Abstract
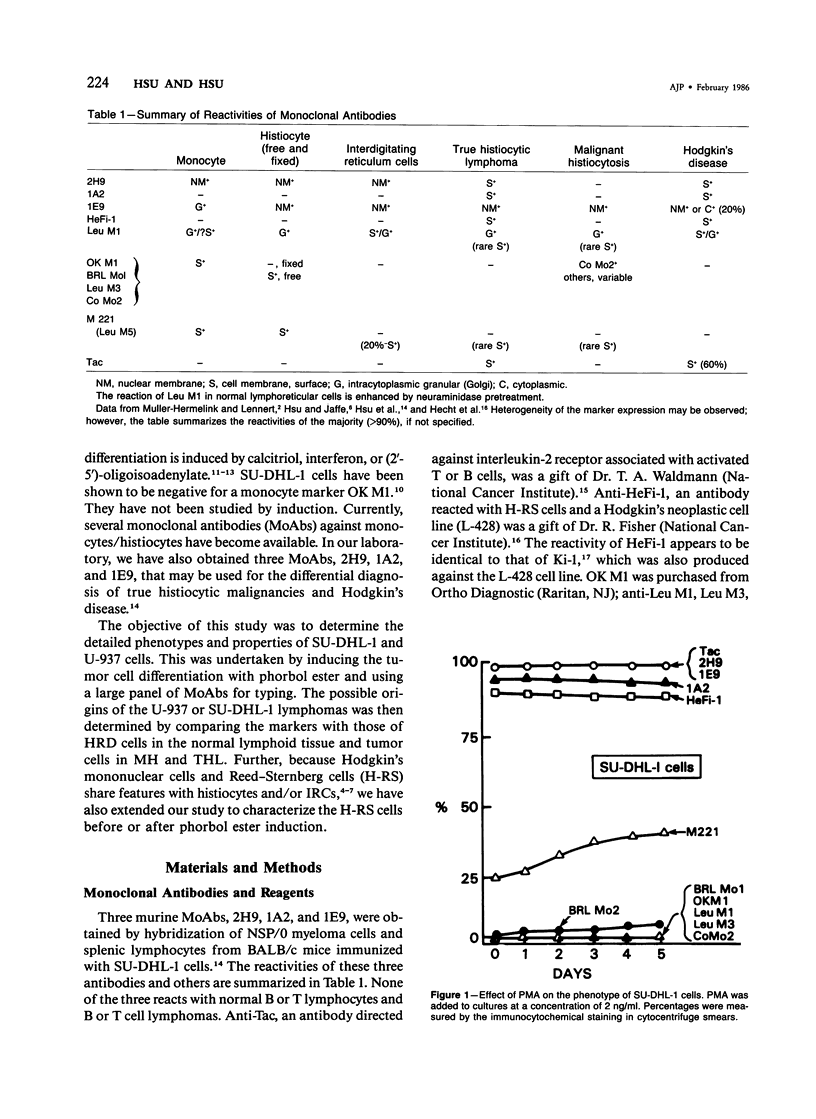
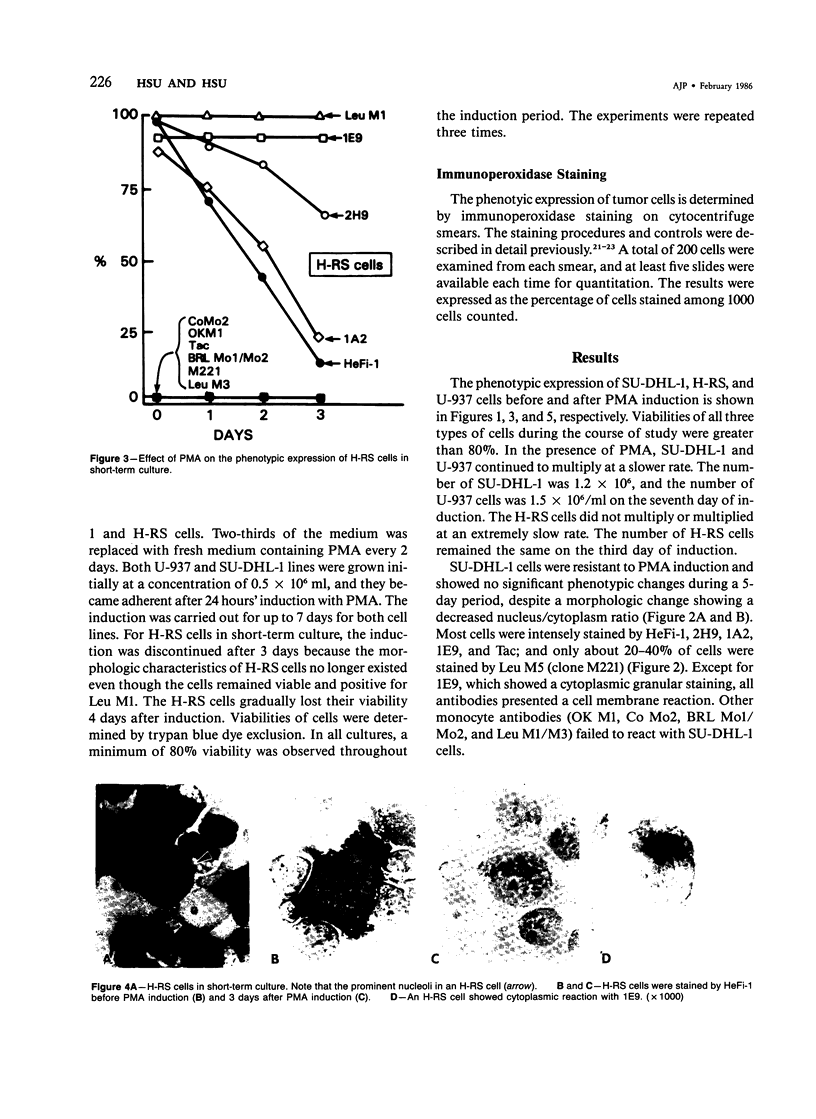
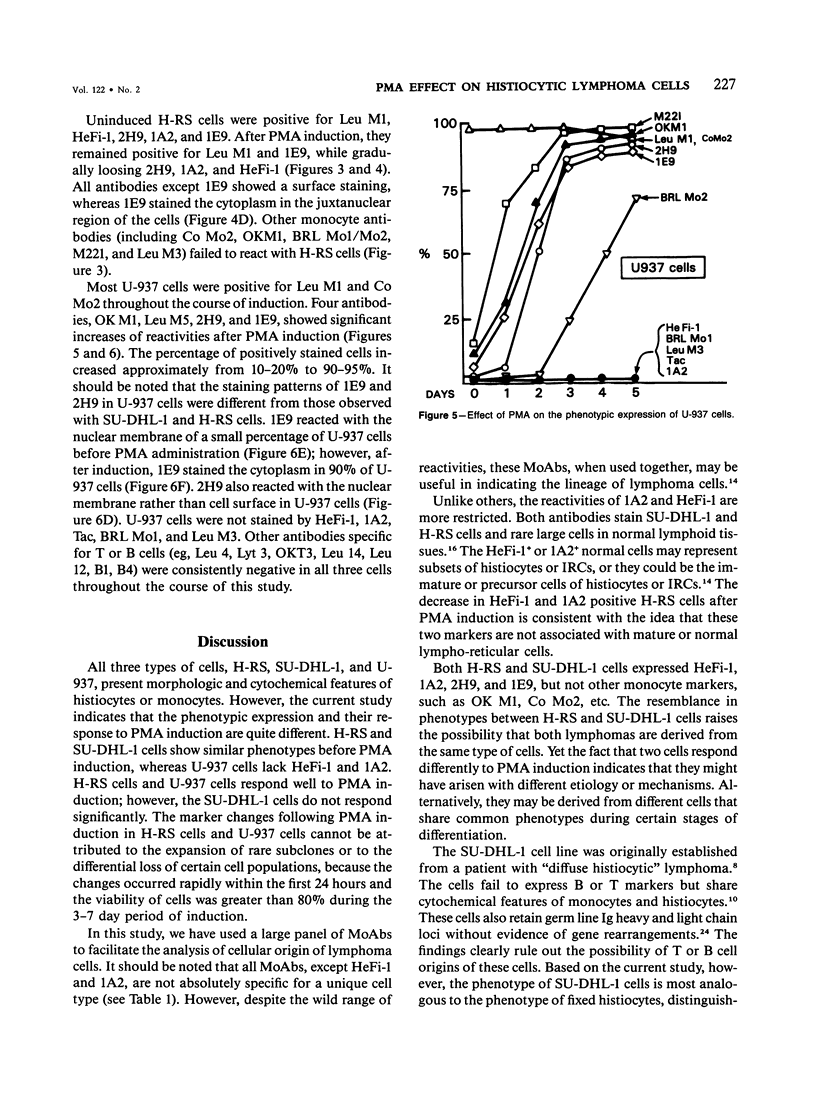
Hodgkin's mononuclear cells, Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) cells, and U-937 and SU-DHL-1 histocytic cell lines were induced to differentiate by phorbol ester in cultures. The phenotypes of cells were determined by a panel of antibodies specific for monocytes, histiocytes, and interdigitating reticulum cells. Before induction, SU-DHL-1 cells and H-RS cells expressed similar markers, such as HeFi-1, 2H9, 1A2, and 1E9. In addition, SU-DHL-1 cells were also stained by Tac and Leu M5. Other monocyte markers, including OK M1, Co Mo2, BRL Mo1, BRL Mo2, and Leu M3 were consistently negative in both types of cells. After induction, SU-DHL-1 cells conserved the same phenotype, but H-RS cells became negative for HeFi-1, 1A2, and 2H9. The U-937 cells expressed Leu M1 and Co Mo2 and became positive for Leu M5, OK M1, Co Mo2, BRL Mo2, 2H9, and 1E9 after phorbol ester induction. The U-937 cells did not express HeFi-1 or 1A2. The marker expression of H-RS cells, SU-DHL-1 cells, and U-937 cells were compared with those of histiocytes or interdigitating reticulum cells in lymphoid tissues and with neoplastic cells in true histiocytic lymphoma and malignant histiocytosis. It is concluded that SU-DHL-1, U-937, and H-RS cells are derived from or most closely related to fixed histiocytes, free histiocytes, and interdigitating reticulum cells, respectively. Our study further confirms the diagnosis of SU-DHL-1 as true histiocytic lymphoma but reveals that U-937 is a case of malignant histiocytosis rather than the previously diagnosed histiocytic lymphoma. The phenotypes and induction properties of SU-DHL-1 cells are quite different from those of U-937 cells, which suggests that true histiocytic lymphoma and malignant histiocytosis are two distinct disease entities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckstead J. H., Warnke R., Bainton D. F. Histochemistry of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):609–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl V., Kirchner H. H., Burrichter H., Stein H., Fonatsch C., Gerdes J., Schaadt M., Heit W., Uchanska-Ziegler B., Ziegler A. Characteristics of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):615–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. L., Levy R., Kim H., Henle W., Henle G., Kaplan H. S. Biology of the human malignant lymphomas. IV. Functional characterization of ten diffuse histiocytic lymphoma cell lines. Cancer. 