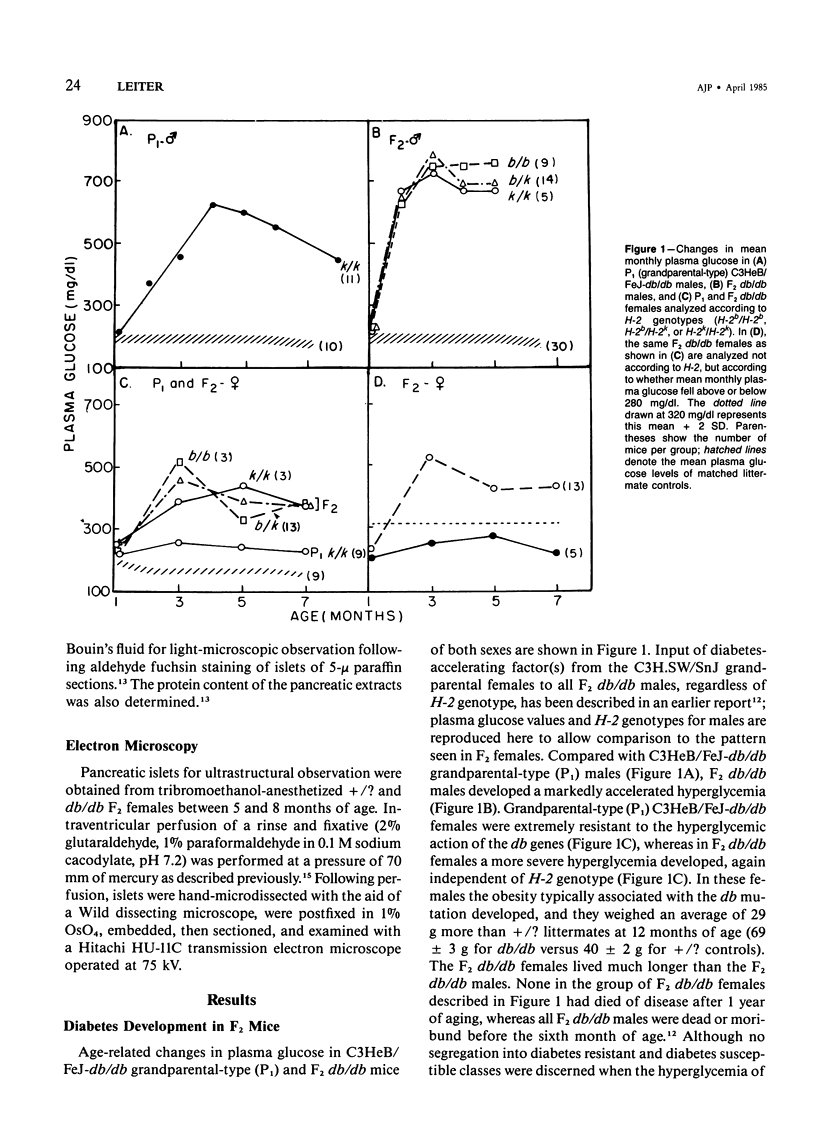
Abstract
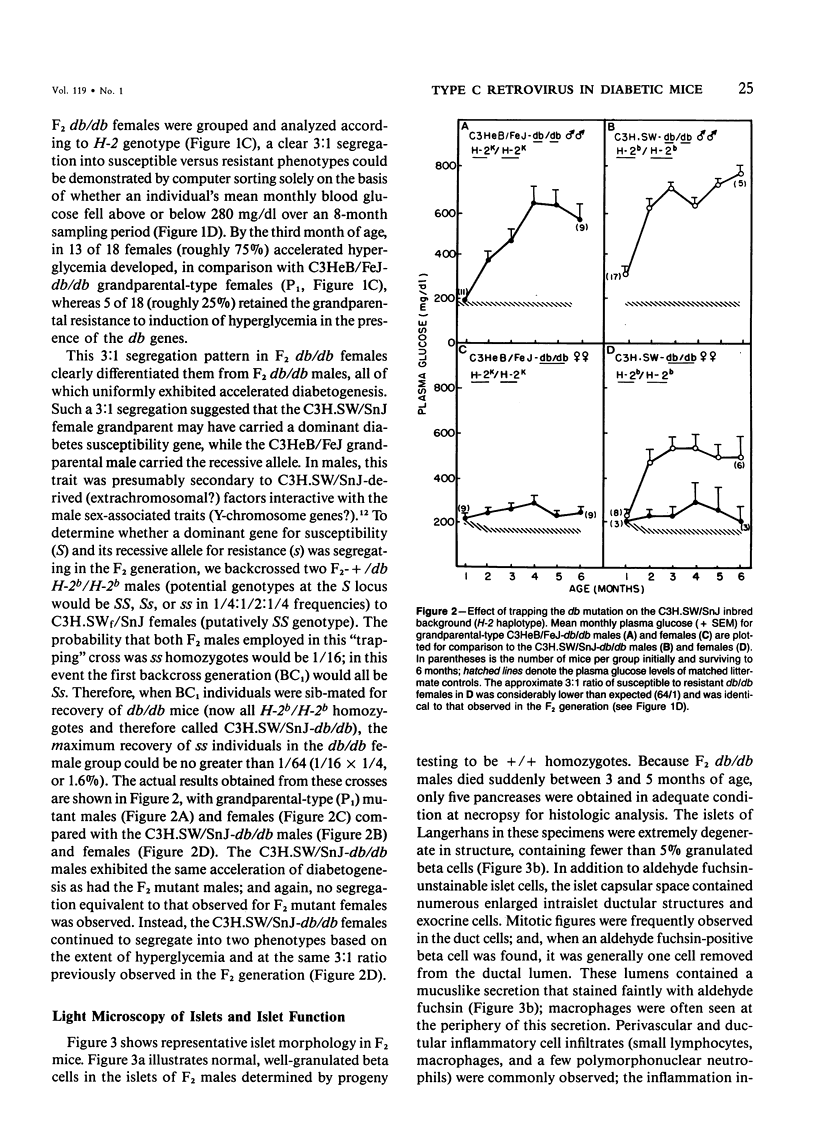
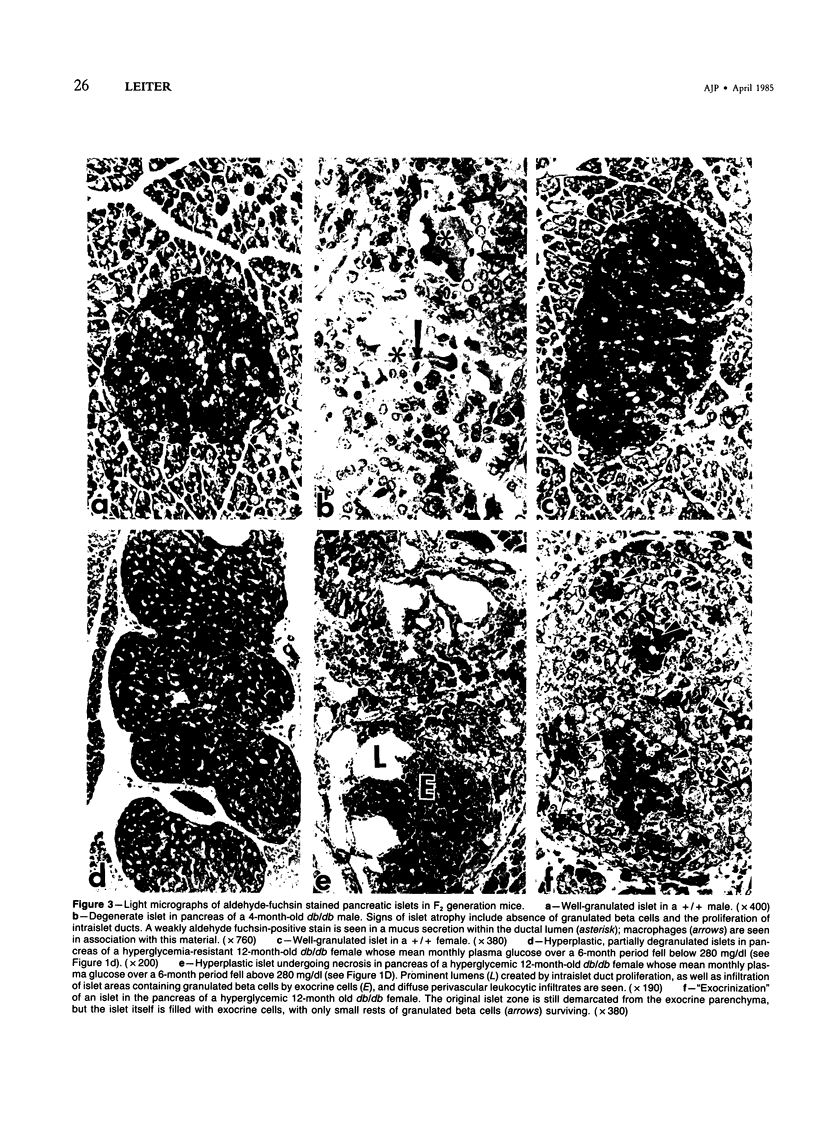
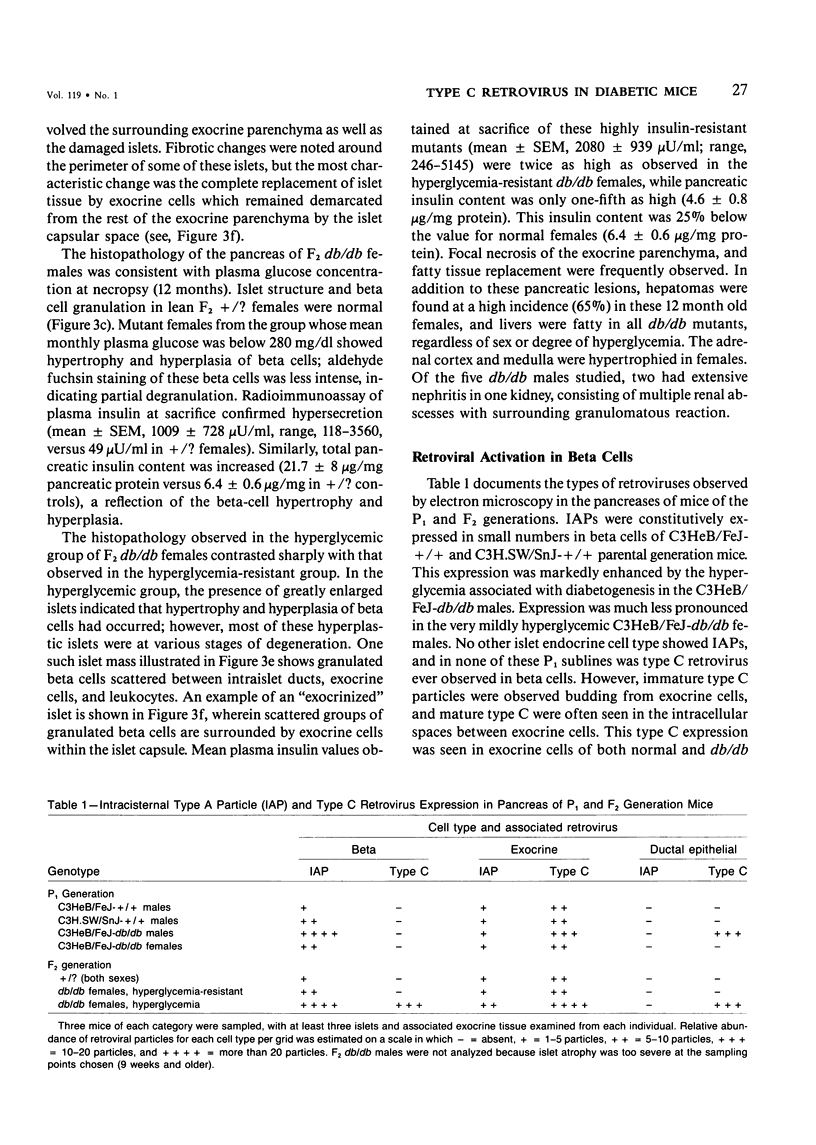
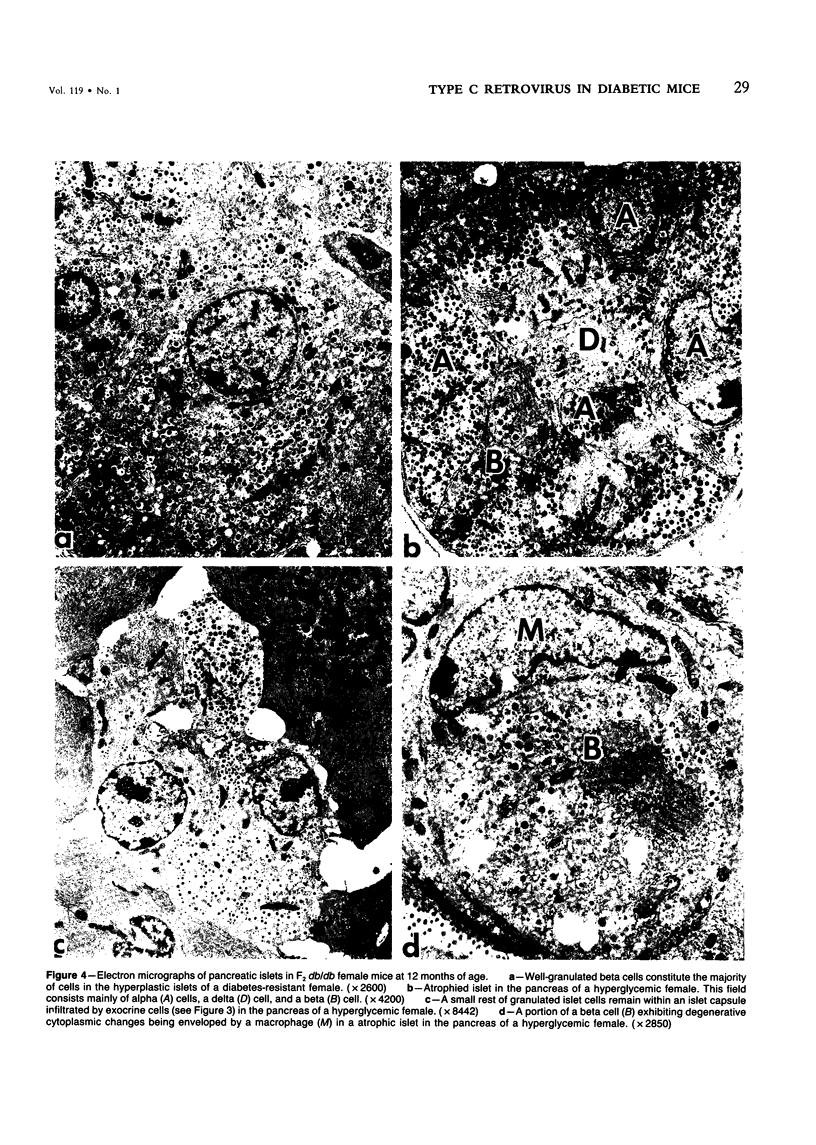
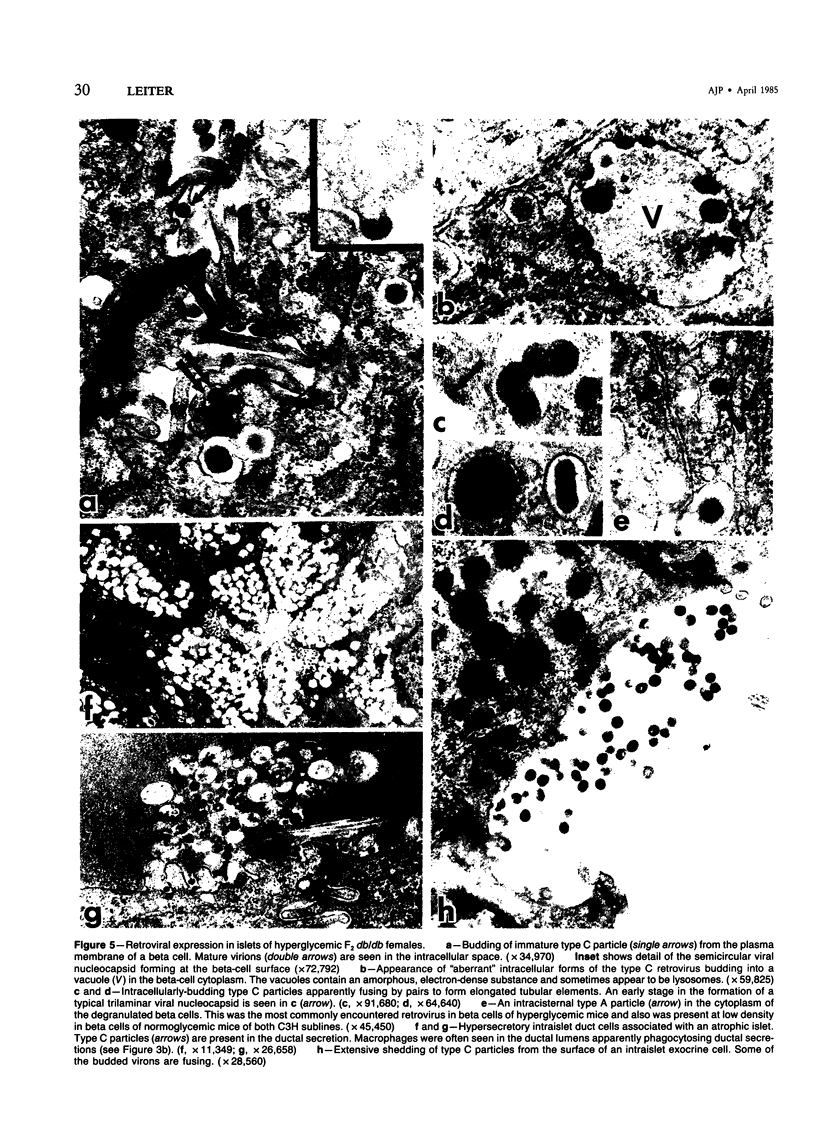
C3H.SW/SnJ females (haplotype H-2b) were mated with C3HeB/FeJ males (haplotype H-2k), which were heterozygous for the recessive mutation, diabetes (db). The object of the study was to analyze whether the H-2b haplotype conferred diabetes resistance to db/db males in the F2 generation. Severity of diabetes did not segregate with H-2 haplotype in this mouse model of diabetes. Instead, all F2 male mutants developed a much more severe diabetes syndrome than did "grandparental-type" C3HeB/FeJ-db/db males. Most surprisingly, unlike grandparental-type db/db females, which were uniformly resistant to the diabetogenic action of the db mutation, 75% of F2 db/db females developed severe diabetes. Ultrastructural comparison of beta cells in islets of these diabetic females versus those in the diabetes-resistant F2 mutants showed expression in the susceptible females of a type C retrovirus which budded extracellularly and intracellularly into vacuoles. No other islet endocrine cell type showed this expression, but intraislet exocrine cells as well as some ductal