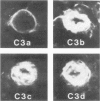
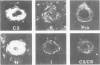
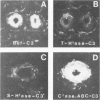
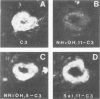
Abstract
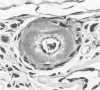
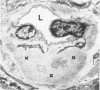
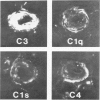
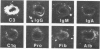
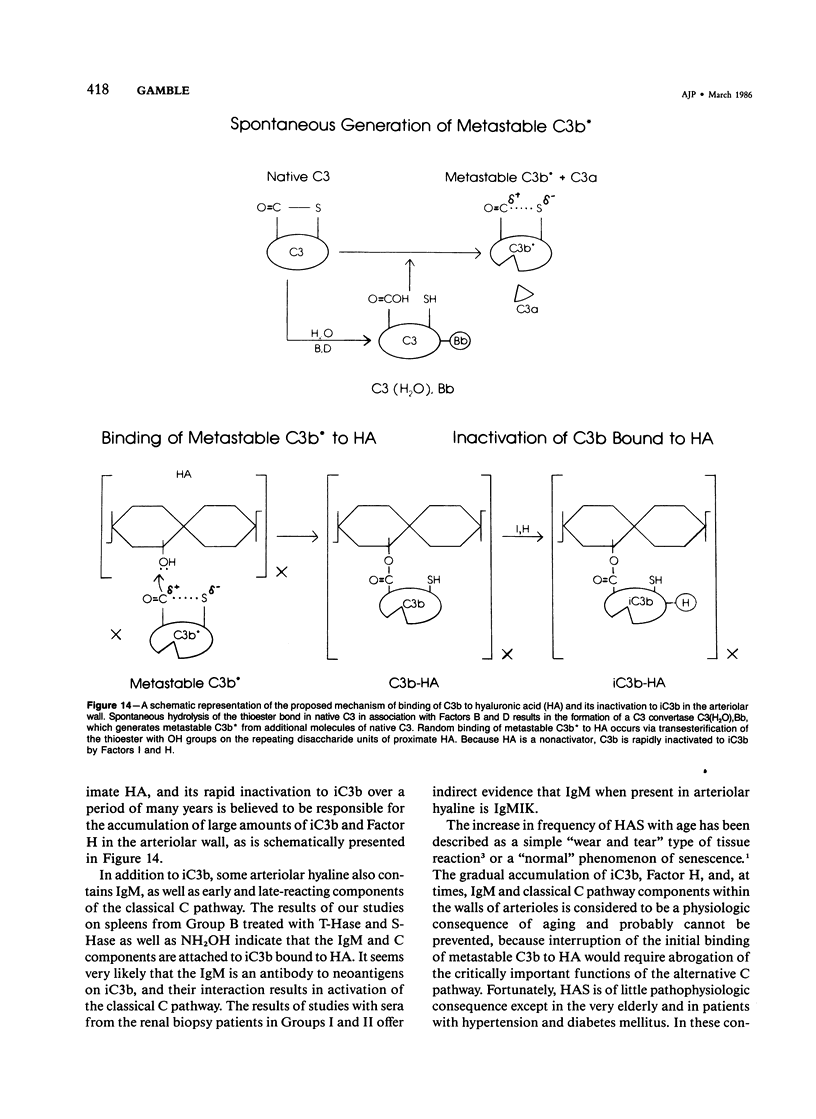
Although hyaline arteriolosclerosis is very common and has been of interest to pathologists for well over 100 years, its pathogenesis has never been determined. This study demonstrates that iC3b bound via an ester linkage to hydroxyl groups on the repeating disaccharide units of hyaluronic acid is a major component of arteriolar hyaline. The deposition of iC3b within the walls of arterioles appears to be due to slow spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway and random binding of metastable C3b to proximate hyaluronic acid within the arteriolar wall. Since hyaluronic acid does not activate the alternative complement pathway, bound C3b is rapidly inactivated by factors I and H to iC3b, which, along with factor H, remains bound to hyaluronic acid. The hyaline in some hyalinized arterioles also contains IgM and early and late classical complement pathway components. Indirect evidence suggests that the IgM represents immunoconglutinin, an autoantibody to neoantigens on iC3b and that their interaction results in activation of the classical complement pathway. The gradual accumulation of iC3b, factor H, and, at times, IgM and classical complement pathway components within the walls of arterioles is considered to be a physiologic consequence of aging and probably cannot be prevented, because interruption of the initial binding of metastable C3b to hyaluronic acid would require abrogation of the critically important functions of the alternative complement pathway.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausprunk D. H., Boudreau C. L., Nelson D. A. Proteoglycans in the microvasculature. I. Histochemical localization in microvessels of the rabbit eye. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):353–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. T. Renal vascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1953 Sep-Oct;2(5):376–389. doi: 10.2337/diab.2.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIAVA C. G., DYRDA I., GENEST J., BENCOSME S. A. RENAL HYALINE ARTERIOLOSCLEROSIS. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. Am J Pathol. 1964 Mar;44:349–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollinger A., Frey J., Jäger K., Furrer J., Seglias J., Siegenthaler W. Patterns of diffusion through skin capillaries in patients with long-term diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 18;307(21):1305–1310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211183072103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
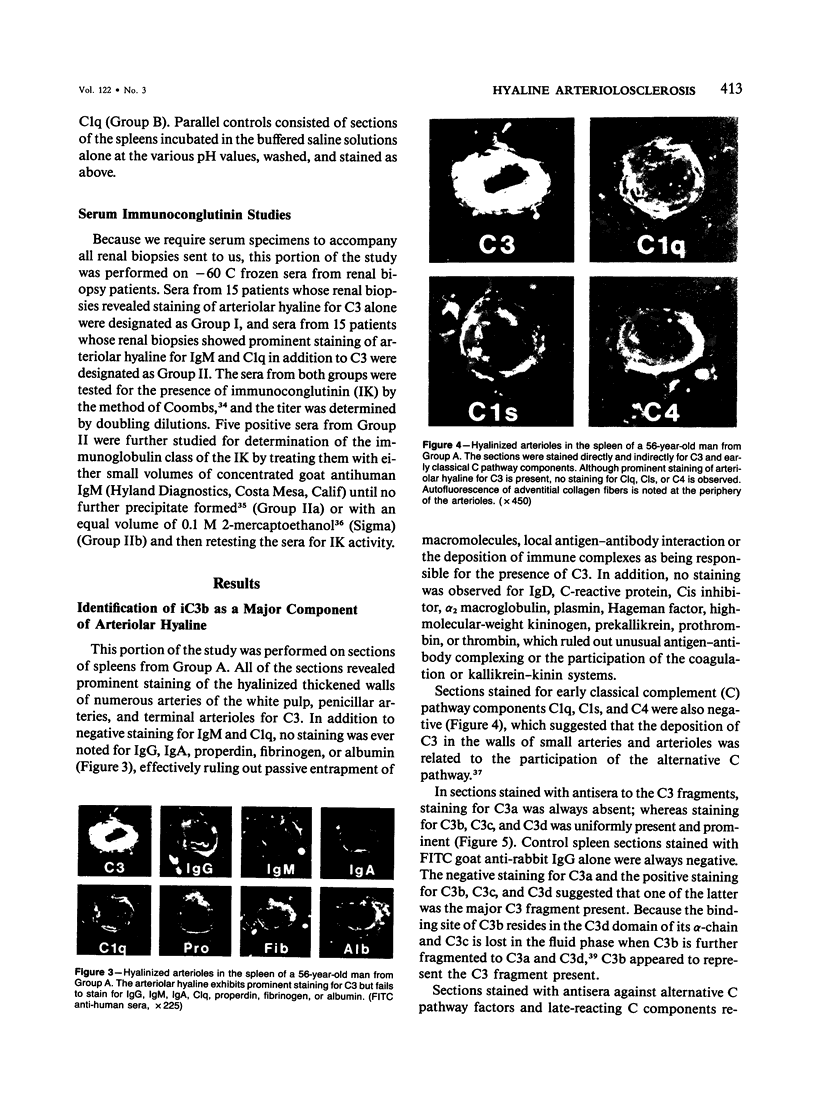
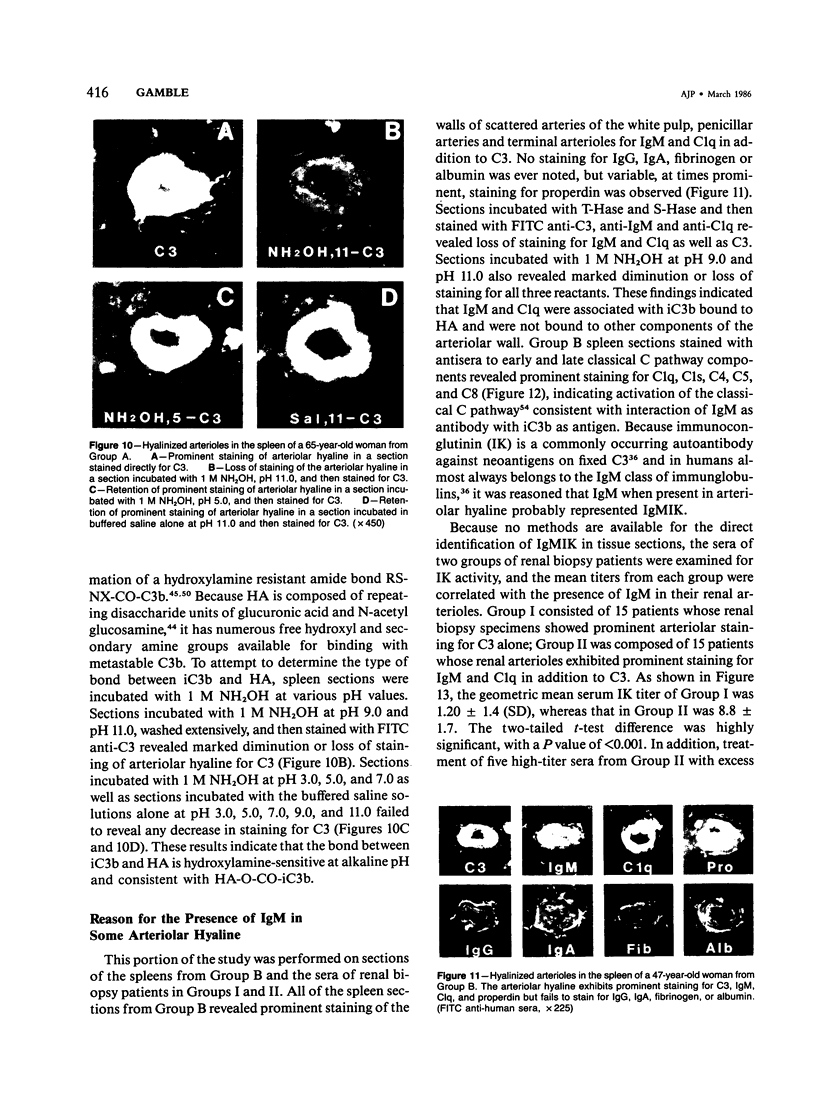
