Abstract
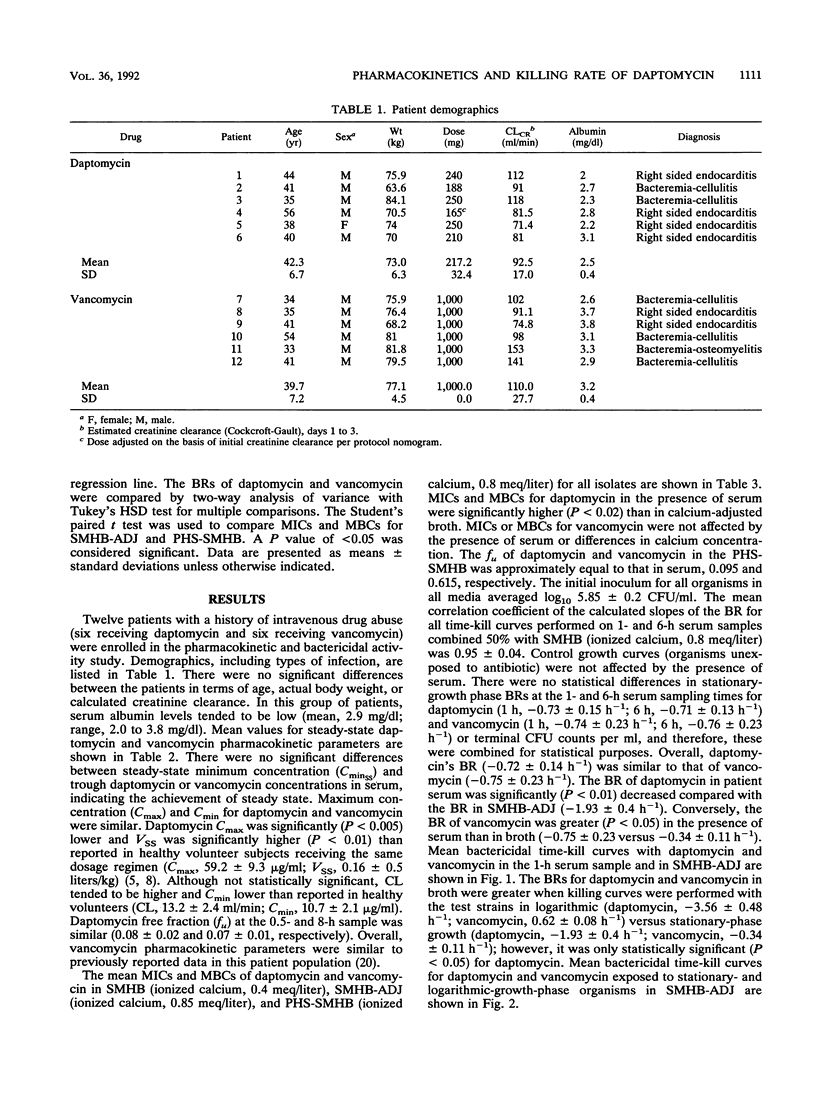
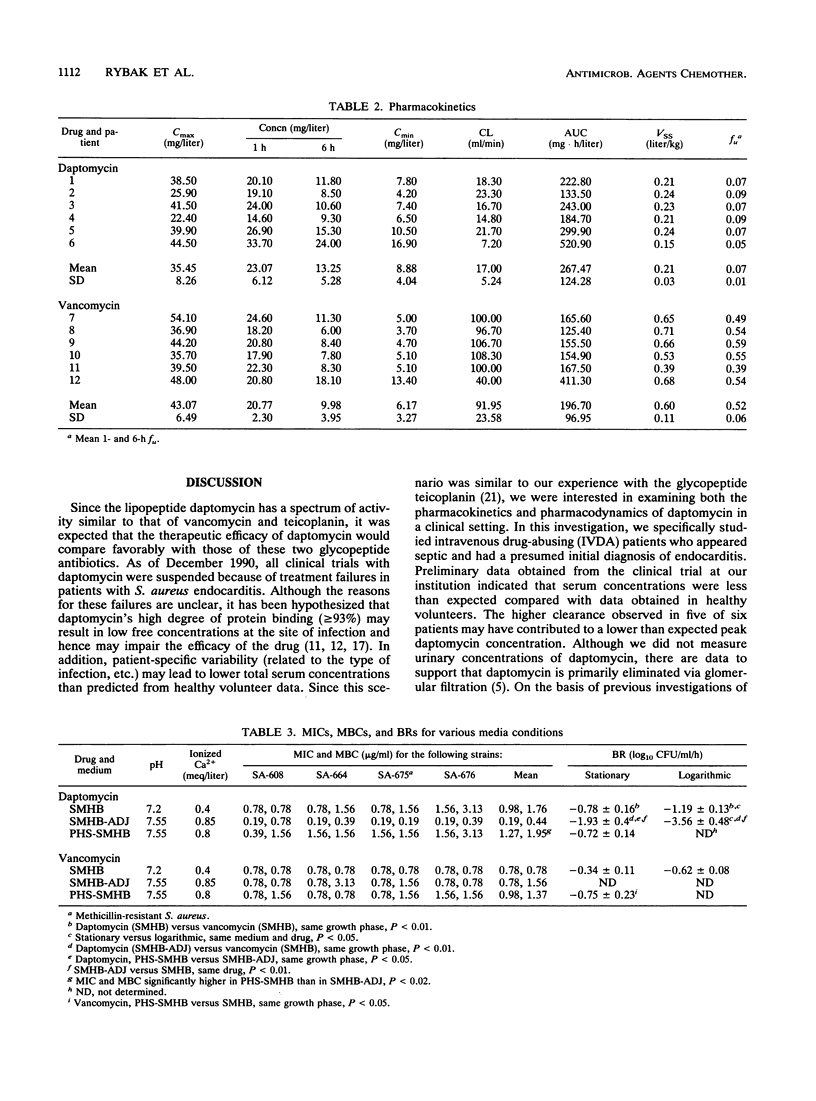
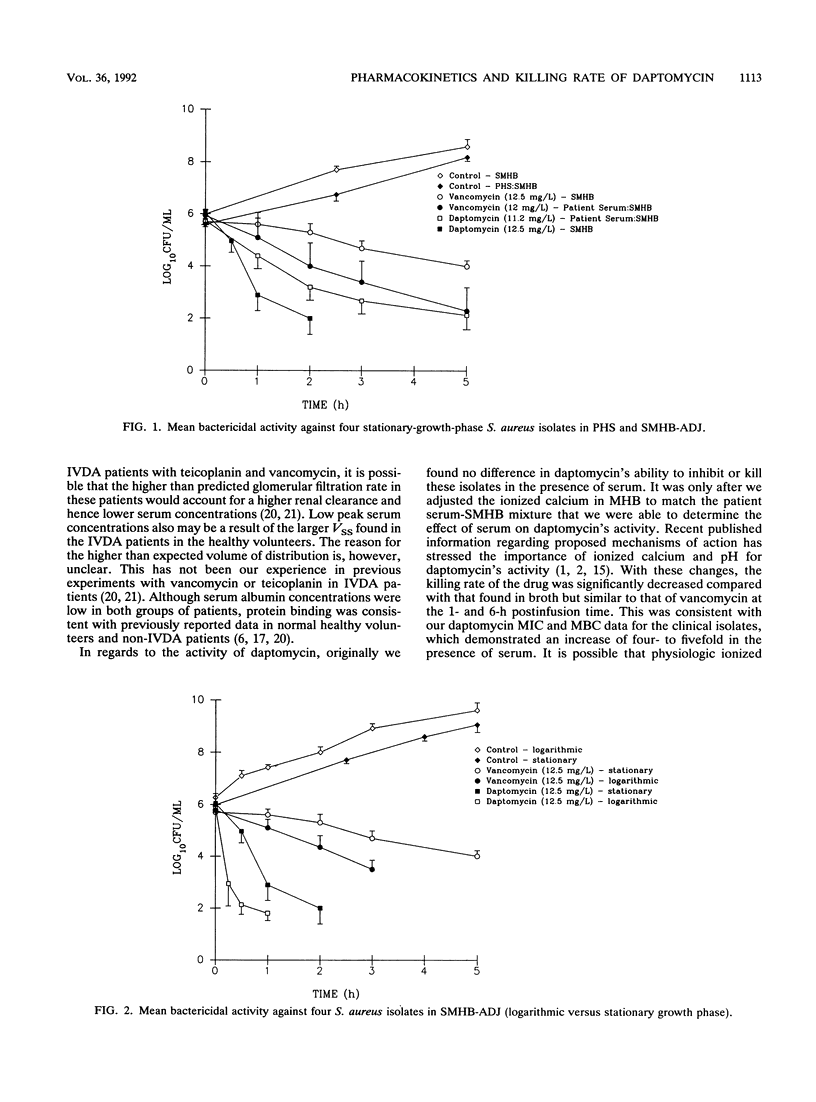
The pharmacokinetics and bactericidal killing rates (BR) of daptomycin (D) and vancomycin (V) in 12 intravenous drug abusers (6 treated with daptomycin and 6 treated with vancomycin) were evaluated. Pharmacokinetic parameters were determined from multiple serum samples drawn at steady state over a 12-h dosing interval after intravenous infusions of 3 mg of D per kg of body weight and 1,000 mg of V. The BRs were determined from the 1- and 6-h serum samples by using four isolates of Staphylococcus aureus (three methicillin susceptible and one methicillin resistant) obtained from the patients enrolled in the study. Peak serum daptomycin concentrations were lower and volumes of distribution were higher than reported in healthy volunteers. Although not statistically different, D clearance was 22% higher than reported in healthy volunteers. V pharmacokinetics were similar to those reported in previous studies. Daptomycin's BRs, although comparable to those of V in patients' serum, were significantly decreased compared with those found in broth. This may be related to the high degree of protein binding of D (93% versus 50% for V). Conversely, the BRs of V in serum were significantly greater than those in broth. The BRs of D and V in broth were greater when killing curves were performed with test strains in logarithmic versus stationary-phase growth. The ability to kill organisms in stationary phase may be an important factor in determining the performance of an antibiotic in deep-seated infections such as endocarditis.3+
