Abstract
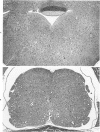
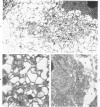
Newborn inbred CFW/D mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with ts1, a neurotropic temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB (MoMuLV-TB), with the parental wild type (wt) MoMuLV-TB, or with culture medium. A progressive symmetric hindlimb paresis that progressed to paralysis was observed in ts1-infected mice. Wt-infected mice and control mice had no neurologic signs. The severity and progression of neurologic signs correlated with the location, development, and progression of lesions. Lesions consisted of neuronal and glial cell vacuolization in the brain and the anterior horn of the spinal cord, spongiform change in the associated neuropil, spongiform change in lateral and ventral funiculi, and late fibrillary gliosis in the brainstem. There was no inflammation. Lesions were symmetric, increased in severity with time, and consistently arose at specific times in specific nuclei and areas of the brain and spinal cord. Similar, but less severe, histologic lesions were observed in corresponding areas of the central nervous system from wt-infected mice. Ultrastructurally, neuronal and glial cell vacuolization in ts1-infected mice at 31 days after inoculation was caused by dilatation of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Virions were observed in extremely low numbers predominantly in extracellular space and budding from membranes of neurons and glial cells. Virions were not observed in the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi complex of neurons, nor were there cytoplasmic vacuoles that contained abnormal virions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Schneck L., Cara J., Volk B. W. Spongy degeneration of the central nervous system (van Bogaert and Bertrand type; Canavan's disease). A review. Hum Pathol. 1973 Sep;4(3):331–347. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(73)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews J. M., Gardner M. B. Lower motor neuron degeneration associated with type C RNA virus infection in mice: neuropathological features. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Apr;33(2):285–307. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197404000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL J. K., HUH T. Y., MCCARTER J. A. ON THE STATISTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF EPIDERMAL PAPILLOMATA IN MICE. Br J Cancer. 1964 Mar;18:120–123. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1964.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Feussner G. K., Lust W. D. Spinal cord metabolic changes in murine retrovirus-induced motor neuron disease. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Dec;11(6):681–686. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Gossage J., Johnson R. T. Age-dependent in vitro restriction of mouse neurotropic retrovirus replication in central nervous system-derived cells from susceptible Fv-1nn mice. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1981;106:238–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. I. Pathogenesis of infection in newborn mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Narayan O., Johnson R. T. Murine neurotropic retrovirus spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy: acceleration of disease by virus inoculum concentration. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):540–544. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.540-544.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Retroviral spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):99–110. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B. Type C viruses of wild mice: characterization and natural history of amphotropic, ecotropic, and xenotropic MuLv. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;79:215–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66853-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Subacute spongiform virus encephalopathies. Scrapie, Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a review. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):626–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarter J. A., Ball J. K., Frei J. V. Lower limb paralysis induced in mice by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Moloney leukemia virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. II. Role of virus and host gene products. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):180–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Lampert P. W., Lee S., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with WM 1504 E virus. I. Relationship of strain susceptibility and replication to disease. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jul;88(1):193–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rude R., Gallick G. E., Wong P. K. A fast replica plating technique for the isolation of post-integration mutants of the Moloney strain of murine leukaemia virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Aug;49(2):367–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarz J. R., Brooks B. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. II. Ultrastructural localization of virus replication and spongiform changes in the central nervous system. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Sep-Oct;7(5):365–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Knupp C., Yuen P. H., Soong M. M., Zachary J. F., Tompkins W. A. ts1, a Paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, has an enhanced ability to replicate in the central nervous system and primary nerve cell culture. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.760-767.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Russ L. J., McCarter J. A. Rapid, selective procedure for isolation of spontaneous temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., MacLeod R., Gallick G. E., Yuen P. H. A group of temperature-sensitive mutants of Moloney leukemia virus which is defective in cleavage of env precursor polypeptide in infected cells also induces hind-limb paralysis in newborn CFW/D mice. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Soong M. M., Yuen P. H. Replication of murine leukemia virus in heterologous cells: interaction between ecotropic and xenotropic viruses. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Nau C., Soong M. M., Wong P. K. Molecular cloning of two paralytogenic, temperature-sensitive mutants, ts1 and ts7, and the parental wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):178–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.178-185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Malehorn D., Nau C., Soong M. M., Wong P. K. Molecular cloning of two paralytogenic, temperature-sensitive mutants, ts1 and ts7, and the parental wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):178–185. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.178-185.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Soong M. M., Kissil M. S., Wong P. K. Restriction of Moloney murine leukemia virus replication in Moloney murine sarcoma virus-infected cells. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary J. F., O'Brien D. P. Spongy degeneration of the central nervous system in two canine littermates. Vet Pathol. 1985 Nov;22(6):561–571. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]