Abstract
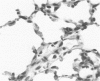
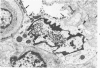
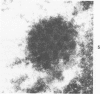
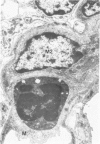
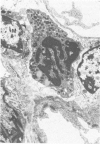
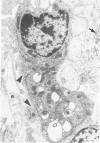
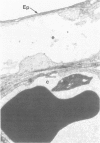
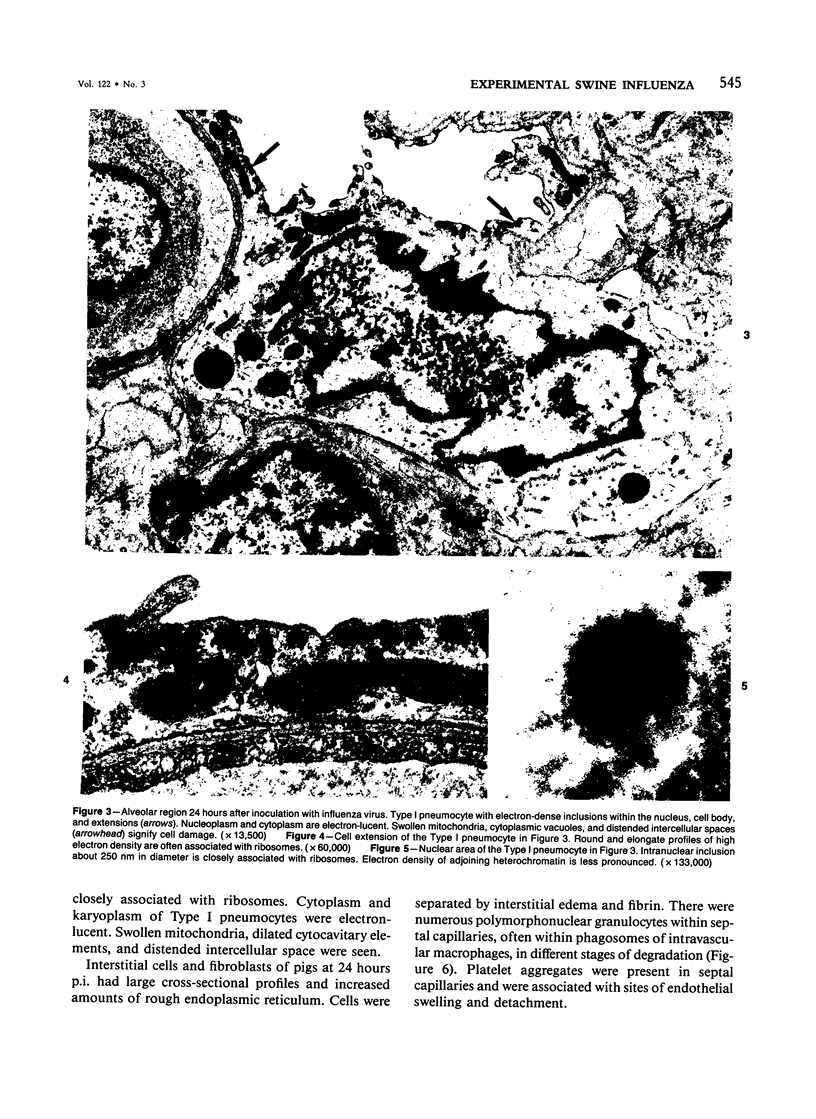
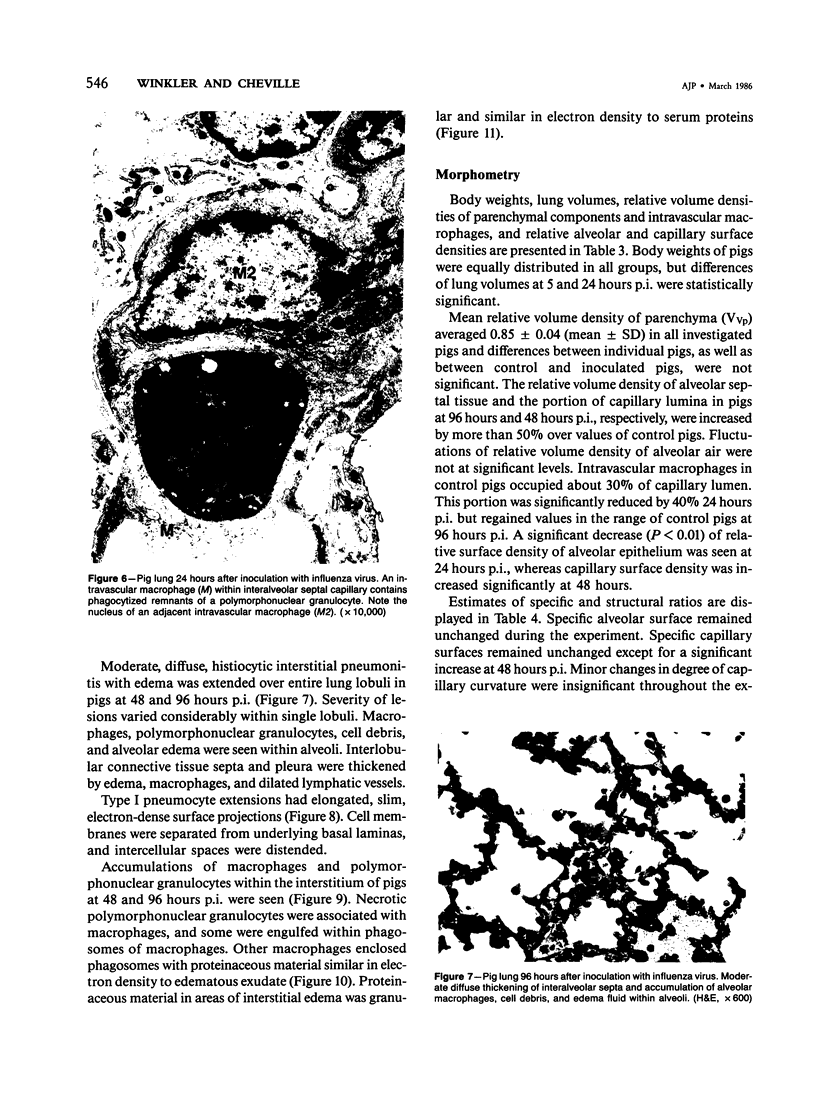
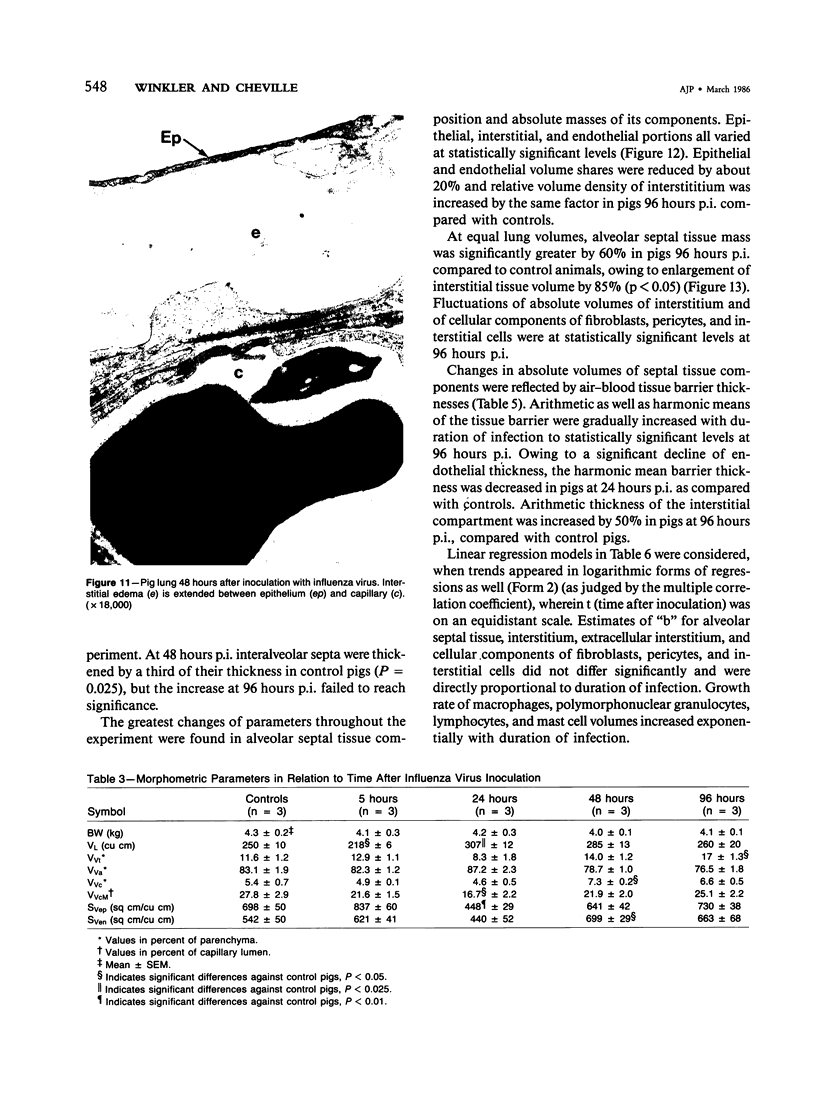
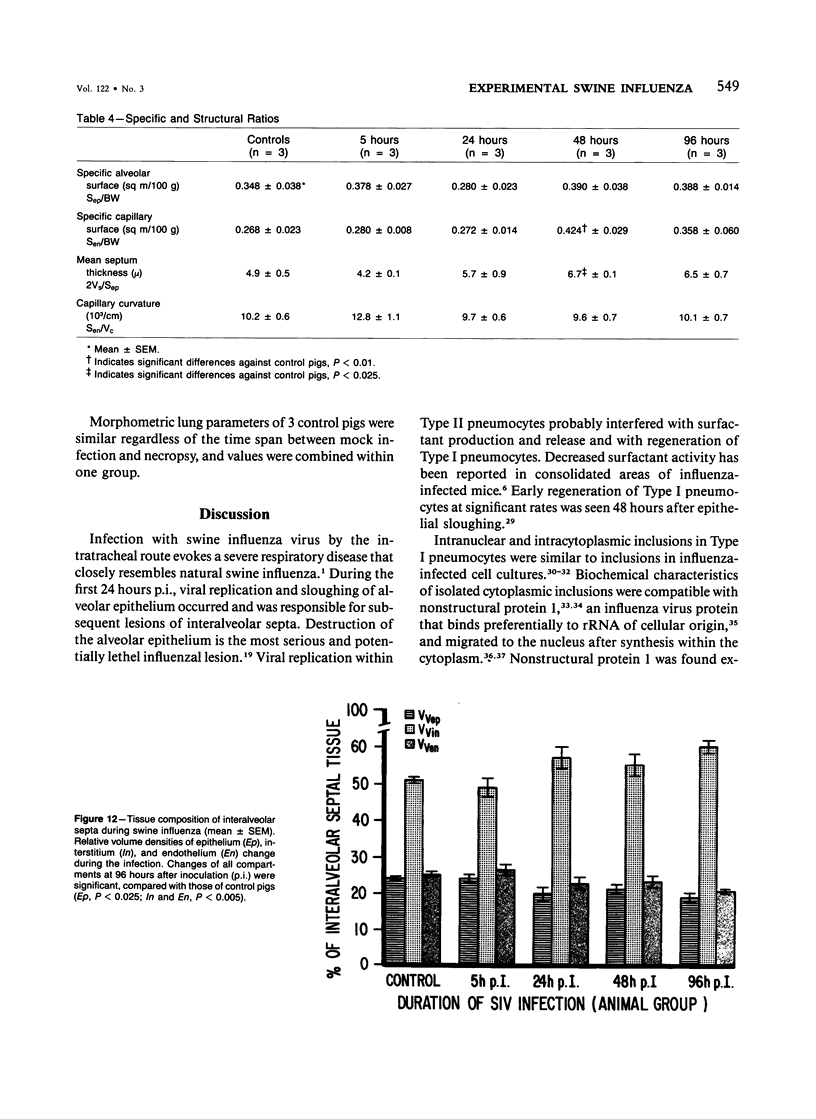
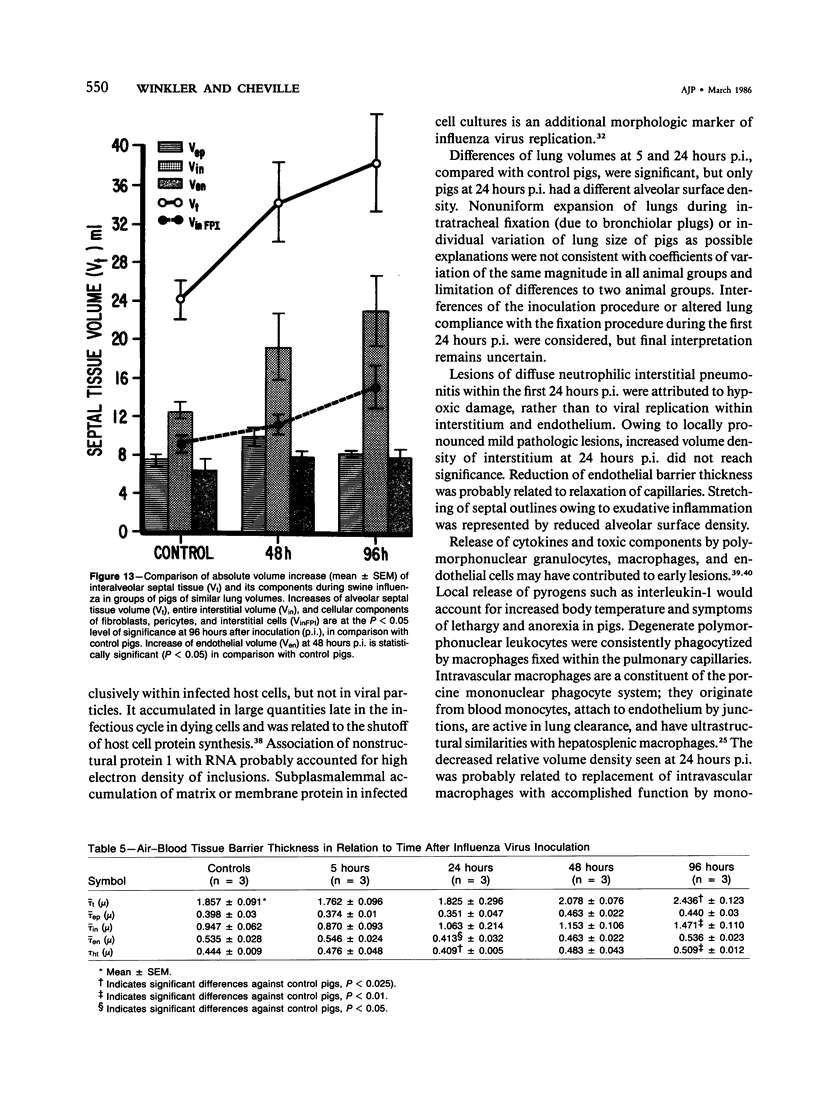
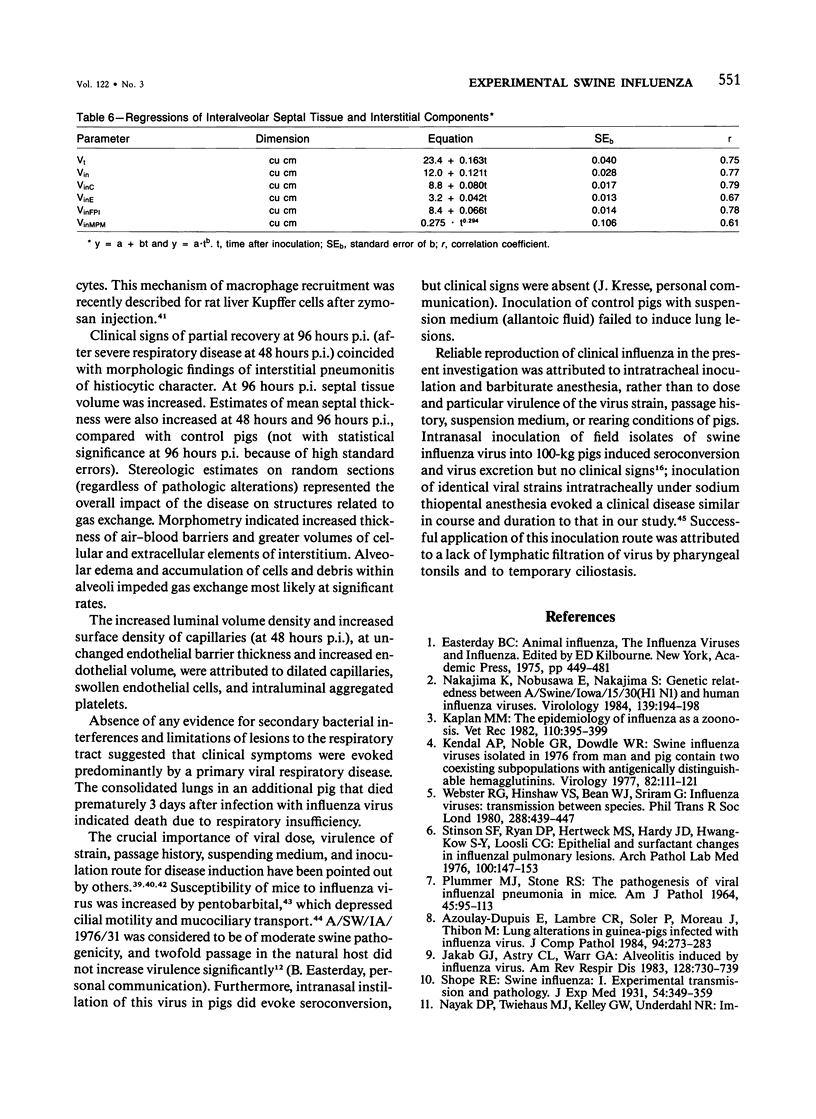
Experimental infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs with swine influenza virus by the intratracheal route resulted in a severe respiratory disease that closely resembled natural swine influenza in clinical course and pathologic lesions. Alveolar epithelial necrosis with sloughing of necrotic cells occurred from 24 to 96 hours after inoculation (p.i.) and was associated with alveolar edema and diffuse interstitial pneumonitis. The latter, initially of neutrophilic character, became histiocytic 48 hours p.i. Ultrastructural analysis of alveolar parenchyma disclosed viral replication in epithelial cells beginning at 5 hours p.i. and lasting to 96 hours. Budding of pleomorphic virus particles from the surface of alveolar epithelial cells and accumulation of viral proteins within the nucleus and cytoplasm of epithelial cells were seen. The extent of parenchymal lesions as quantified by stereologic morphometry within the whole lung was characterized by a marked relative and absolute volume increase of interalveolar septa and increased air-blood tissue barrier thickness. The volume increase of interalveolar septa was due to an increase of interstitial tissue volume by 85% in pigs at 96 hours p.i., compared with control pigs with similar lung