1978 Nov;42(5):2379–2391. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197811)42:5<2379::aid-cncr2820420539>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Pack M., Bougnoux P., Chang Z. L., Hoffman T. Interferon-induced differentiation of U937 cells. Comparison with other agents that promote differentiation of human myeloid or monocytelike cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):237–244. doi: 10.1172/JCI110962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Longo D. L., Cossman J., Bolen J. B., Hsu S. M., Israel M., Fisher R. I. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody that binds Reed-Sternberg cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4231–4236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Cossman J., Jaffe E. S. Lymphocyte subsets in normal human lymphoid tissues. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jul;80(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of B-lymphocytes. 1. Identification with monoclonal antibodies in normal lymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):387–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Hairy cell leukemia: a B cell neoplasm with a unique antigenic phenotype. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Oct;80(4):421–428. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E. Possible origin of the Reed-Sternberg cell from an interdigitating reticulum cell. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):601–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the biology and immunology of Hodgkin's disease. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1981;26:11–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67984-1_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Greene W. C., Cossman J., Hsu S. M., Jensen J. P., Neckers L. M., Marshall S. L., Bakhshi A., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J. Rearrangement and expression of immunoglobulin genes and expression of Tac antigen in hairy cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4522–4526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzun H. J., Parwaresch M. R., Feller A. C., Hansmann M. L. Monocyte/macrophage-specific monoclonal antibody Ki-M1 recognizes interdigitating reticulum cells. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):441–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F., Shen L., Ball E. D., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Differentiation of a human monocytic cell line by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol): a morphologic, phenotypic, and functional analysis. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1110–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A., Hattori T., Hoffman T. Differentiation of a human monocyte-like cell line by (2'-5') oligoisoadenylate. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Feb;150(2):292–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90571-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab U., Stein H., Gerdes J., Lemke H., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):65–67. doi: 10.1038/299065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiyama T., Broder S., Waldmann T. A. A monoclonal antibody (anti-Tac) reactive with activated and functionally mature human T cells. I. Production of anti-Tac monoclonal antibody and distribution of Tac (+) cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnke R. A., Kim H., Dorfman R. F. Malignant histiocytosis (histiocytic medullary reticulosis). I. Clinicopatholigic study of 29 cases. Cancer. 1975 Jan;35(1):215–230. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197501)35:1<215::aid-cncr2820350127>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter J. N., Variakojis D., Epstein A. L. Phenotypic analysis of established diffuse histiocytic lymphoma cell lines utilizing monoclonal antibodies and cytochemical techniques. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):140–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Cohn Z. A., Hirsch J. G., Humphrey J. H., Spector W. G., Langevoort H. L. The mononuclear phagocyte system: a new classification of macrophages, monocytes, and their precursor cells. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(6):845–852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]