Abstract
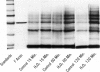
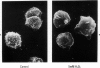
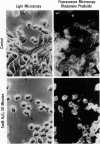
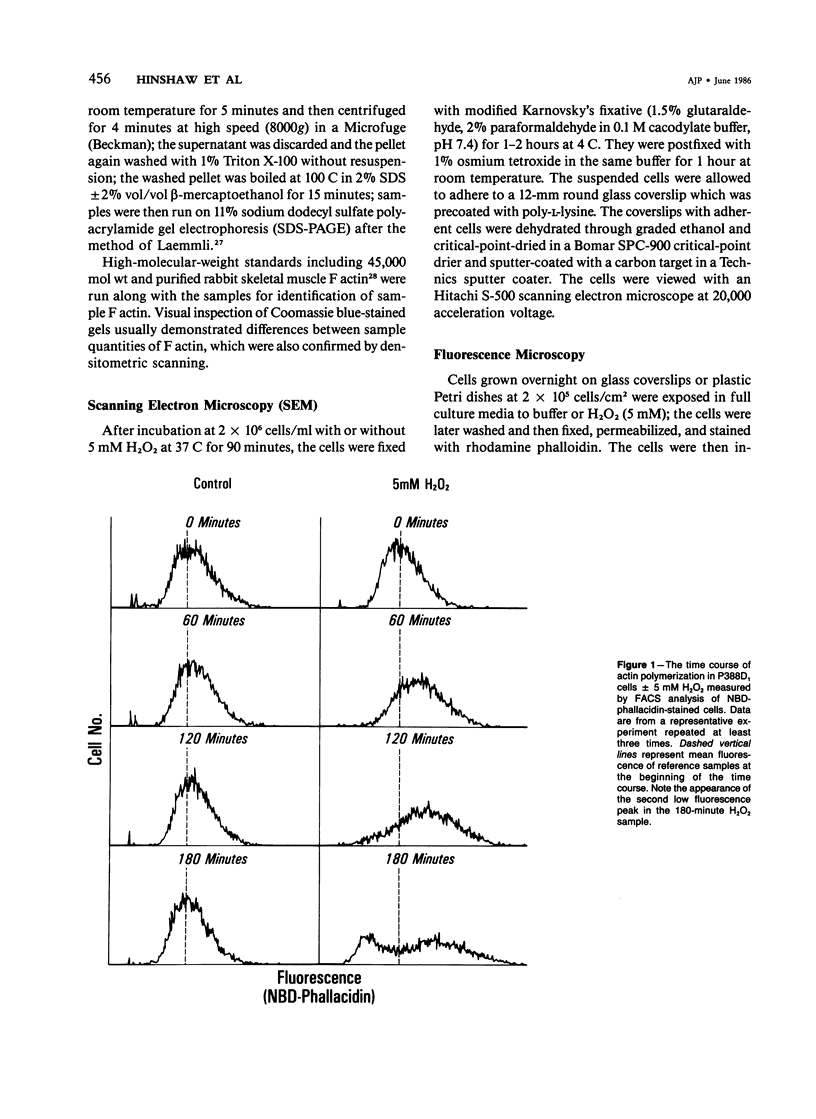
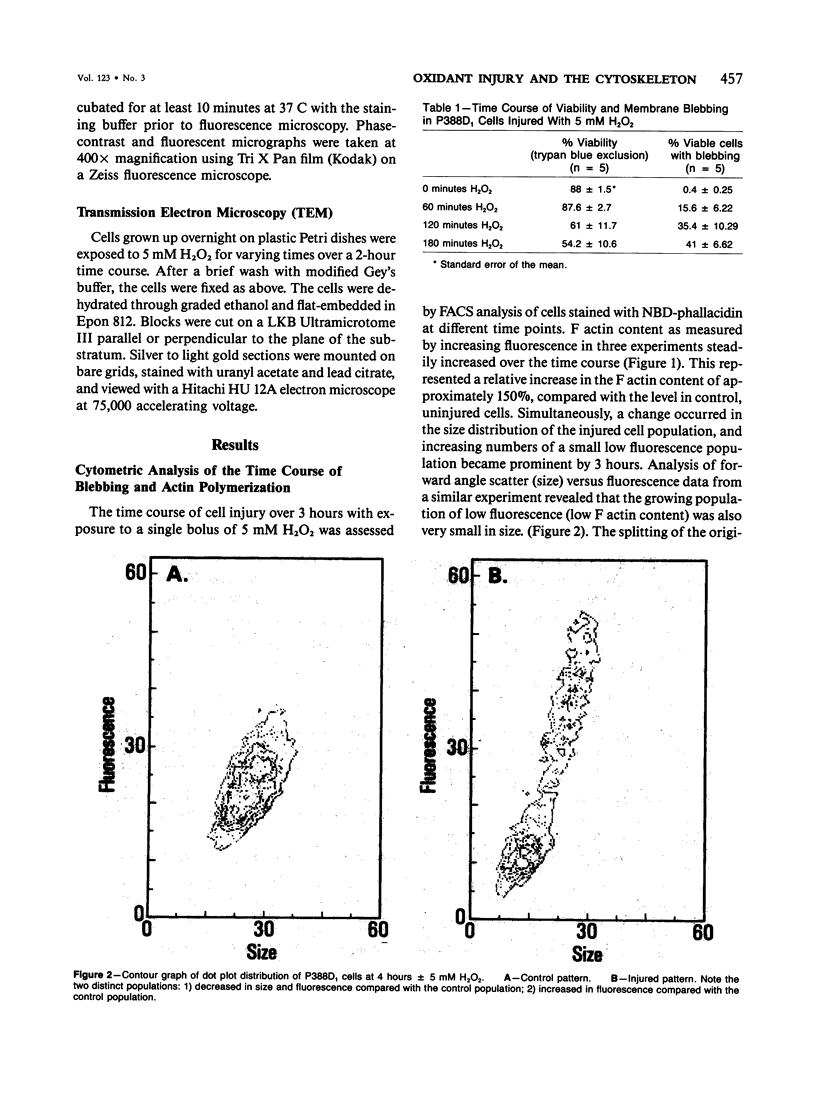
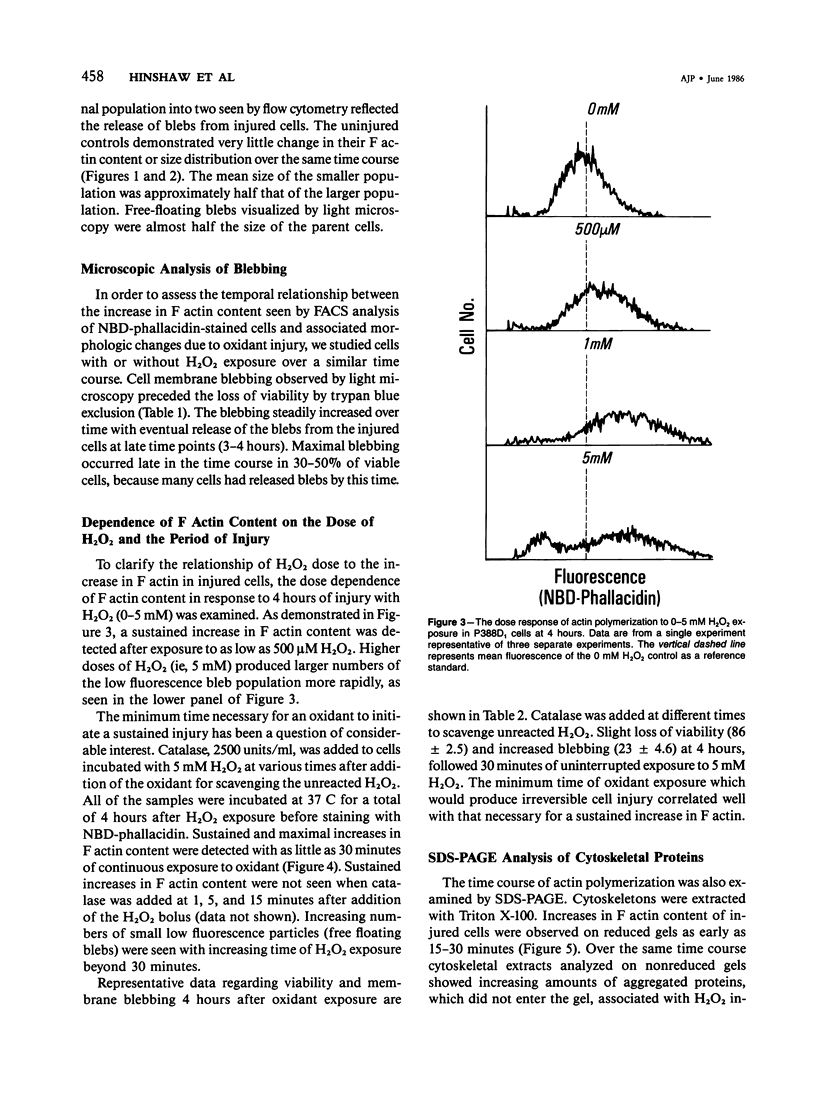
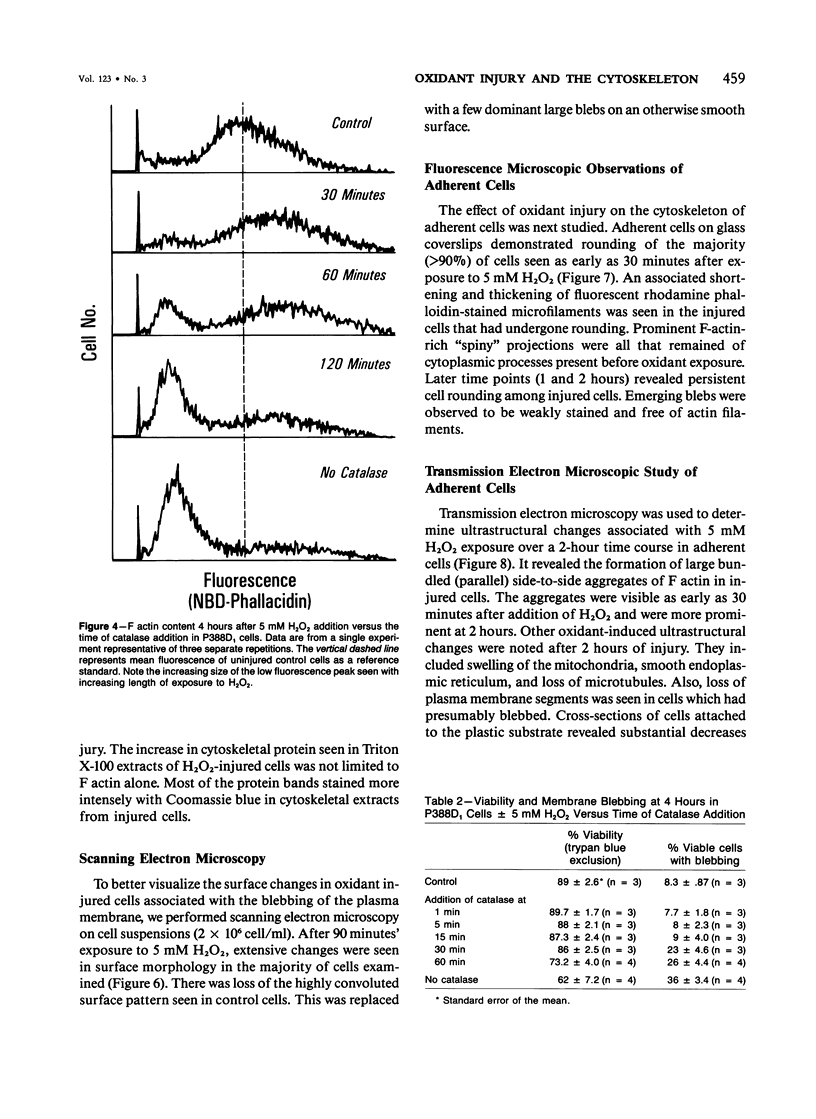
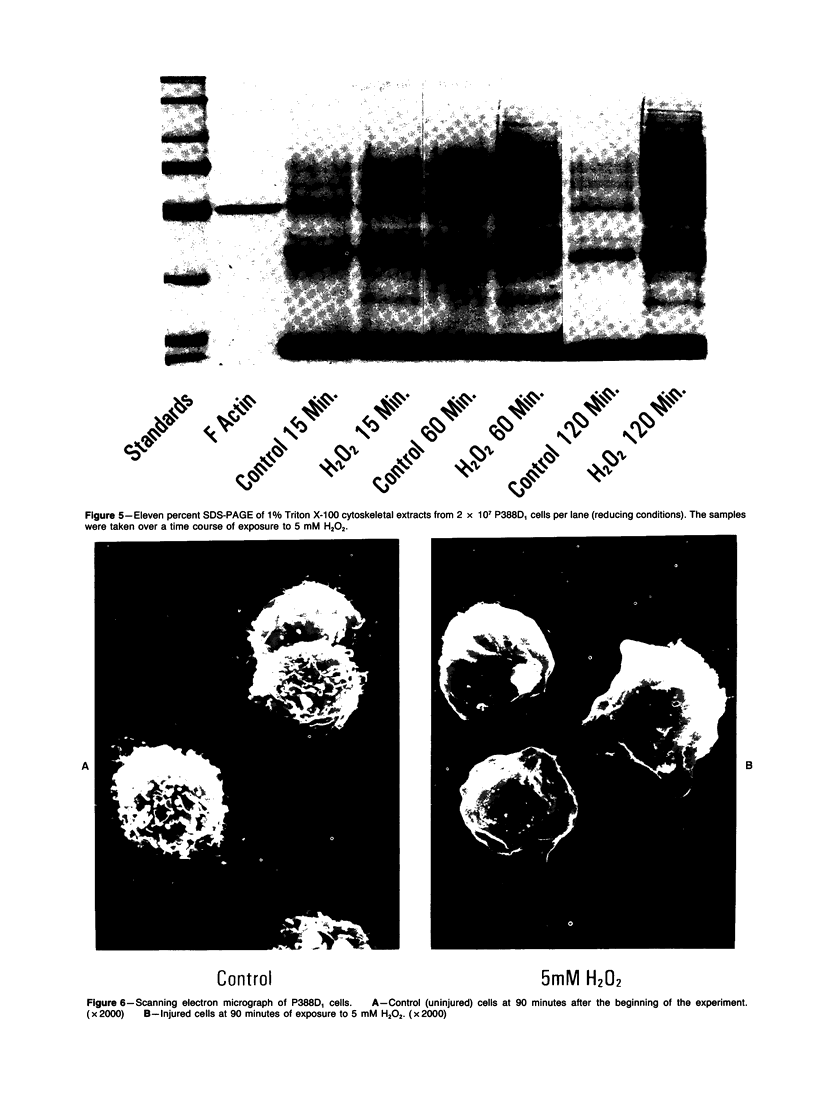
The relationship between changes in cell morphology and the cytoskeleton in oxidant injury was examined in the P388D1 cell line. Flow cytometry of cells stained with NBD-phallacidin, a fluorescent probe specific for filamentous (F) actin, revealed a substantial increase in F actin content in H2O2-injured cells over 3-4 hours. Doses of H2O2 as low as 500 microM produced sustained increases in F actin content. Experiments where catalase was used to interrupt H2O2 exposure over a long time course revealed 15-30 minutes to be the critical period of exposure to 5 mM H2O2 necessary for a sustained increase in F actin as well as large increases in membrane blebbing and later cell death. The increase in F actin with H2O2 injury was confirmed with the use of electrophoresis in acrylamide gels of 1% Triton X-100 cytoskeletal extracts from P388D1 cells. Scanning electron microscopy revealed major loss of surface convolutions in addition to the formation of blebs. Fluorescence microscopy of adherent cells using rhodamine phalloidin showed considerable cell rounding and rearrangement of cellular F actin by 30 minutes of exposure to H2O2. Transmission electron microscopy revealed side to side aggregation of F actin bundles (microfilaments) developing during this time. Considerable swelling of mitochondria and other subcellular organelles was seen after 2 hours of injury. The apparent area of attachment to the substrate was markedly diminished in injured cells. H2O2 injury produced a marked increase in F actin with an associated rearrangement of the microfilaments and simultaneous changes in the plasma membrane prior to cell death in the P388D1 cell line.