Abstract
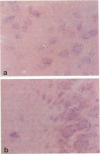
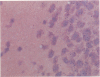
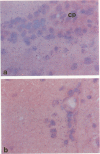
Scrapie is a slow degenerative encephalopathy of animals caused by unusual infectious particles termed prions. A cDNA encoding the only apparent component of the prion, a protein designated PrP 27-30, has recently been cloned and sequenced. By measuring mRNA levels using in situ hybridization with the PrP cDNA, the authors found that prion proteins are synthesized almost exclusively within neurons. The levels of PrP mRNA varied among different types of neurons, but did not change during scrapie infection. A cDNA encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was a positive control; GFAP mRNA was confined to astrocytes. Our finding of PrP mRNA in neurons may explain the degeneration and vacuolation that occurs in these cells during scrapie infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK E., DANIEL P. M., PARRY H. B. DEGENERATION OF THE CEREBELLAR AND HYPOTHALAMONEUROHYPOPHYSIAL SYSTEMS IN SHEEP WITH SCRAPIE; AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO HUMAN SYSTEM DEGENERATIONS. Brain. 1964 Mar;87:153–176. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Stowring L., Figus A., Montgomery C. K., Haase A. T., Vyas G. N. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes, bile duct epithelium, and vascular elements by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6685–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of the major scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5898–5906. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Meyer R. K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie PrP 27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):596–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.596-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., McKinley M. P., Barry R. A., Braunfeld M. B., McColloch J. R., Prusiner S. B. Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Viroids and prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5220–5224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection as the etiology of spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease). Science. 1969 Sep 5;165(3897):1023–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3897.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie A. Immunohistochemical demonstration of glial fibrillary acidic protein in scrapie. J Comp Pathol. 1983 Apr;93(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(83)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome with an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus-induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain. 1981 Sep;104(3):559–588. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Masiarz F. R., Isaacs S. T., Hearst J. E., Prusiner S. B. Resistance of the scrapie agent to inactivation by psoralens. Photochem Photobiol. 1983 May;37(5):539–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1983.tb04515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Cochran S. P., Masiarz F. R., McKinley M. P., Martinez H. M. Molecular properties, partial purification, and assay by incubation period measurements of the hamster scrapie agent. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4883–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohwer R. G. Scrapie infectious agent is virus-like in size and susceptibility to inactivation. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):658–662. doi: 10.1038/308658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowring L., Haase A. T., Petursson G., Georgsson G., Palsson P., Lutley R., Roos R., Szuchet S. Detection of visna virus antigens and RNA in glial cells in foci of demyelination. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90264-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]