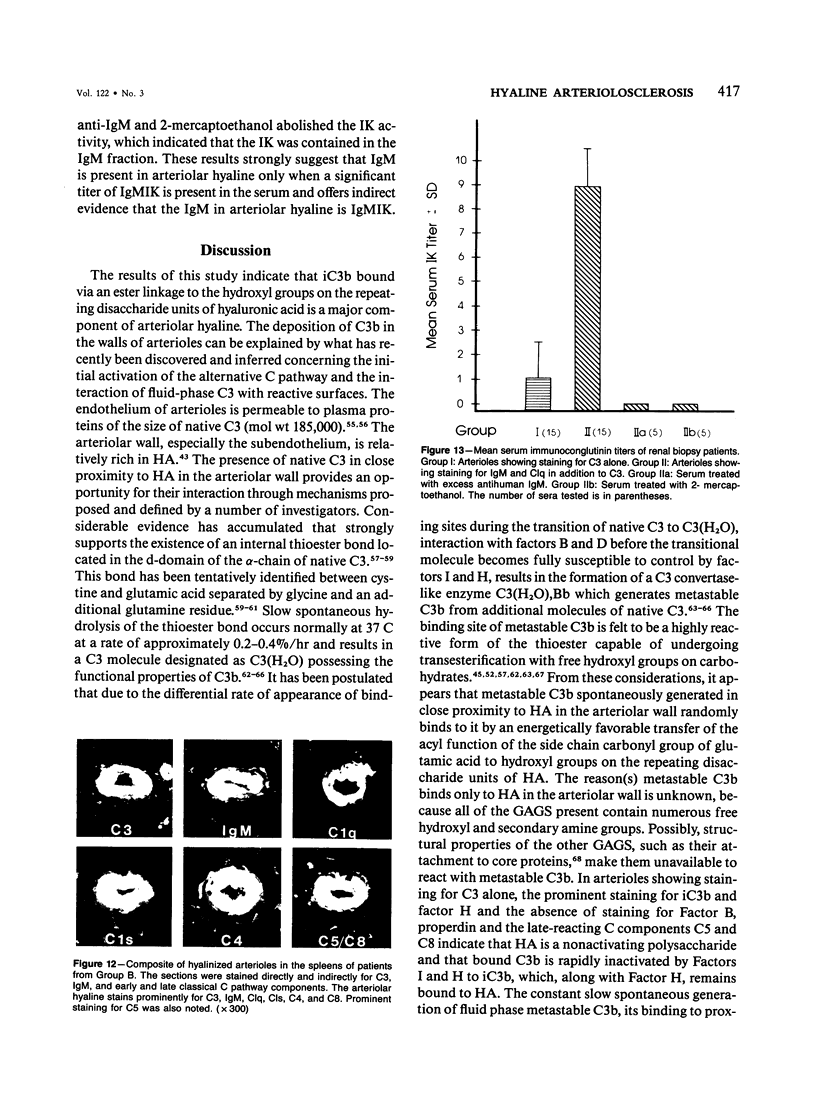
- CRAWFORD T., WOOLF N. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis in the spleen: an immuno-histochemical study. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:221–225. doi: 10.1002/path.1700790202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. Amino acid sequence around the thiol and reactive acyl groups of human complement component C4. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):359–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1990359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlo J. R., Ruddy S., Sauter S., Yount W. J. Deposition of beta 1H globulin in kidneys of patients with immune renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Apr;22(4):403–411. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlo J. R., Ruddy S., Studer E. J., Conrad D. H. Complement receptor binding of C3b-coated cells treated with C3b inactivator, beta 1H globulin and trypsin. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. B., ANDERSON G. S. The pathogenesis of hyaline arteriolosclerosis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(3):519–522. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUSTIN P., Jr, BARTMAN J. [Anatomo-clinical research on splenic hyalinosis in the child]. Rev Belg Pathol Med Exp. 1961 Jul;28:152–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derby M. A., Pintar J. E. The histochemical specificity of Streptomyces hyaluronidase and chondroitinase ABC. Histochem J. 1978 Sep;10(5):529–547. doi: 10.1007/BF01003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditzel J. Functional microangiopathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1968 Jun;17(6):388–397. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.6.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishelson Z., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Characterization of the initial C3 convertase of the alternative pathway of human complement. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1430–1434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. R., Perez-Stable E., Pardo V. Ultrastructural studies in hypertension. I. Comparison of renal vascular and juxtaglomerular cell alterations in essential and renal hypertension in man. Lab Invest. 1966 Sep;15(9):1409–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaither T. A., Hammer C. H., Frank M. M. Studies of the molecular mechanisms of C3b inactivation and a simplified assay of beta 1H and the C3b inactivator (C3bINA). J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1195–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble C. N., Kimchi A., Depner T. A., Christensen D. Immune complex glomerulonephritis and dermal vasculitis following intestinal bypass for morbid obesity. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Mar;77(3):347–352. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble C. N., Reardan J. B. Immunopathogenesis of syphilitic glomerulonephritis. Elution of antitreponemal antibody from glomerular immune-complex deposits. N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 27;292(9):449–454. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502272920903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble C. N., Ruggles S. W. The immunopathogenesis of glomerulonephritis associated with mixed cryoglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jul 13;299(2):81–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197807132990206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grekas D., Morley A. R., Wilkinson R., Kerr D. N. Isolated C3 deposition in patients without systemic disease. Clin Nephrol. 1984 May;21(5):270–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gull W. W., Sutton H. G. On the Pathology of the Morbid State commonly called Chronic Bright's Disease with Contracted Kidney, ("Arterio-capillary Fibrosis."). Med Chir Trans. 1872;55:273–330.1. doi: 10.1177/095952877205500116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadley W. K., Rosenau W. Study of human renal disease by immunofluorescent methods. Arch Pathol. 1967 Apr;83(4):342–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. A., Thomas M. L., Tack B. F. Sequence determination of the thiolester site of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7388–7392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner I., Boutet M., More R. H. Studies on protein passage through arterial endothelium. II. Regional differences in permeability to fine structural protein tracers in arterial endothelium of normotensive rat. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):678–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman D. E., Kells D. I., Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Pangburn M. K. Nucleophilic modification of human complement protein C3: correlation of conformational changes with acquisition of C3b-like functional properties. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4458–4467. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J., Lorenz P. E., Schechter A. N., Prahl J. W., Tack B. F. Third component of human complement: appearance of a sulfhydryl group following chemical or enzymatic inactivation. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4471–4478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janatova J., Tack B. F., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: structural requirements for its function. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 16;19(19):4479–4485. doi: 10.1021/bi00560a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENDRUM A. C. The hypertensive diabetic kidney as a model of the so-called collagen diseases. Can Med Assoc J. 1963 Mar 2;88:442–452. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDOWIEG J., VENNESLAND B., DORFMAN A. The mechanism of action of hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:333–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Covalent binding and hemolytic activity of complement proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7194–7198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Minich T. M., Levine R. P. Binding reaction between the third human complement protein and small molecules. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7457–7463. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGEE W. G., ASHWORTH C. T. FINE STRUCTURE OF CHRONIC HYPERTENSIVE ARTERIOPATHY IN THE HUMAN KIDNEY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Aug;43:273–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTGOMERY P. O., MUIRHEAD E. E. A characterization of hyaline arteriolar sclerosis by histochemical procedures. Am J Pathol. 1954 May-Jun;30(3):521–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIRHEAD E. E., TURNER L. B., GROLLMAN A. Hypertensive cardiovascular disease; nature and pathogenesis of the arteriolar sclerosis induced by bilateral nephrectomy as revealed by a study of its tinctorial characteristics. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Sep;52(3):266–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Complement. Historical perspectives and some current issues. Complement. 1984;1(1):2–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritz A. R., Oldt M. R. Arteriolar Sclerosis in Hypertensive and Non-Hypertensive Individuals. Am J Pathol. 1937 Sep;13(5):679–728.7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Schreiber R. D. Molecular biology and chemistry of the alternative pathway of complement. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag S., Robertson D. M., Dinsdale H. B. Intracerebral arteriolar permeability to lanthanum. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jun;107(3):336–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P. F., Aber G. M., Boyd W. N. C3 deposition in renal arterioles in the loin pain and haematuria syndrome. Br Med J. 1975 Sep 27;3(5986):746–746. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5986.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya T., Kaneko Y. Novel hyaluronidase from streptomyces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orfila C., Pieraggi M. T., Suc J. M. Mesangial isolated C3 deposition in patients with recurrent or persistent hematuria. Lab Invest. 1980 Jul;43(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K. Activation of complement via the alternative pathway. Fed Proc. 1983 Jan;42(1):139–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Relation of putative thioester bond in C3 to activation of the alternative pathway and the binding of C3b to biological targets of complement. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1102–1114. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Formation of the initial C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Acquisition of C3b-like activities by spontaneous hydrolysis of the putative thioester in native C3. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):856–867. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H. Microvascular permeability to plasma proteins in hypertension and diabetes mellitus in man--on the pathogenesis of hypertensive and diabetic microangiopathy. Dan Med Bull. 1975 Sep;22(6):217–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen H. L. Subcutaneous interstitial fluid concentrations of albumin and immunoglobulin G in relation to the serum values in normal, hypertensive and diabetic men. Bibl Anat. 1975;13:74–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodén L., Koerner T., Olson C., Schwartz N. B. Mechanisms of chain initiation in the biosynthesis of connective tissue polysaccharides. Fed Proc. 1985 Feb;44(2):373–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. P. Hyaline arteriolosclerosis in the kidney. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):147–168. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILL W. J., HILL K. R. The pathogenesis of hyaline arteriolar sclerosis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1959 Jul;68(1):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Twose T. M., Paterson D. S., Sim E. The covalent-binding reaction of complement component C3. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):115–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1930115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Harrison R. A., Janatova J., Thomas M. L., Prahl J. W. Evidence for presence of an internal thiolester bond in third component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5764–5768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamerius J. D., Pangburn M. K., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Detection of a neoantigen on human C3bi and C3d by monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2015–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela R., Gogate P. A., Deodhar S. D., Gifford R. W. Hyaline arteriolar nephrosclerosis. Immunofluorescence findings in the vascular lesions. Lab Invest. 1980 Dec;43(6):530–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh Y. P., Minich T. M., Law S. K., Levine R. P. Natural release of covalently bound C3b from cell surfaces and the study of this phenomenon in the fluid-phase system. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1435–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIENER J., SPIRO D., LATTES R. G. THE CELLULAR PATHOLOGY OF EXPERIMENTAL HYPERTENSION. II. ARTERIOLAR HYALINOSIS AND FIBRINOID CHANGE. Am J Pathol. 1965 Sep;47:457–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Czop J. K., Abrahamson D. R., Davies M., Austen K. F. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by isolated human glomerular basement membrane. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. The effect of digestion with Streptomyces hyaluronidase upon certain histochemical reactions of hyaluronic acid-containing tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Sep;21(9):794–803. doi: 10.1177/21.9.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]