epithelial cells did produce type C particles. Macrophages were frequently observed in close association with the virus-expressing cell types. Failure of the diabetes acceleration factor(s) to segregate according to Mendelian expectations further suggested that type C retrovirus induction was linked to the accelerated pathogenesis of diabetes in the F2 generation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. M., Gardner M. B. Lower motor neuron degeneration associated with type C RNA virus infection in mice: neuropathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Apr;33(2):285–307. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197404000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appel M. C., Rossini A. A., Williams R. M., Like A. A. Viral studies in streptozotocin-induced pancreatic insulitis. Diabetologia. 1978 Oct;15(4):327–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02573827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiocchi M., Della Torre G., Della Porta G. Genetic control of endogenous C-type virus production in pancreatic acinar cells of C57BL/He and C57BL/6J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1892–1894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copelan E. A., Rinehart J. J., Lewis M., Mathes L., Olsen R., Sagone A. The mechanism of retrovirus suppression of human T cell proliferation in vitro. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):2017–2020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardenne M., Savino W., Gastinel L. N., Nabarra B., Bach J. F. Thymic dysfunction in the mutant diabetic (db/db) mouse. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1195–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray-Sachs M., Saï P., Boitard C., Assan R., Hamburger J. Anti-pancreatic immunity in genetically diabetic mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jan;51(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A. K., Murphy F. A. Murine oncornavirus activation in the pancreas during infection with Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Oct;55(4):917–923. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.4.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. T., Jr, Calarco P. G. Evidence for the cell surface expression of intracisternal A particle-associated antigens during early mouse development. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Hara I., Hang L. M., Elder J. H., McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Association of elevated serum glycoprotein gp70 with increased gp70 immune complex formation and accelerated lupus nephritis in autoimmune