Abstract
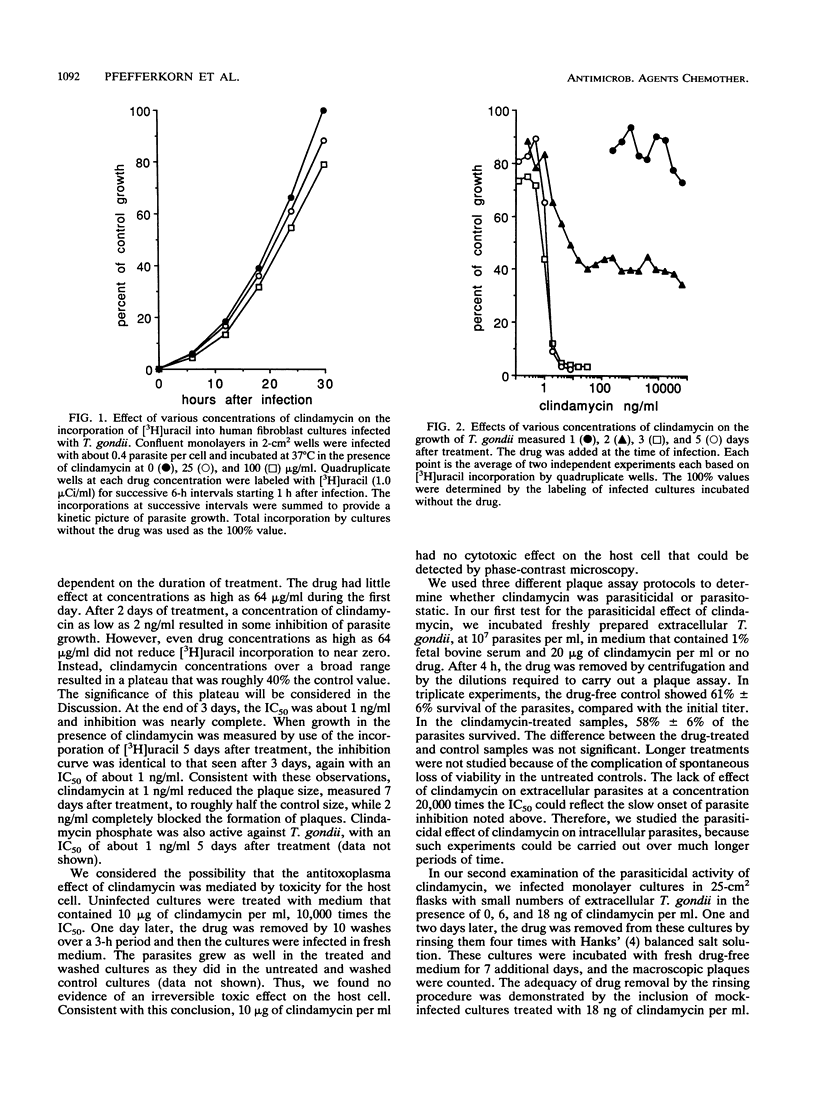
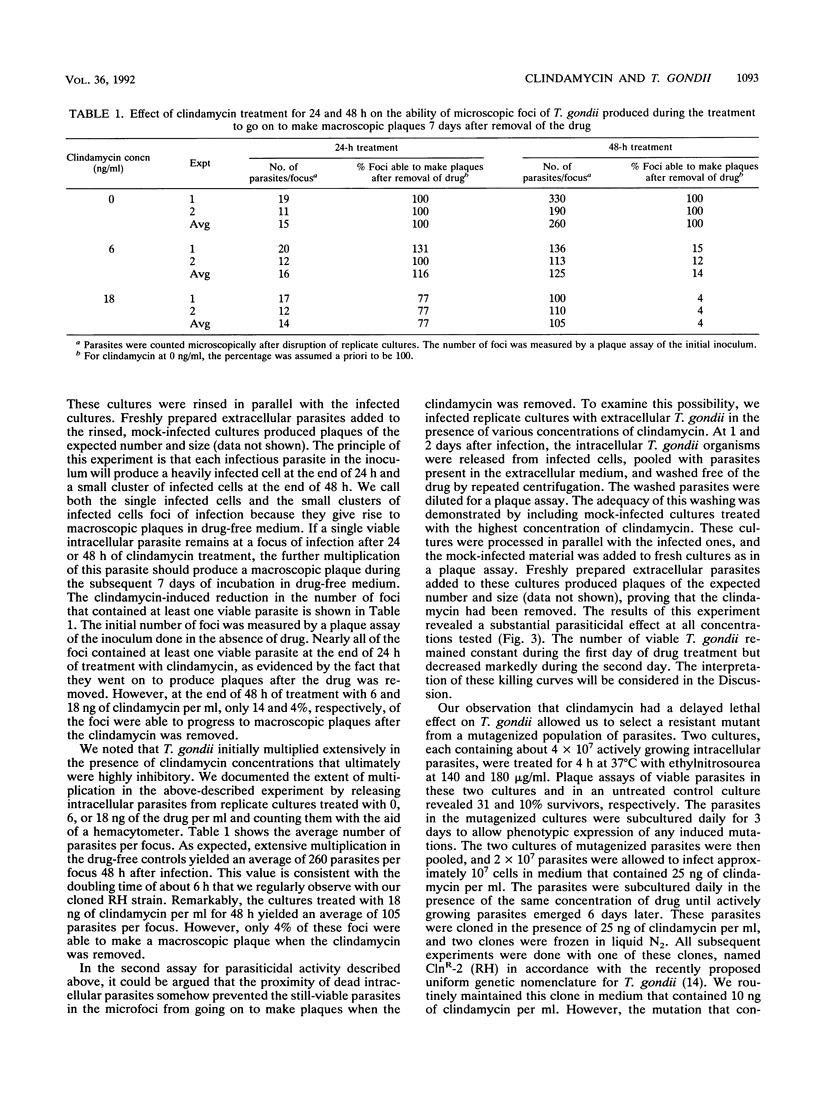
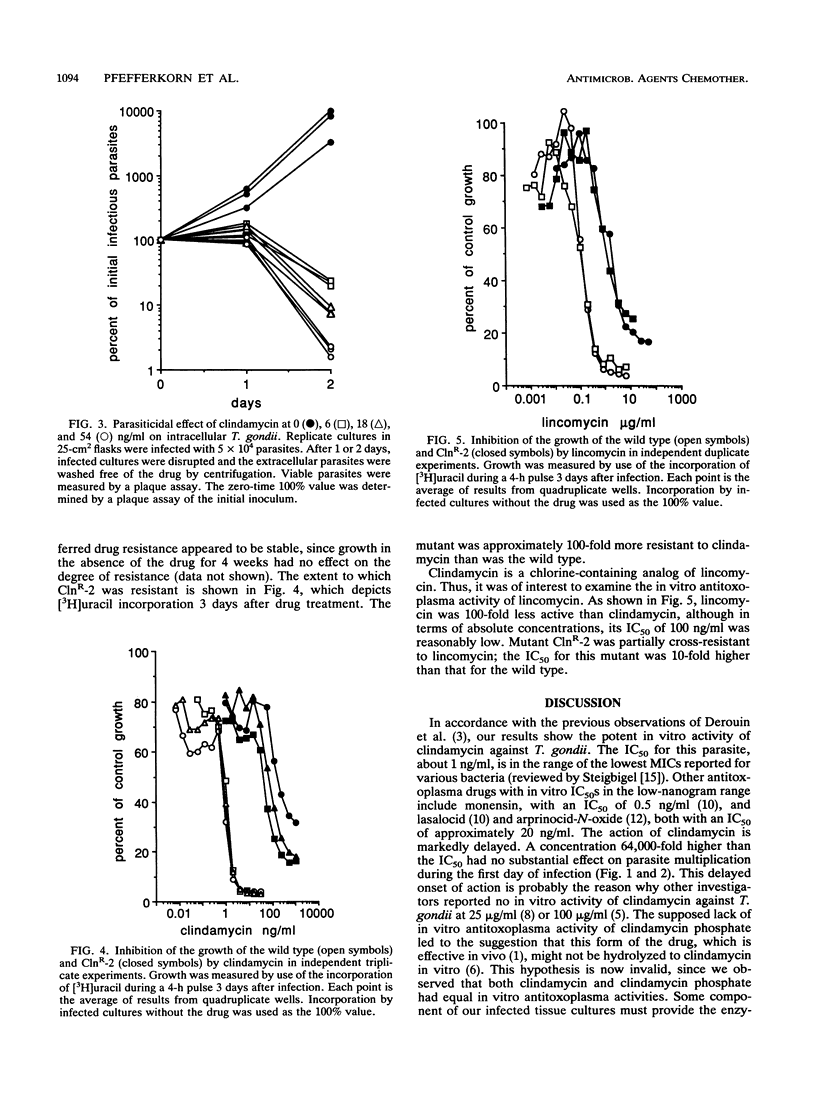
Clindamycin, which has been reported to have no significant in vitro activity against Toxoplasma gondii, actually markedly inhibits the growth of this parasite in infected human fibroblasts. When measured 3 days after treatment, the concentration required to reduce parasite growth by 50% is about 1 ng/ml. Some observers failed to note this inhibition because of its markedly delayed onset. At 6 ng/ml, clindamycin is parasiticidal, and the rate and extent of parasite killing increase with higher drug concentrations. With the aid of chemical mutagenesis, we isolated a parasite mutant that is approximately 100-fold more resistant to clindamycin than is the wild type. Lincomycin inhibits T. gondii at a higher 50% inhibitory concentration, about 100 ng/ml. The clindamycin-resistant mutant is partially cross-resistant to lincomycin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Remington J. S. Effect of clindamycin on acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jun;5(6):647–651. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.6.