Abstract
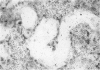
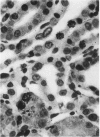
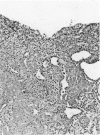
After an initial episode of acute tubular necrosis, apparent resistance to gentamicin nephrotoxicity develops in rats during prolonged drug administration. The authors studied this phenomenon by examining the autoradiographic distribution of 3H-gentamicin and 3H-thymidine during 5 weeks of gentamicin treatment and by analyzing renal structure and function after a 12-week course of treatment. These studies show that regenerating cells exclude gentamicin, but concentrate it again after maturation, and that the rate of thymidine incorporation is still high well after recovery from acute toxic injury. After 12 weeks of gentamicin, the glomerular filtration rate was only modestly diminished, whereas in vitro cortical organic ion transport was substantially impaired. Light and electron microscopy demonstrated all phases of injury and recovery among cells of most proximal tubules and evidence of chronic tubulointerstitial disease. It is concluded that "resistance" to gentamicin is a state of persistent tubular cell injury obscured functionally by preservation of the glomerular filtration rate and histologically by asynchrony of cell necrosis and regeneration.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramowsky C. R., Swinehart G. L. The nephropathy of cystic fibrosis: a human model of chronic nephrotoxicity. Hum Pathol. 1982 Oct;13(10):934–939. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., 3rd, Parker R. A., Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Porter G. A. Alterations in organic ion transport induced by gentamicin nephrotoxicity in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jan;95(1):32–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS R. J., TAGGART J. V. Renal tubular transport: accumulation of p-aminohippurate by rabbit kidney slices. Am J Physiol. 1950 Apr 1;161(1):181–190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.161.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott W. C., Houghton D. C., Gilbert D. N., Baines-Hunter J., Bennett W. M. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity. I. Degree and permanence of acquired insensitivity. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Oct;100(4):501–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre J., Rudhardt M., Blanchard P., Regamey C. Persistence of sisomicin and gentamicin in renal cortex and medulla compared with other organs and serum of rats. Kidney Int. 1976 Dec;10(6):444–449. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M., Plamp C. E., Reger K., Porter G. A. Reversibility of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats: recovery during continuous drug administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Jan;160(1):99–103. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon W. E., Cohen H. J., Schneeberger E. E., Grupe W. E. Chronic renal failure in children treated with methyl CCNU. N Engl J Med. 1979 May 24;300(21):1200–1203. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197905243002106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton D. C., Hartnett M., Campbell-Boswell M., Porter G., Bennett W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):589–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Erdmann G., Habermann E. The renal handling of polybasic drugs. 1. Gentamicin and aprotinin in intact animals. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00505080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaloyanides G. J., Pastoriza-Munoz E. Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 1980 Nov;18(5):571–582. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Maldague P., Carlier M. B., Tulkens P. M. Increased renal DNA synthesis in vivo after administration of low doses of gentamicin to rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):586–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Kleit S. A. Renal parenchymal accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):656–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N. Recovery from aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity with continued drug administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):284–287. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüllmann H., Lüllmann-Rauch R., Wassermann O. Drug-induced phospholipidoses. II. Tissue distribution of the amphiphilic drug chlorphentermine. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1975 Nov;4(2):185–218. doi: 10.1080/10408447509164014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micetich K. C., Jensen-Akula M., Mandard J. C., Fisher R. I. Nephrotoxicity of semustine (methyl-CCNU) in patients with malignant melanoma receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. Am J Med. 1981 Dec;71(6):967–972. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schentag J. J., Jusko W. J., Vance J. W., Cumbo T. J., Abrutyn E., DeLattre M., Gerbracht L. M. Gentamicin disposition and tissue accumulation on multiple dosing. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Dec;5(6):559–577. doi: 10.1007/BF01059684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solez K. Pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:277–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Lifschitz M. D., Barnes L. D. Current concepts on the pathophysiology of acute renal failure. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):F171–F181. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.3.F171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trollfors B. Gentamicin-associated changes in renal function reversible during continued treatment. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Sep;12(3):285–287. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M. Drug-induced lysosomal changes and nephrotoxicity in rats. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1978 Nov;28(6):867–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1978.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]