male BXSB mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 May;56(2):272–280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Elder J. H. Antibody directed to determinants of a Moloney virus derived MCF GP70 recognizes a thymic differentiation antigen. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1751–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka S., Satoh J., Fujiya H., Toyota T., Suzuki R., Itoh K., Kumagai K. Immunologic aspects of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse. Abnormalities of cellular immunity. Diabetes. 1983 Mar;32(3):247–253. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromann H., Christy M., Lernmark A., Nedergaard M., Nerup J. The low dose streptozotocin murine model of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: studies in vivo and in vitro of the modulating effect of sex hormones. Diabetologia. 1982 Mar;22(3):194–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00283752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIKE A. A., STEINKE J., JONES E. E., CAHILL G. F., Jr PANCREATIC STUDIES IN MICE WITH SPONTANEOUS DIABETES MELLITUS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:621–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Bedigian H. G. Intracisternal A-particles in genetically diabetic mice: identification in pancreas and induction in cultured beta cells. Diabetologia. 1979 Sep;17(3):175–185. doi: 10.1007/BF01219746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Coleman D. L., Hummel K. P. The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse. III. Effect of H-2 haplotype and sex. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1029–1034. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H. Genetic control of pathogenesis of diabetes in C3H mice. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex. Diabetes. 1984 Nov;33(11):1068–1071. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.11.1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal Type A particles in murine pancreatic B cells. Immunocytochemical demonstration of increased antigen (p73) in genetically diabetic mice. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):46–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiter E. H. The influence of genetic background on the expression of mutations at the diabetes locus in the mouse IV. Male lethal syndrome in CBA/Lt mice. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1035–1044. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melief C. J., Louie S., Schwartz R. S. Ecotropic leukemia viruses in congenic C57BL mice: natural dissemination by milk-borne infection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Sep;55(3):691–698. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.3.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Southern P., Rodriquez M., Lampert P. Virus persists in beta cells of islets of Langerhans and is associated with chemical manifestations of diabetes. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1440–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.6203172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass B., Vernon M. L., Peters R. L., Kelloff G. J. Mammary tumors, hepatocellular carcinomas, and pancreatic islet changes in C3H-Avy Mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Mar;60(3):611–621. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwizer R. W., Leiter E. H., Evans R. Macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity against cultured pancreatic islet cells. Transplantation. 1984 Jun;37(6):539–544. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198406000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staats J. Standardized nomenclature for inbred strains of mice: seventh listing for the International Committee on Standardized Genetic Nomenclature for Mice. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2083–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]