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannemann B. R., Israelski D. M., Remington J. S. Treatment of toxoplasmic encephalitis with intravenous clindamycin. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Nov;148(11):2477–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Nalpas J., Chastang C. Mesure in vitro de l'effet inhibiteur de macrolides, lincosamides et synergestines sur la croissance de Toxoplasma gondii. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1988 Dec;36(10):1204–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C., Salgo M. P., Tanowitz H. B., Wittner M. In vitro assessment of antimicrobial agents against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):14–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofflin J. M., Remington J. S. Clindamycin in a murine model of toxoplasmic encephalitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):492–496. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiatfuengfoo R., Suthiphongchai T., Prapunwattana P., Yuthavong Y. Mitochondria as the site of action of tetracycline on Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 May 1;34(2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Debs R. J., Ryan J. L. Incorporation of recombinant gamma interferon into liposomes enhances its ability to induce peritoneal macrophage antitoxoplasma activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):132–137. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.132-137.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton M. L., Sheffield H. G. Activity of the anticoccidial compound, lasalocid, against Toxoplasma gondii in cultured cells. J Parasitol. 1975 Aug;61(4):713–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Eckel M. E., McAdams E. Toxoplasma gondii: in vivo and in vitro studies of a mutant resistant to arprinocid-N-oxide. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Apr;65(2):282–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Toxoplasma gondii: isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Jun;39(3):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Toxoplasma gondii: the enzymic defect of a mutant resistant to 5-fluorodeoxyuridine. Exp Parasitol. 1978 Feb;44(1):26–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(78)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Pfefferkorn E. R., Boothroyd J. C. Proposal for a uniform genetic nomenclature in Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol Today. 1991 Dec;7(12):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90210-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