volumes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anisimová E., Tucková E., Vonka V. Morphological changes in BHK-21 cells infected with S-N (H2N1) influenza virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;43(3):221–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01250417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azoulay-Dupuis E., Lambre C. R., Soler P., Moreau J., Thibon M. Lung alterations in guinea-pigs infected with influenza virus. J Comp Pathol. 1984 Apr;94(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(84)90046-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen H., Weber J., Wangensteen D., Weibel E. R. Morphometric estimates of diffusing capacity in lungs fixed under zone II and zone III conditions. Respir Physiol. 1983 Apr;52(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(83)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwens L., Wisse E. Proliferation, kinetics, and fate of monocytes in rat liver during a zymosan-induced inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 May;37(5):531–543. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.5.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briedis D. J., Conti G., Munn E. A., Mahy B. W. Migration of influenza virus-specific polypeptides from cytoplasm to nucleus of infected cells. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. T., Jr, Mengeling W. L., Pirtle E. E. Failure of swine influenza virus to cause transplacental infection of porcine fetuses. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):817–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampor F. Electron microscopy of tissue culture cells infected with myxoviruses. I. Nucleo-cytoplasmic changes in A0-WSN influenza virus-infected chick embryo cells. Acta Virol. 1972 Jun;16(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W., Dimmock N. J. An electron microscopic study of single-cycle infection of chick embryo fibroblasts by influenza virus. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):499–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R. B. The effects of influenza on host defenses. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):284–291. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Cabral L. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Transformation of alveolar type 2 cells to type 1 cells following exposure to NO2. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Feb;22(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine M., Fontaine M., Gastellu J., Gourreau J. M., Kaiser C., Aymard M. Grippe porcine expérimentale. Comparaison du pouvoir pathogène entre souches sauvages de virus grippal de type swine et souches de type humain H3 N2 dont le porc est réservoir. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(1):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J. Organization of microcirculation in the lung. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:177–186. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyward J. T., Klimas R. A., Stapp M. D., Obijeski J. F. The rapid concentration and purification of influenza virus from allantoic fluid. Arch Virol. 1977;55(1-2):107–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01314484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab G. J., Astry C. L., Warr G. A. Alveolitis induced by influenza virus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):730–739. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab G. J. Viral-bacterial interactions in pulmonary infection. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1982;26:155–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M. The epidemiology of influenza as a zoonosis. Vet Rec. 1982 Apr 24;110(17):395–399. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.17.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendal A. P., Noble G. R., Dowdle W. R. Swine influenza viruses isolated in 1976 from man and pig contain two coexisting subpopulations with antigenically distinguishable hemagglutinins. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D., McGregor S., Easterday B. C. Hemagglutinin mutants of swine influenza virus differing in replication characteristics in their natural host. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):197–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.197-201.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight P. R., Bedows E., Nahrwold M. L., Maassab H. F., Smitka C. W., Busch M. T. Alterations in influenza virus pulmonary pathology induced by diethyl ether, halothane, enflurane, and pentobarbital anesthesia in mice. Anesthesiology. 1983 Mar;58(3):209–215. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The gene structure and replication of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:467–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCauley J. W., Mahy B. W. Structure and function of the influenza virus genome. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):281–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2110281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrongiello M. P., Dales S. Characterization of cytoplasmic inclusions formed during influenza/WSN virus infection of chick embryo fibroblast cells. Intervirology. 1977;8(5):281–293. doi: 10.1159/000148903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Nobusawa E., Nakajima S. Genetic relatedness between A/Swine/Iowa/15/30(H1N1) and human influenza viruses. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Twiehaus M. J., Kelley G. W., Underdahl N. R. Immunocytologic and histopathologic development of experimental swine influenza infection in pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1965 Nov;26(115):1271–1283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUMMER M. J., STONE R. S. THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRAL INFLUENZAL PNEUMONIA IN MICE. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jul;45:95–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle W. A simple method for volumetry of organs in quantitative stereology. Mikroskopie. 1970 Jun;26(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. W., Compans R. W. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic inclusions from influenza A virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Feb;25(2):608–615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.2.608-615.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson S. F., Ryan D. P., Hertweck S., Hardy J. D., Hwang-Kow S. Y., Loosli C. G. Epithelial and surfactant changes in influenzal pulmonary lesions. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Mar;100(3):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet C., Smith H. Pathogenicity of influenza virus. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):303–330. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.303-330.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toms G. L., Davies J. A., Woodward C. G., Sweet C., Smith H. The relation of pyrexia and nasal inflammatory response to virus levels in nasal washings of ferrets infected with influenza viruses of differing virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1977 Aug;58(4):444–458. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URMAN H. K., UNDERDAHL N. R., YOUNG G. A. Comparative histopathology of experimental swine influenza and virus pneumonia of pigs in disease-free, antibody-devoid pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Oct;19(73):913–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., KNIGHT B. W. A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY ON THE THICKNESS OF THE PULMONARY AIR-BLOOD BARRIER. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:367–396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner A. Clinical aspects of mucociliary transport. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jul;116(1):73–125. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Hinshaw V. S., Bean W. J., Sriram G. Influenza viruses: transmission between species. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Feb 25;288(1029):439–447. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. C., Cheville N. F. Monocytic origin and postnatal mitosis of intravascular macrophages in the porcine lung. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Oct;38(4):471–480. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. C., Cheville N. F. Morphometry of postnatal development in the porcine lung. Anat Rec. 1985 Apr;211(4):427–433. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092110409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. C., Cheville N. F. The neonatal porcine lung: ultrastructural morphology and postnatal development of the terminal airways and alveolar region. Anat Rec. 1984 Oct;210(2):303–313. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092100205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Shaw M. W., Young J. F., Compans R. W. Characterization of the RNA associated with influenza A cytoplasmic inclusions and the interaction of NS1 protein with RNA. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]