Abstract
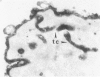
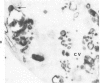
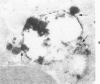
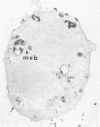
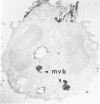
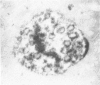
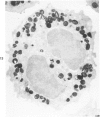
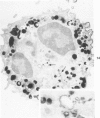
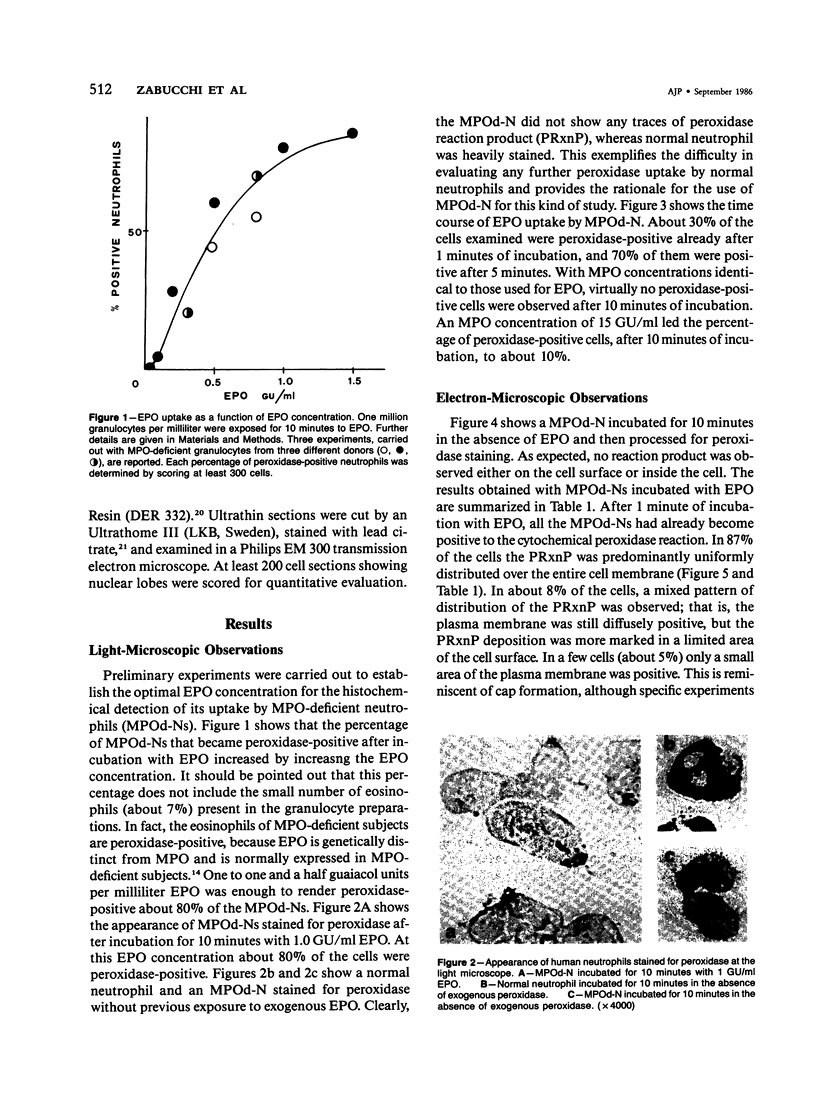
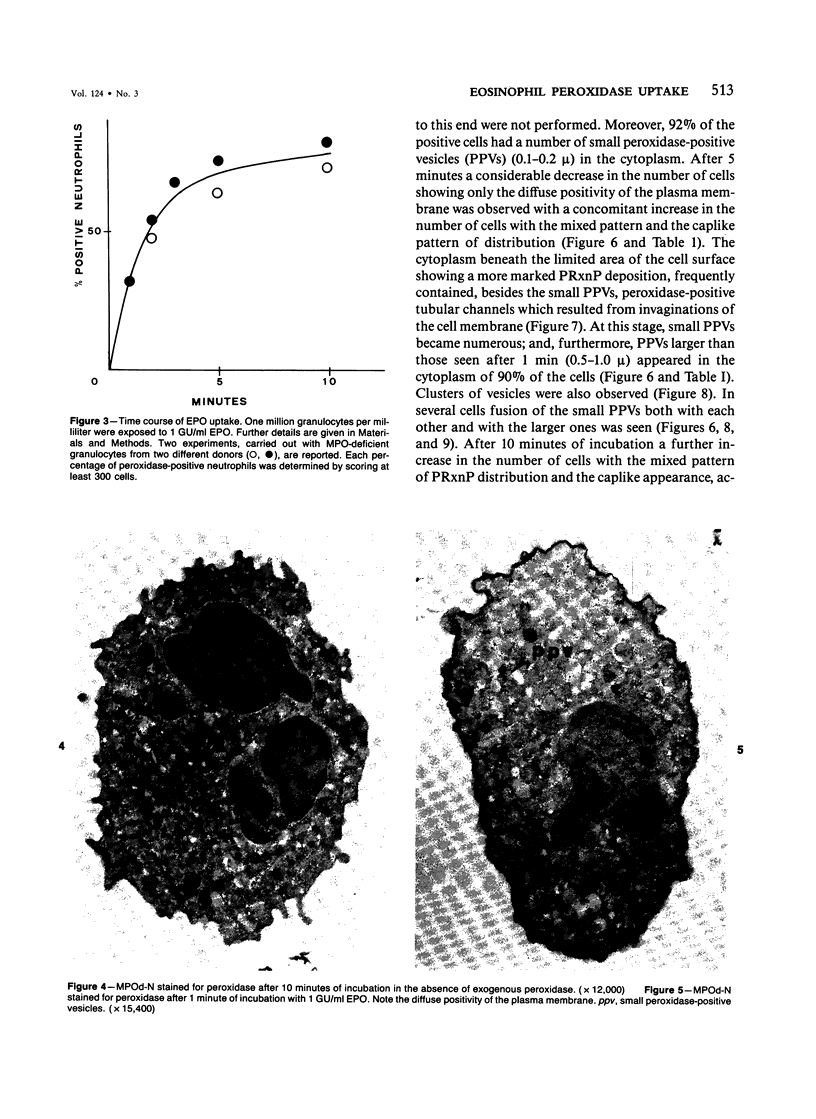
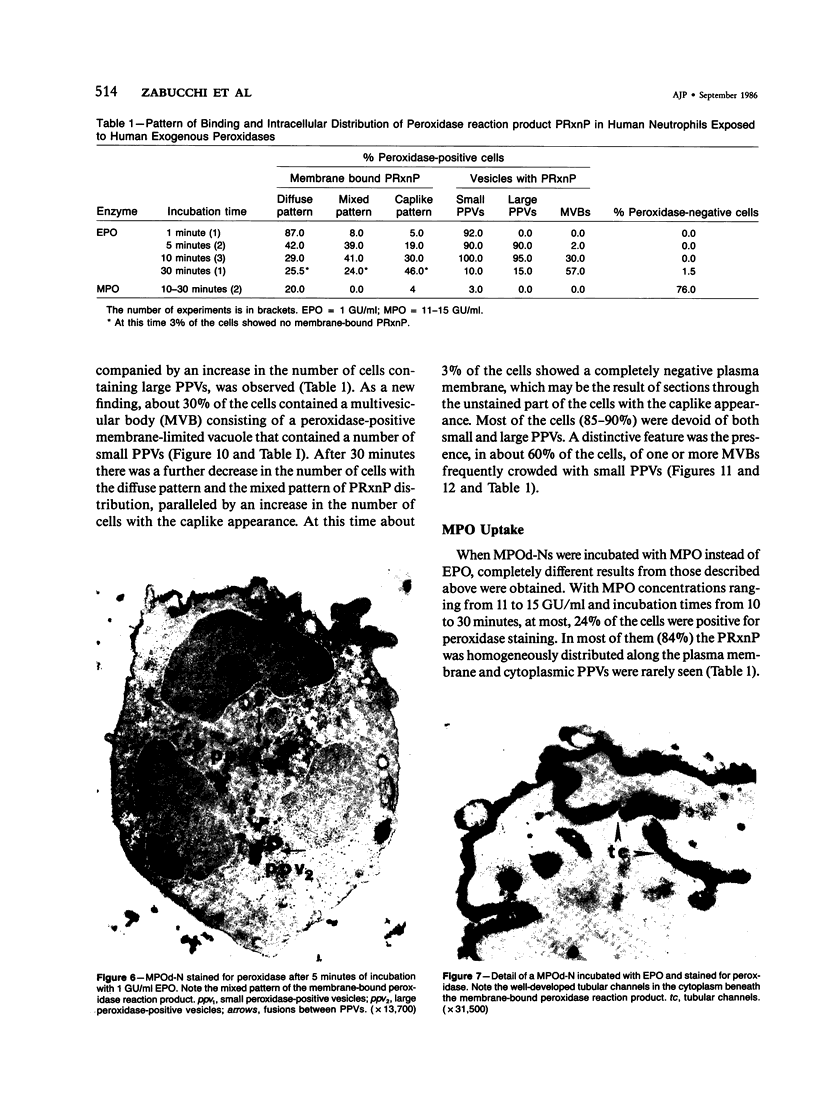
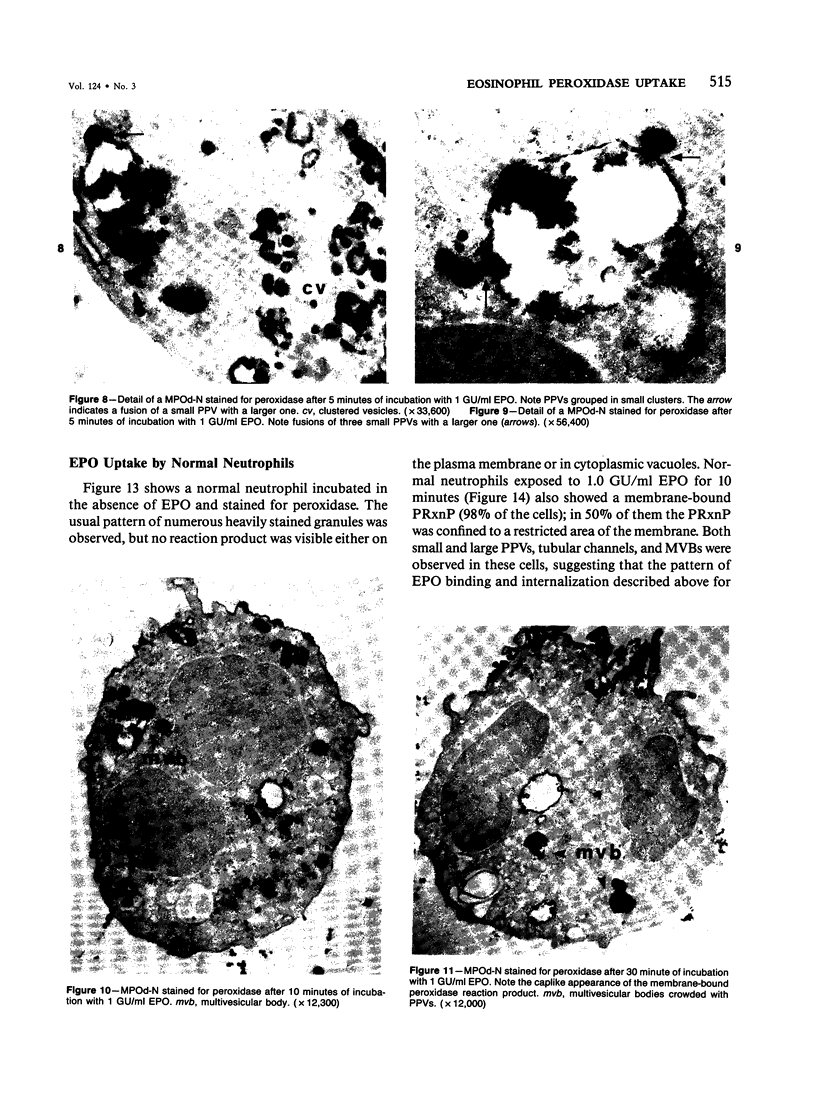
A cytochemical analysis was carried out for study of the interaction between human eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) and human neutrophils. To this end, neutrophils with a genetic deficiency of myeloperoxidase (MPO) were used to avoid the otherwise inevitable interference of the high endogenous MPO activity of normal neutrophils. The data show that human neutrophils incubated with EPO (1 GU/ml) rapidly bind the enzyme all over the cell surface and internalize it in small vesicles. Part of bound EPO concentrates in a limited area on the cell surface and is then internalized by means of coarse tubular channels. Fusion of the small vesicles to each other or possibly with the tubular channels gives rise ultimately to EPO-containing multivesicular bodies, which, after 30 minutes of incubation, are the only peroxidase-positive structures in the cytoplasm. Under identical experimental conditions, no binding of human MPO to the neutrophils was detected. At concentrations 10 times as high as those used for EPO, a minority of neutrophils bound MPO, but the binding pattern remained diffuse on the plasma membrane and the internalization was negligible. It seems, therefore, that the EPO trapping system of human neutrophils exhibits specificity at least among leukocyte peroxidases. Furthermore, it operates at much lower concentrations of EPO than those reported for EPO uptake by mast cells and basophils. The uptake of EPO by neutrophils may serve to sequester a potentially toxic agent, thus limiting damage to the tissue in eosinophil-rich inflammatory lesions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach M. K. Mediators of anaphylaxis and inflammation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:371–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkenist A. R., Wever R., Vulsma T., Plat H., van Gelder B. F. Isolation procedure and some properties of myeloperoxidase from human leucocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 11;524(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y. S., Jones A. L., Hradek G. T., Windler E. E., Havel R. J. Autoradiographic localization of the sites of uptake, cellular transport, and catabolism of low density lipoproteins in the liver of normal and estrogen-treated rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):597–601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J., Shannon L. M. The isolation and characterization of the glycopeptides from horseradish peroxidase isoenzyme C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):428–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90186-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S., Litt M. The entry of granule-associated peroxidase into the phagocytic vacuoles of eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1291–1306. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer R., Soranzo M. R., Dri P., Rottini G. D., Bramezza M., Cirielli S., Patriarca P. Incidence of myeloperoxidase deficiency in an area of northern Italy: histochemical, biochemical and functional studies. Br J Haematol. 1982 May;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb07292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. B., Fells G. A., Sun X. H., Gadek J. E., Venet A., Crystal R. G. Eosinophil-mediated injury to lung parenchymal cells and interstitial matrix. A possible role for eosinophils in chronic inflammatory disorders of the lower respiratory tract. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):269–278. doi: 10.1172/JCI111411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Ishizaka T., Galli S. J. Ultrastructure of human basophils developing in vitro. Evidence for the acquisition of peroxidase by basophils and for different effects of human and murine growth factors on human basophil and eosinophil maturation. Lab Invest. 