Abstract
Intracellular neurofibrillary tangles is one of the most characteristic findings in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia of Alzheimer type. In the present paper the authors show that intracellular accumulation of paired helical filaments is also a constant finding in the epithelial cells of the choroid plexus of aging persons. Like the neurofibrillary tangles, the fibrils of the choroid plexus show staining properties typical of amyloid. The nature of the fibrils could not be clarified by electron microscopy or by immunohistochemistry with the use of antisera to gamma-trace or to amyloid fibril proteins of AA and prealbumin type. Amyloid protein AP, found in all amyloid substances except for neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid of senile plaques in the brain, was not demonstrated in the inclusions of the choroid plexus.
Full text
PDF

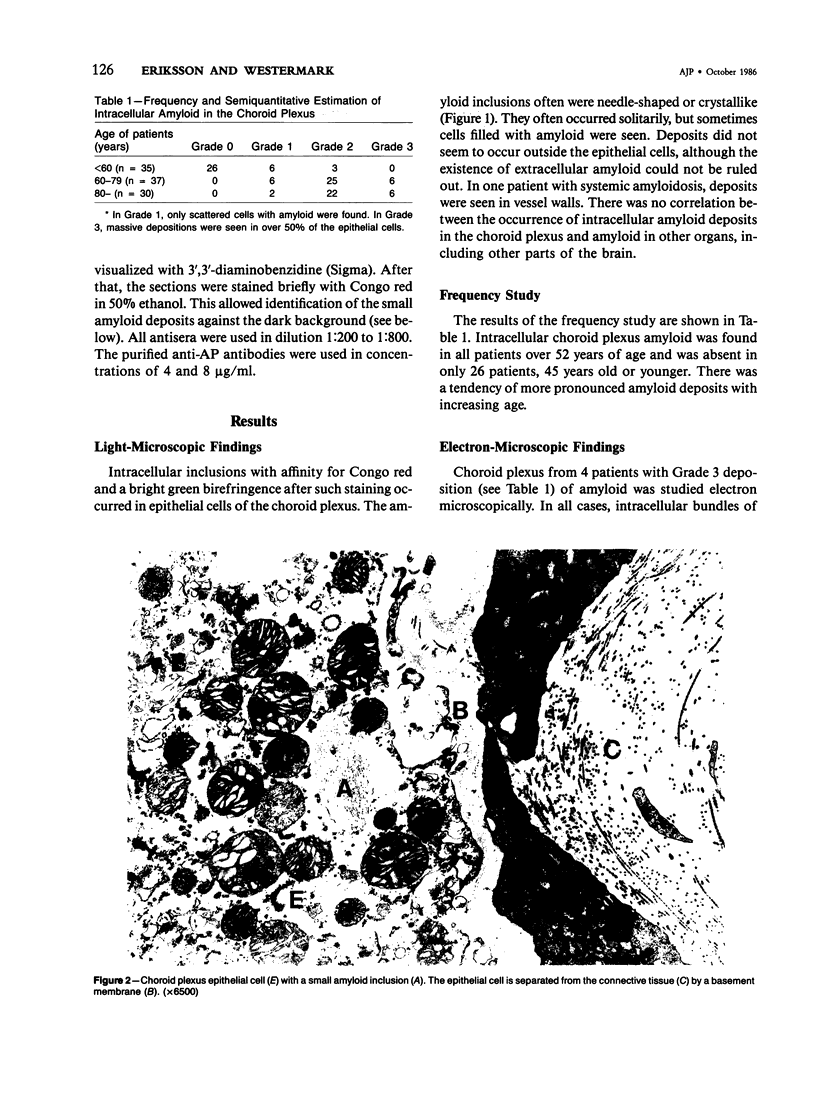
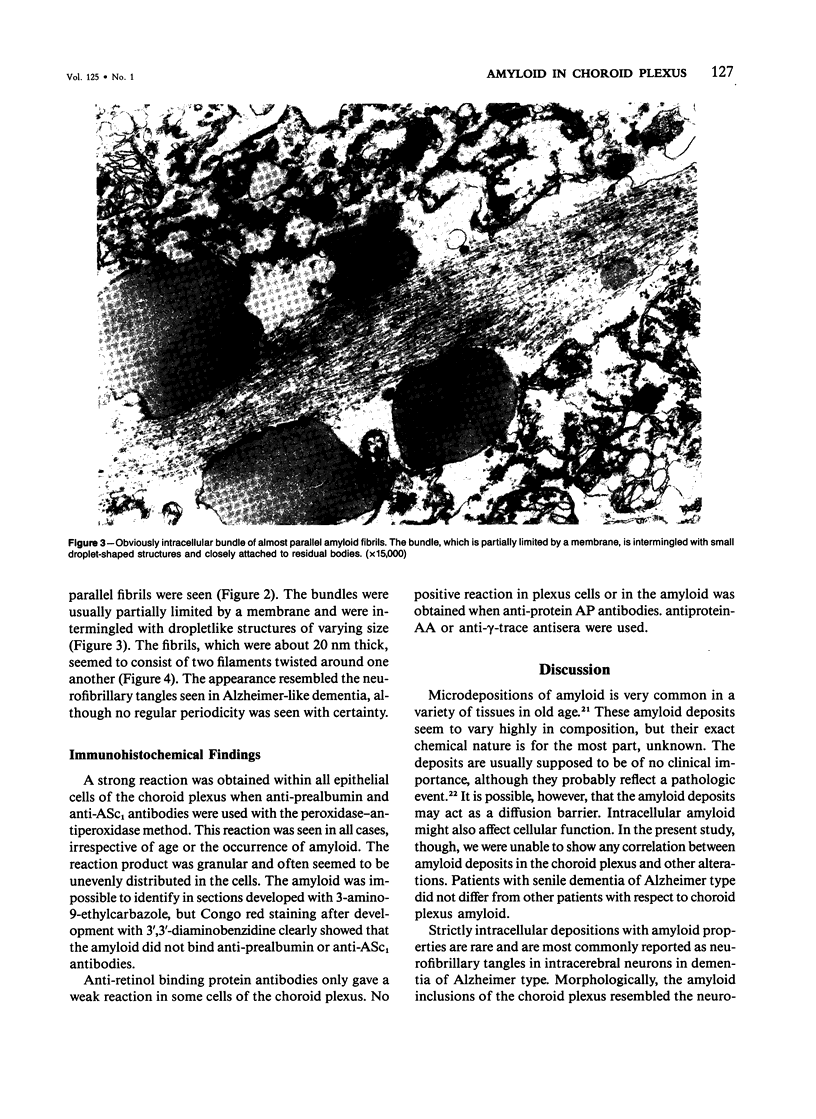


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aleshire S. L., Bradley C. A., Richardson L. D., Parl F. F. Localization of human prealbumin in choroid plexus epithelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 May;31(5):608–612. doi: 10.1177/31.5.6341455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann W., Katritsis E. Uber die sog. Filamente und das Pigment im Plexus Chorioideus des Menschen. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;75(1):366–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Vogel F. S. The development of the pathologic changes of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia in patients with Down's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1973 Nov;73(2):457–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell G. G., 3rd, Husby G., Westermark P., Natvig J. B., Michaelsen T. E., Skogen B. Identification and characterization of different amyloid fibril proteins in tissue sections. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(11):1071–1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell G. G., 3rd, Westermark P. Senile amyloidosis: a protean manifestation of the aging process. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1146–1152. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIVRY P. De la nature des formations argentophiles des plexus chorïdes. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1955 Mar;55(3):282–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson P. W., Howlett G. J., Schreiber G. Rat transthyretin (prealbumin). Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and gene expression in liver and brain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8214–8219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohrmann G. J., Bucy P. C. Human choroid plexus: a light and electron microscopic study. J Neurosurg. 