Abstract
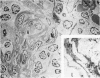
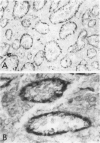
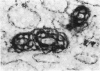
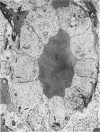
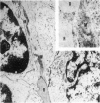
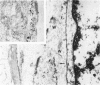
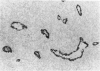
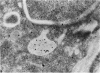
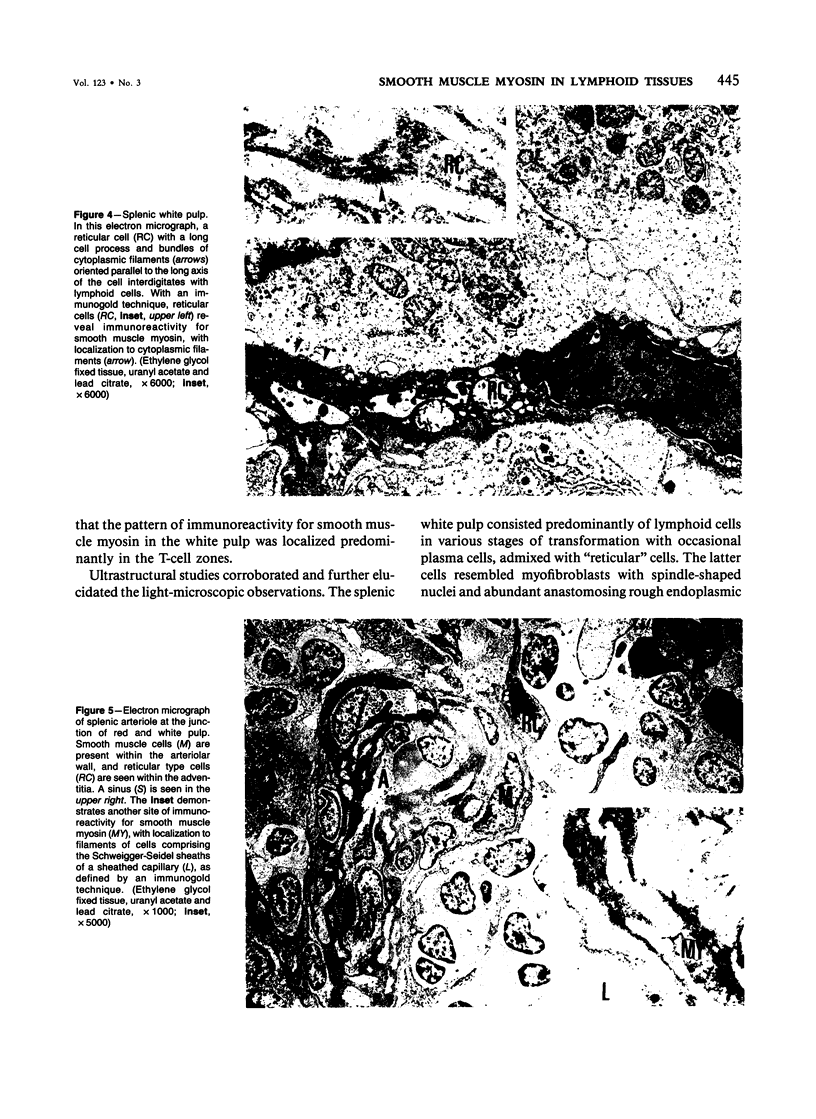
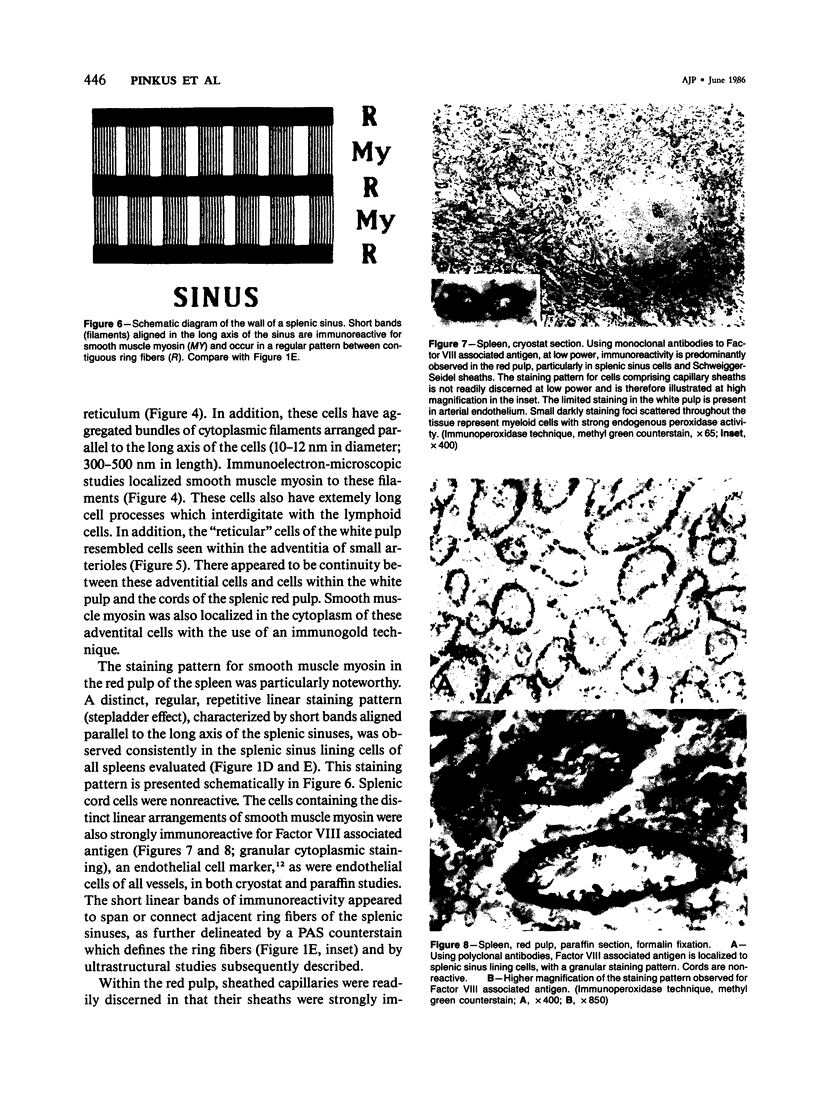
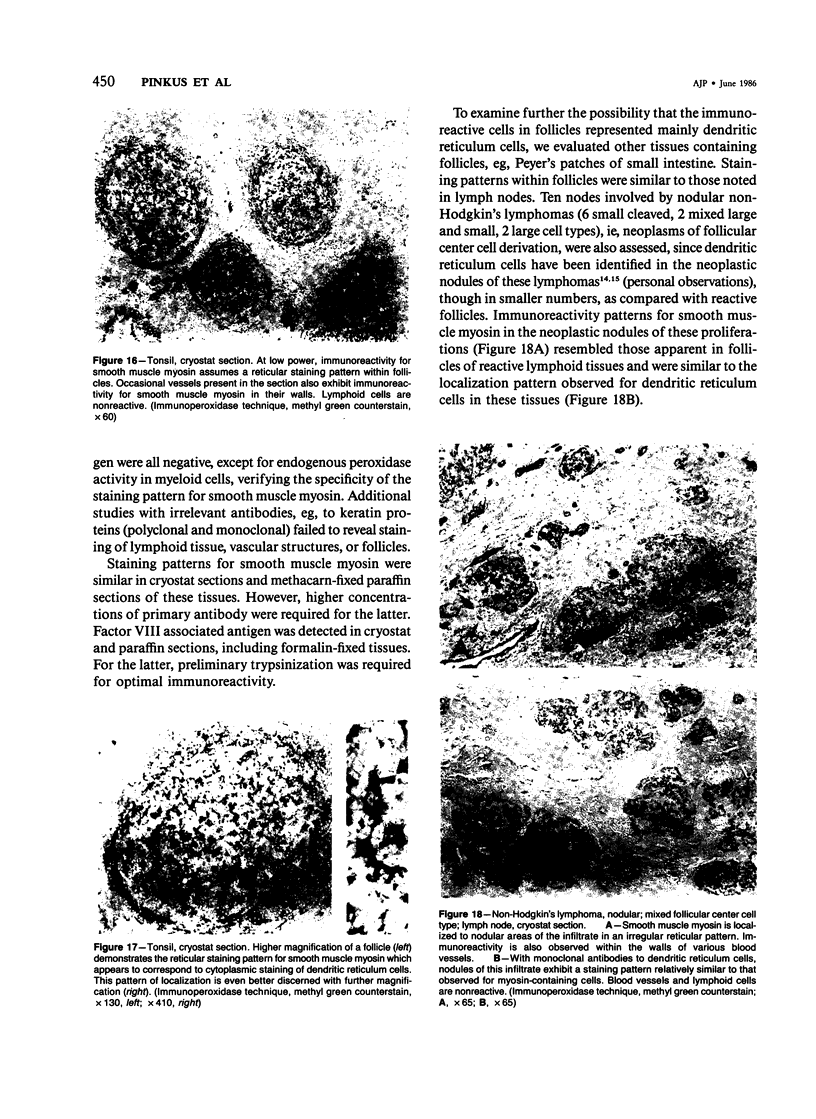
The anatomic distribution of smooth muscle myosin, a contractile protein, was determined in a variety of lymphoid tissues (spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils) with the use of highly specific rabbit antibodies to human uterine smooth muscle myosin and an indirect immunoperoxidase technique. In the spleen, in addition to the anticipated immunoreactivity in the walls of arteries, veins, splenic capsule, and trabeculas, other staining patterns were observed. Smooth muscle myosin-containing cells which comprised the adventitia of the trabecular arteries appeared continuous with myosin-containing reticular cells of the white pulp. The latter cells assumed a circumferential pattern within the periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, then blended delicately with the red pulp at the marginal zone. Ultrastructurally, immunogold techniques demonstrated that smooth muscle myosin in these cells was localized to cytoplasmic filaments. Within the red pulp, a different and distinct staining pattern was observed for the splenic sinuses. Short, regular, orderly, and repetitive bands of immunoreactivity, aligned parallel to the long axis of the sinus, extended between contiguous ring fibers. By immunoelectron microscopy these structures corresponded to distinct bundles of filaments in the endothelial lining cells of the splenic sinuses. Factor VIII associated antigen was also identified in the splenic lining cells in cryostat and paraffin sections, and ultrastructurally. Within the red pulp of the spleen, the sheaths of sheathed capillaries also revealed strong immunoreactivity for smooth muscle myosin. Other sites of immunohistochemical localization of smooth muscle myosin included dendritic reticulum cells present in reactive follicles and in nodular non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Certain