1985 Jul;53(1):57–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Klebanoff S. J., Henderson W. R., Monahan R. A., Pyne K., Galli S. J. Vesicular uptake of eosinophil peroxidase by guinea pig basophils and by cloned mouse mast cells and granule-containing lymphoid cells. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):425–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Farquhar M. G. Functions of coated vesicles during protein absorption in the rat vas deferens. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):357–376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Chi E. Y., Jörg A., Klebanoff S. J. Horse eosinophil degranulation induced by the ionophore A23187. Ultrastructure and role of phospholipase A2. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jun;111(3):341–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson W. R., Chi E. Y., Klebanoff S. J. Eosinophil peroxidase-induced mast cell secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):265–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Lawley T. J., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of neutrophil accumulation in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):259–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong E. C., Henderson W. R., Klebanoff S. J. Bactericidal activity of eosinophil peroxidase. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1378–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Nydegger U. E. The human alternative complement pathway: biology and immunopathology of activation and regulation. Prog Allergy. 1982;30:193–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalife J., Capron M., Grzych J. M., Bazin H., Capron A. Extracellular release of rat eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) I. Role of anaphylactic immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKWOOD W. R. A RELIABLE AND EASILY SECTIONED EPOXY EMBEDDING MEDIUM. Anat Rec. 1964 Oct;150:129–139. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091500204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A. Uptake and digestion of horseradish peroxidase in rabbit alveolar macrophages. Formation of a pathway connecting lysosomes to the cell surface. Lab Invest. 1982 Sep;47(3):235–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. L., Syse K., Little C., Christensen T. B. Further characterization of human eosinophil peroxidase. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):779–784. doi: 10.1042/bj2290779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Campbell E. J. Neutral proteinases from human inflammatory cells. A critical review of their role in extracellular matrix degradation. Clin Lab Med. 1983 Dec;3(4):645–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus W. Mannose-specific binding sites for horseradish peroxidase in various cells of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jan;31(1):78–84. doi: 10.1177/31.1.6833741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Nelson R. S., Silverstein S. C. The role of the mannose/N-acetylglucosamine receptor in the pinocytosis of horseradish peroxidase by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jul;116(1):21–25. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wever R., Plat H., Hamers M. N. Human eosinophil peroxidase: a novel isolation procedure, spectral properties and chlorinating activity. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):327–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Bowie J. U., Nelson R. D. Influence of yeast mannan on release of myeloperoxidase by human neutrophils: determination of structural features of mannan required for formation of myeloperoxidase-mannan-neutrophil complexes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):467–471. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabucchi G., Skerlavaj B., Menegazzi R., Talarico Bidoli L., Patriarca P. A simple method to obtain pure granule-rich eosinophil fragments (cytosomes) from normal human blood. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 27;85(2):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]