1970 Nov;33(5):506–516. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.33.5.0506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L., Perry G., Shecket G., Crane R. C. Antibodies to neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease raised from human and animal neurofilament fractions. Lab Invest. 1983 Oct;49(4):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Johnson A. B., Wisniewski H. M., Terry R. D., Iqbal K. Evidence that Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles originate from neurotubules. Lancet. 1979 Mar 17;1(8116):578–580. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen M., Jacobsen G. K., Clausen P. P., Saunders N. R., Møllgård K. Intracellular plasma proteins in human fetal choroid plexus during development. II. The distribution of prealbumin, albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, transferrin, IgG, IgA, IgM, and alpha 1-antitrypsin. Brain Res. 1982 Feb;255(2):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:192–193. doi: 10.1038/197192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. X-ray diffraction from intraneuronal paired helical filaments and extraneuronal amyloid fibers in Alzheimer disease indicates cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Duffy L. K., Dowling M. M., Abraham C., McCluskey A., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Dash A. C. Isolation of amyloid P component (protein AP) from normal serum as a calcium-dependent binding protein. Lancet. 1977 May 14;1(8020):1029–1031. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91260-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Rizzuto N., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasool C. G., Selkoe D. J. Alzheimer's disease: exposure of neurofilament immunoreactivity in SDS-insoluble paired helical filaments. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 19;322(1):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermark P., Shirahama T., Skinner M., Brun A., Cameron R., Cohen A. S. Immunohistochemical evidence for the lack of amyloid P component in some intracerebral amyloids. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):457–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Stewart M., Roth M. Subunit structure of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1905–1912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Merz P. A., Iqbal K. Ultrastructure of paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Nov;43(6):643–656. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Narang H. K., Terry R. D. Neurofibrillary tangles of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]