vascular structures, specifically sinus lining cells and Schweigger-Seidel capillary sheaths of the spleen and postcapillary venules of lymph nodes and tonsils, coexpressed smooth muscle myosin and Factor VIII associated antigen. The patterns of localization of smooth muscle myosin are correlated with anatomic structures and possible tissue functions.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke J. S., Simon G. T. Electron microscopy of the spleen. I. Anatomy and microcirculation. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):127–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn P. P., Cho Y. Contractile structures in endothelial cells of splenic sinusoids. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Oct;49(1):24–33. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Gröschel-Stewart U., Kendrick-Jones J., Scholey J. M. Antibody to thymus myosin: its immunological characterization and use for immunocytochemical localization of myosin in vertebrate nonmuscle cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;30(1):100–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. M., Fujiwara K., Alexander R. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Heterogeneity of myosin antigenic expression in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Lab Invest. 1984 Apr;50(4):401–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine G. D., Dorfman R. F. Nodular lymphoma: an ultrastructural study of its relationship to germinal centers and a correlation of light and electron microscopic findings. Cancer. 1975 Jan;35(1):148–164. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197501)35:1<148::aid-cncr2820350121>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine J. A., Pinkus G. S., Fujiwara K., Corson J. M. Immunohistochemical localization of smooth muscle myosin in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Mar;33(3):179–184. doi: 10.1177/33.3.3882826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloan S. N., Waldrop F. S., Puchtler H., Valentine L. S. Cross-striated myoendothelial cells in splenic venous sinuses. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Jun;11(6):566–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai K., Rosai J., Burgdorf W. H. Localization of factor VIII-related antigen in vascular endothelial cells using an immunoperoxidase method. Am J Surg Pathol. 