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo G., Jewell S. A., Thor H., Orrenius S. Regulation of intracellular calcium compartmentation: studies with isolated hepatocytes and t-butyl hydroperoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6842–6846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bershadsky A. D., Gelfand V. I. Role of ATP in the regulation of stability of cytoskeletal structures. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 Mar;7(3):173–187. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bershadsky A. D., Gelfand V. I., Svitkina T. M., Tint I. S. Destruction of microfilament bundles in mouse embryo fibroblasts treated with inhibitors of energy metabolism. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jun;127(2):421–429. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90446-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Bell W. R., Kaiser D., Wong A. Disorganization of cultured vascular endothelial cell monolayers by fibrinogen fragment D. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1487–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.4038818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhauser H. F., Van Horn D. L., Miller P., Pederson H. J. Effect of thiol-oxidation of glutathione with diamide on corneal endothelial function, junctional complexes, and microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):567–578. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard T. H., Meyer W. H. Chemotactic peptide modulation of actin assembly and locomotion in neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1265–1271. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop P. A., Sklar L. A. A quantitative fluorimetric assay for the determination of oxidant production by polymorphonuclear leukocytes: its use in the simultaneous fluorimetric assay of cellular activation processes. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):280–286. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewell S. A., Bellomo G., Thor H., Orrenius S., Smith M. Bleb formation in hepatocytes during drug metabolism is caused by disturbances in thiol and calcium ion homeostasis. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1257–1259. doi: 10.1126/science.7112127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinn S. R., Allen T. D. Conversion of blebs to microvilli: cell surface reorganisation after trypsin. Differentiation. 1981;20(2):168–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W., Williams R. C. The mechanism of microtubule assembly in vitro. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(2-4):412–428. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama R., Sakai H. Viscometric demonstration of tubulin polymerization. J Biochem. 1974 Mar;75(3):463–471. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., 2nd Neutrophils kill pulmonary endothelial cells by a hydrogen-peroxide-dependent pathway. An in vitro model of neutrophil-mediated lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;130(2):209–213. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):164–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger-Brändle E., Gabbiani G. The role of cytoskeletal and cytocontractile elements in pathologic processes. Am J Pathol. 1983 Mar;110(3):361–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Sanger J. M., Jockusch B. M. Differential response of three types of actin filament bundles to depletion of cellular ATP levels. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;31(2):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstatter I. U., Hinshaw D. B., Hyslop P. A., Spragg R. G., Cochrane C. G. Oxidant injury of cells. DNA strand-breaks activate polyadenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase and lead to depletion of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1312–1320. doi: 10.1172/JCI112436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schraufstätter I. U., Hinshaw D. B., Hyslop P. A., Spragg R. G., Cochrane C. G. Glutathione cycle activity and pyridine nucleotide levels in oxidant-induced injury of cells. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1131–1139. doi: 10.1172/JCI112068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Perkins R. G., Zschunke M. A., Hoerl B. J., Maercklein P. B. Plasma membrane vesiculation in 3T3 and SV3T3 cells. I. Morphological and biochemical characterization. J Cell Sci. 1979 Feb;35:229–243. doi: 10.1242/jcs.35.1.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E. Plasma membrane vesiculation: a new technique for isolation of plasma membranes. Science. 1976 Nov 12;194(4266):743–745. doi: 10.1126/science.982044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Scoggin C. H., Patterson D. Hydrogen peroxide causes the fatal injury to human fibroblasts exposed to oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7181–7186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Omann G. M., Painter R. G. Relationship of actin polymerization and depolymerization to light scattering in human neutrophils: dependence on receptor occupancy and intracellular Ca++. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1161–1166. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper J. R., Bernard G. R., Hinson J. M., Jr, Hutchison A. A., Loyd J. E., Ogletree M. L., Brigham K. L. Endotoxemia-induced leukopenia in sheep. Correlation with lung vascular permeability and hypoxemia but not with pulmonary hypertension. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Mar;127(3):306–309. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg R. G., Hinshaw D. B., Hyslop P. A., Schraufstätter I. U., Cochrane C. G. Alterations in adenosine triphosphate and energy charge in cultured endothelial and P388D1 cells after oxidant injury. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1471–1476. doi: 10.1172/JCI112126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tank D. W., Wu E. S., Webb W. W. Enhanced molecular diffusibility in muscle membrane blebs: release of lateral constraints. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):207–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace P. J., Wersto R. P., Packman C. H., Lichtman M. A. Chemotactic peptide-induced changes in neutrophil actin conformation. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1060–1065. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland T., Faulstich H. Amatoxins, phallotoxins, phallolysin, and antamanide: the biologically active components of poisonous Amanita mushrooms. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978 Dec;5(3):185–260. doi: 10.3109/10409237809149870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu E. S., Tank D. W., Webb W. W. Unconstrained lateral diffusion of concanavalin A receptors on bulbous lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4962–4966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf E., Deboben A., Bautz F. A., Faulstich H., Wieland T. Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]