Abstract
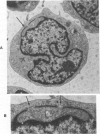
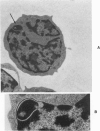
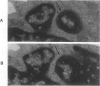
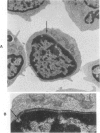
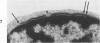
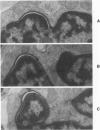
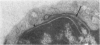
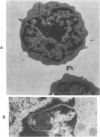
Ultrastructural investigation of the nuclei of the lymphoid cell population of bone marrow and blood of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia regularly shows the presence of two types of nuclear pockets and nuclear clefts. The incidences of these nuclear features decrease significantly during cytostatic therapy. The pockets consist of either a cytoplasmic segment enclosed by a nuclear heterochromatin bridge or a nuclear segment enclosed by an intranuclear cleft. One type of nuclear cleft is, for its greater part of whole length, situated just under the nuclear surface. The other type of cleft is oriented more or less perpendicular to the nuclear surface. It is proposed that these four types be designated as nuclear pockets and nuclear clefts "Type 1" and "Type 2."
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn M. J., Lewis C. W., Campbell L. A., Luce J. K. Nuclear bleb formation in human bone marrow cells during cytosine arabinoside therapy. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):196–197. doi: 10.1038/215196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahearn M. J., Trujillo J. M., Cork A., Fowler A., Hart J. S. The association of nuclear blebs with aneuploidy in human acute leukemia. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):2887–2896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babai F., Tremblay G., Dumont A. Intranuclear and intranucleolar tubular structures in Novikoff hepatoma cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jul;28(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhawan J., Silva W. Junctions of endoplasmic reticulum and virus like intranuclear inclusions and virus like intranuclear inclusions in amelanotic melanoma metastatic to the jejunum. Tumori. 1980 Aug 31;66(4):507–514. doi: 10.1177/030089168006600413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns E. R., Soloff B. L., Hamma C., Buxton D. F. Nuclear pockets associated with the nucleolus in normal and neoplastic cells. Cancer Res. 1971 Feb;31(2):159–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN M. A., ACHONG B. G. FINE STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS OF A TISSUE CULTURE STRAIN (EB1) FROM BURKIT'S LYMPHOMA. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Feb;34:241–253. doi: 10.1093/jnci/34.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUEHNS E. R., LUTZNER M., HECHT F. NUCLEAR ABNORMALITIES OF THE NEUTROPHILS IN D1 (13-15)-TRISOMY SYNDROME. Lancet. 1964 Mar 14;1(7333):589–590. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes M. E., Davies H. G. Observations on the origin and significance of the nuclear envelope-limited monolayers of chromatin unit threads associated with the cell nucleus. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jul;13(1):139–171. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna R. W., Parkin J., Brunning R. D. Morphologic and ultrastructural characteristics of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer. 1979 Oct;44(4):1290–1297. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197910)44:4<1290::aid-cncr2820440419>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkow L., Slifkin M., Pardo M., Rapoza N. P. Studies on the pathogenesis of Simian adenovirus-induced tumors. 3. The histopathology and ultrastructure of intracranial neoplasms induced by SV20. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Nov;41(5):1051–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollo F., Canese M. G., Stramignoni A. Nuclear sheets in epithelial and connective tissue cells. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):869–870. doi: 10.1038/221869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. G., Murray A. S., Pizzo A. The fine structure of mitosis in rat thymic lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):601–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi P. P., Algeri A. Role of the mitochondrion in the regulation of protein synthesis in the eucaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;110(2):110–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00332642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralfkiaer E., Geisler C., Hansen M. M., Hou-Jensen K. Nuclear clefts in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. A light microscopic and ultrastructural study of a new prognostic parameter. Scand J Haematol. 1983 Jan;30(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1983.tb00628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STALZER R. C., KIELY J. M., PEASE G. L., BROWN A. L., Jr EFFECT OF 5-FLUOROURACIL ON HUMAN HEMATOPOIESIS. A MORPHOLOGIC STUDY. Cancer. 1965 Sep;18:1071–1078. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196509)18:9<1071::aid-cncr2820180904>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalzl F., Huhn D., Abbrederis K., Braunsteiner H. Acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cytochemistry and ultrastructure. Blut. 1974 Aug;29(2):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01633832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Szekely I. E., Park S. A., Fisher D. R. Ultrastructural studies on the acute leukemic lymphoblast. Blut. 1973 Dec;27(6):369–406. doi: 10.1007/BF01630783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., O'Hara P. T. Nuclear pockets in normal leukocytes. Nature. 1967 Aug 12;215(5102):773–773. doi: 10.1038/215773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., O'Hara P. T. Structure of nuclear pockets in human leukocytes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Dec;21(5):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H., Collins R. J., Martin N. J., Siskind V. A ? developmental characteristic of the ultrastructure of childhood leukaemic lymphoblasts. Leuk Res. 1982;6(5):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(82)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]