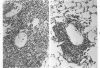
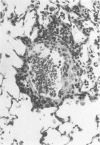
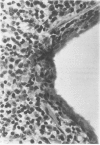
Abstract
Early detection of lupus pneumonitis is difficult because it requires lung biopsy. The authors describe here in detail the age-related histologic changes in pulmonary inflammation, the age-related changes in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), and the effect of cyclophosphamide (8 mg/kg) on pulmonary inflammation and bronchoalveolar lavage in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mouse, an animal model of systemic lupus erythematosus. To assess the evolution of pulmonary inflammation and response to cyclophosphamide therapy, they compared the age-related progression of pulmonary inflammation with sequential changes in BAL cell populations in this autoimmune mouse model. A striking similarity was noted between age-related changes in pulmonary inflammation and lymphocyte counts in BAL. A trend to reduction in histologic evidence of inflammation was reflected by lymphocytes in BAL in cyclophosphamide-treated (8 mg/kg/day) males but not in females. There was a striking sex-related difference in that the histologic evidence of pulmonary inflammation and bronchoalveolar lavage lymphocyte count in cyclophosphamide-treated males was significantly lower than cyclophosphamide-treated females of the same age.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berden J. H., Hang L., McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Analysis of vascular lesions in murine SLE. I. Association with serologic abnormalities. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1699–1705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Analysis of airspace and interstitial mononuclear cell populations in human diffuse interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jul;118(1):7–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney L., Wissig S. L. A biochemical and radioautographic analysis of protein secretion by thyroid lobes incubated in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):510–522. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulmer J. D. Bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Dec;126(6):961–963. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.6.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Esterly J. R., Earle R. H. Pulmonary alterations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Apr;105(4):572–577. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.4.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H. M., Moore G. W., Hutchins G. M. The lung in systemic lupus erythematosus. Analysis of the pathologic changes in 120 patients. Am J Med. 1981 Nov;71(5):791–798. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Fauci A. S. Pulmonary involvement in the collagen vascular diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Mar;119(3):471–503. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. E., Giorgi J. V., Warner N. L. Flow cytometry analysis of T cells and continuous T-cell lines from autoimmune MRL/l mice. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):298–300. doi: 10.1038/289298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay R. A., Schwarz M. I., Petty T. L., Stanford R. E., Gupta R. C., Sahn S. A., Steigerwald J. C. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: review of twelve cases of acute lupus pneumonitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1975 Sep;54(5):397–409. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197509000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Case D. B., Drayer D. E., Reis S., Lorenzo B. Development of antinuclear antibody in patients treated with high doses of captopril. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 May;27(5):579–581. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. D., Hurst D. J., Harmon C. E., Esther J. H., Agia G. A., Maltby J. D., Lillard S. B., Held C. N., Wolfe J. F., Sunderrajan E. V. A prospective evaluation emphasizing pulmonary involvement in patients with mixed connective tissue disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1984 Mar;63(2):92–107. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198403000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Eisenberg R. A., Bourdon M., Crowell J. S., Jr, Dixon F. J. Distribution of lymphocytes identified by surface markers in murine strains with systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndromes. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):516–534. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]