1980 Jun;4(3):273–276. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198006000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hermelink H. K., von Gaudecker B., Drenckhahn D., Jaworsky K., Feldmann C. Fibroblastic and dendritic reticulum cells of lymphoid tissue. Ultrastructural, histochemical, and 3H-thymidine labeling studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1981;101(1):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00405075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. M., HOERR N. L. The intermediary circulation in the red pulp of the mouse spleen. Anat Rec. 1951 Mar;109(3):447–477. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091090304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., O'Connor E. M., Etheridge C. L., Corson J. M. Optimal immunoreactivity of keratin proteins in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue requires preliminary trypsinization. An immunoperoxidase study of various tumours using polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 May;33(5):465–473. doi: 10.1177/33.5.2580883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. Cytoplasmic contractile proteins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):156s–165s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.156s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Thomas S. M., Niederman R. Human platelet myosin. I. Purification by a rapid method applicable to other nonmuscle cells. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said J. W., Hargreaves H. K., Pinkus G. S. Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: an ultrastructural study correlating morphology with immunologic cell type. Cancer. 1979 Aug;44(2):504–528. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197908)44:2<504::aid-cncr2820440221>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhol M. J., Sweet J. M. The ultrastructural localization of von Willebrand factor in endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1984 Nov;117(2):310–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. The red pulp of the spleen: structural basis of blood flow. Clin Haematol. 1983 Jun;12(2):375–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]