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alborn W. E., Jr, Allen N. E., Preston D. A. Daptomycin disrupts membrane potential in growing Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2282–2287. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. E., Alborn W. E., Jr, Hobbs J. N., Jr Inhibition of membrane potential-dependent amino acid transport by daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2639–2642. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J., Kaatz G. W. Comparative effect of protein binding on the killing activities of teicoplanin and vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1089–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson C. A., Beaudette F., Trenholm G. Comparative in-vitro activity of LY146032 a new peptolide, with vancomycin and eight other agents against gram-positive organisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):191–196. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Azancot A., Raffoul H., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):938–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flandrois J. P., Fardel G., Carret G. Early stages of in vitro killing curve of LY146032 and vancomycin for Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):454–457. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison M. W., Rotschafer J. C., Crossley K. B. Suboptimal effect of daptomycin in the treatment of bacteremias. South Med J. 1989 Nov;82(11):1414–1415. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198911000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison M. W., Vance-Bryan K., Larson T. A., Toscano J. P., Rotschafer J. C. Assessment of effects of protein binding on daptomycin and vancomycin killing of Staphylococcus aureus by using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1925–1931. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. J., Calmon J., Wendeler M., Levison M. E., Johnson C. C. Synergistic bactericidal activity of rat serum with vancomycin against enterococci. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1358–1361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanberger H., Nilsson L. E., Maller R., Isaksson B. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin and vancomycin on Enterococcus faecalis and Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated by studies of initial killing and postantibiotic effect and influence of Ca2+ and albumin on these drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1710–1716. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Reddy V. N., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. Daptomycin compared with teicoplanin and vancomycin for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2081–2085. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. L., Sachdeva M., Chambers H. F. Effect of protein binding of daptomycin on MIC and antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2505–2508. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocci M. L., Jr, Jusko W. J. LAGRAN program for area and moments in pharmacokinetic analysis. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Jun;16(3):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Albrecht L. M., Berman J. R., Warbasse L. H., Svensson C. K. Vancomycin pharmacokinetics in burn patients and intravenous drug abusers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):792–795. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Lerner S. A., Levine D. P., Albrecht L. M., McNeil P. L., Thompson G. A., Kenny M. T., Yuh L. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in intravenous drug abusers being treated for bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Schentag J. J. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution during multiple dosing. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Feb;73(2):281–282. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600730239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


