Abstract
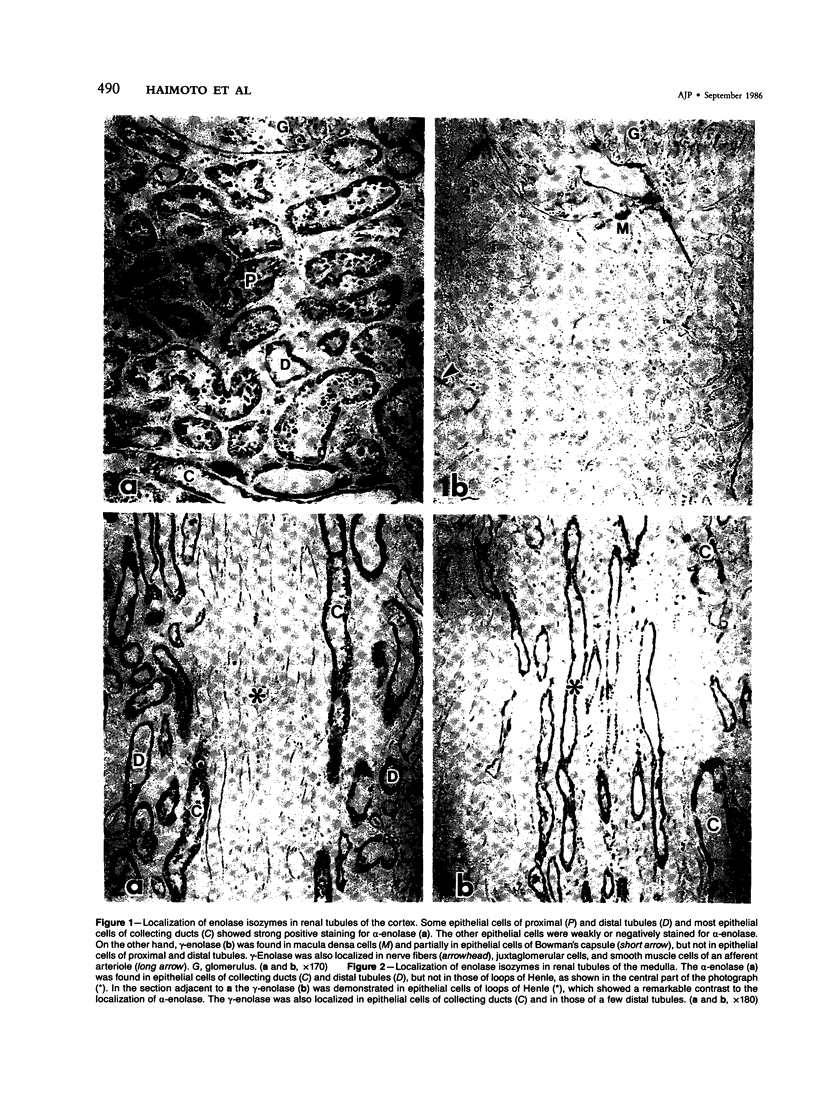
To elucidate the localization of enolase isozymes in renal tubules and renal cell carcinoma, an immunohistochemical study and quantitative analysis by employing the enzyme immunoassay were performed. The alpha-enolase was localized in almost all epithelial cells of renal tubules except for loops of Henle. The gamma-enolase was localized in macula densa cells and epithelial cells of loops of Henle and collecting ducts of the medulla, but not in those of proximal tubules. In renal cell carcinoma, most tumor cells possessed two enolase isozymes. From these immunohistochemical findings, it is suggested that enolases are present mainly in the alpha alpha form in epithelial cells of proximal tubules, in the gamma gamma form in those of loops of Henle, and in the two forms and/or the alpha gamma form in tumor cells of renal cell carcinoma. The levels of gamma-enolase in the normal cortex were 16.8 +/- 3.7 ng/mg protein (n = 7), whereas those in renal cell carcinoma were 928 +/- 554 ng/mg protein (n = 7), about 55-fold higher than those in the normal cortex. The serum gamma-enolase levels were also enhanced in 20 (49%) of 41 patients with renal cell carcinoma. Because it is generally accepted that renal cell carcinoma is derived from epithelium of proximal tubules, the expression of gamma-enolase has occurred during carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Good D. Sodium chloride coupled transport in mammalian nephrons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:533–547. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher L., Rider C. C., Taylor C. B., Adamson E. D., Luke B. M., Graham C. F. Enolase isoenzymes as markers of differentiation in teratocarcinoma cells and normal tissues of mouse. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):462–475. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher L., Rider C. C., Taylor C. B. Enolase isoenzymes. III. Chromatographic and immunological characteristics of rat brain enolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to human intermediate filament proteins. II. Distribution of filament proteins in normal human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1984 Feb;114(2):309–321. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimoto H., Takahashi Y., Koshikawa T., Nagura H., Kato K. Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-enolase in normal human tissues other than nervous and neuroendocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Alfthan O., Virtanen I. Cellular origin and differentiation of renal carcinomas. A fluorescence microscopic study with kidney-specific antibodies, antiintermediate filament antibodies, and lectins. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Asai R., Shimizu A., Suzuki F., Ariyoshi Y. Immunoassay of three enolase isozymes in human serum and in blood cells. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Feb 7;127(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Suzuki F., Semba R. Determination of brain enolase isozymes with an enzyme immunoassay at the level of single neurons. J Neurochem. 1981 Oct;37(4):998–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb04487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt M. J., Keller A., Legault-Demare L. Changes in the expression of the alpha alpha form of enolase during neuroblastoma differentiation. J Neurochem. 1983 Dec;41(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marangos P. J., Parma A. M., Goodwin F. K. Functional properties of neuronal and glial isoenzymes of brain enolase. J Neurochem. 1978 Sep;31(3):727–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Kameya T., Tsumuraya M., Shimosato Y., Kato K. Enolase distribution in human brain tumors, retinoblastomas and pituitary adenomas. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 13;308(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K. Recent progress in the peroxidase-labeled antibody method. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider C. C., Taylor C. B. Enolase isoenzymes in rat tissues. Electrophoretic, chromatographic, immunological and kinetic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers P. A., Brenton D. P., Hopkinson D. A. Changes in the activity and isozyme patterns of glycolytic enzymes during stimulation of normal human lymphocytes with phytohaemagglutinin. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Jan;43(3):213–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D., Marangos P. J., Brightman M. Neurone-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):834–836. doi: 10.1038/276834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D., Marangos P. J., Zis A. P., Brightman M., Goodwin F. K. Brain endolases as specific markers of neuronal and glial cells. Science. 1978 Jan 20;199(4326):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.339349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Suzuki F., Kato K. Purification of two enolases from human brain using a chromatofocusing column. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 6;717(2):348–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90189-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia F. J., Polak J. M., Barbosa A. J., Bloom S. R., Marangos P. J., Dermody C., Pearse A. G. Neuron-specific enolase is produced by neuroendocrine tumours. Lancet. 1981 Apr 11;1(8224):808–811. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92682-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich W., Horvat R., Krisch K. Lectin histochemistry of kidney tumours and its pathomorphological relevance. Histopathology. 1985 Oct;9(10):1037–1050. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinores S. A., Bonnin J. M., Rubinstein L. J., Marangos P. J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of neuron-specific enolase in neoplasms of the CNS and other tissues. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1984 Jul;108(7):536–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







