Abstract
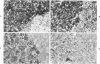
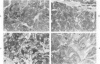
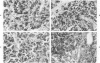
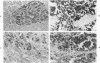
The immunohistochemical localization of epinephrine (E), norepinephrine (NE), and chromogranin was analyzed in normal and neoplastic neuroendocrine cells. The immunohistochemical detection of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), and phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) was used to distinguish between uptake and biosynthesis of catecholamines. E, NE, chromogranin, TH, DBH, and PNMT were found in the normal human adrenal medulla and in pheochromocytomas. Although many neuroendocrine tissues outside of the adrenal gland contained immunoreactive NE, only a small percentage of these tissues contained DBH. E was found in a few neuroendocrine tissues outside of the adrenal, including cardiac paragangliomas, and the enzyme PNMT was localized in some of these neoplasms. There was very close agreement between the localization of chromogranin and of catecholamines in normal and neoplastic neuroendocrine tissues. These results indicate that the presence of catecholamines and chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells and tumors within the adrenal medulla and in many other sites may be closely related.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedeczky I., Puppi A., Tigyi A., Lissák K. Various cell types in the adrenal medulla. Nature. 1966 Feb 5;209(5023):592–594. doi: 10.1038/209592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B. Stages of neurotransmitter development in autonomic neurons. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1198–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4537.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn M. C., Goldstein M., Black I. B. Role of glucocorticoids in expression of the adrenergic phenotype in rat embryonic adrenal gland. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90423-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Barajas L., Latta H. The ultrastructure of the human adrenal medulla: with comparative studies of white rat. Anat Rec. 1971 Feb;169(2):173–183. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091690204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E., PYPER A. S., HOPWOOD D. A METHOD FOR DIFFERENTIATING BETWEEN NORADRENALINE- AND ADRENALINE-STORING CELLS IN THE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1240–1242. doi: 10.1038/2011240b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Elting J. J., Frick M., Elde R. Selective localization of the parathyroid secretory protein-I/adrenal medulla chromogranin A protein family in a wide variety of endocrine cells of the rat. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):1963–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Berneis K. H., Pletscher A. Storage of catecholamines in adrenal medullary granules: formation of aggregates with nucleotides. Life Sci I. 1971 Jun 1;10(11):639–646. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLellis R. A., Tischler A. S., Wolfe H. J. Multidirectional differentiation in neuroendocrine neoplasms. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Aug;32(8):899–904. doi: 10.1177/32.8.6146648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman K., Hammond W. G. Adrenaline production by an intrathoracic phaeochromocytoma. Lancet. 1968 Mar 23;1(7543):609–611. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENNER G. G., CROUT J. R., ROBERTS W. C. A functional carotid-body-like tumor. Secreting levarterenol. Arch Pathol. 1962 Mar;73:230–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G., Rush R. A. Immunohistochemical localizatio of protein components of catecholamine storage vesicles. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):593–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberger C. A., Hamberger C. B., Wersäll J., Wågermark J. Malignant catecholamine-producing tumour of the carotid body. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;69(4):489–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb03758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey R. M., DiStefano V. Control of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase by glucocorticoids in cultured bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Apr;209(1):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm R., Sobrinho-Simões M., Nesland J. M., Gould V. E., Johannessen J. V. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland: an immunocytochemical study. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1985;8(1):25–41. doi: 10.3109/01913128509141506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Joh T. H. Immunohistochemical localization of three catecholamine synthesizing enzymes: aspects on methodology. Histochemie. 1973;33(3):231–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00274236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaques S., Jr, Tobes M. C., Sisson J. C., Baker J. A., Wieland D. M. Comparison of the sodium dependency of uptake of meta-lodobenzylguanidine and norepinephrine into cultured bovine adrenomedullary cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonakait G. M., Wolf J., Cochard P., Goldstein M., Black I. B. Selective loss of noradrenergic phenotypic characters in neuroblasts of the rat embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4683–4686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Blaivas M., Wilson B. S. Distribution of chromogranin and S100 protein in normal and abnormal adrenal medullary tissues. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Jul;109(7):633–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Shapiro B., Sisson J. C., Kalff V., Thompson N. W., Beierwaltes W. A. An immunohistochemical study of pheochromocytomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1984 Jul;108(7):541–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros L. J., Wolf B. C., Balogh K., Federman M. Adrenal pheochromocytoma: a clinicopathologic review of 60 cases. Hum Pathol. 1985 Jun;16(6):580–589. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(85)80107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Hogue-Angeletti R. Neurons and neuroendocrine cells contain chromogranin: detection of the molecule in normal bovine tissues by immunochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Aug;33(8):791–798. doi: 10.1177/33.8.3894497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin: widespread immunoreactivity in polypeptide hormone producing tissues and in serum. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D. H., Baetge E. E., Kaplan B. B., Albert V. R., Reis D. J., Joh T. H. Different forms of adrenal phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase: species-specific posttranslational modification. J Neurochem. 1982 Feb;38(2):410–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08644.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen M., Rapoport S. I., Reis D. J., Joh T. H., Stolk J. M., Linnoila I., Teitelman G., Hervonen A. Catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes in paraganglia of aged Fischer-344 rats. Immunohistochemistry and fluorescence microscopy. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;238(2):217–220. doi: 10.1007/BF00217291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The diffuse neuroendocrine system and the apud concept: related "endocrine" peptides in brain, intestine, pituitary, placenta, and anuran cutaneous glands. Med Biol. 1977 Jun;55(3):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H. Dynamic aspects of chromaffin granule structure. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1595–1609. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohorecky L. A., Wurtman R. J. Adrenocortical control of epinephrine synthesis. Pharmacol Rev. 1971 Mar;23(1):1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra J. M., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J., Axelrod J. Localisation of phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase in the rat brain nuclei. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):695–696. doi: 10.1038/248695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Sharp R. R., Domino L. E., Domino E. F. Composition of the aqueous phase of chromaffin granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 20;587(1):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R. R., Richards E. P. Molecular mobilities of soluble components in the aqueous phase of chromaffin granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):260–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., DePotter R. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M., Winkler H., Chubb I. W. Chromogranin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Immunochemical characterisation, distribution and relationship to catecholamine and enkephalin pathways. Brain Res. 1984 Dec;320(2-3):193–230. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAN T. L., YOUNG B. W. Pheochromocytoma of the bladder: case report. J Urol. 1962 Jan;87:63–67. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)64908-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelman G., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Transformation of catecholaminergic precursors into glucagon (A) cells in mouse embryonic pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Aborg C. H. In vitro studies on a two-pool stage of adrenaline and noradrenaline in granule material from bovine adrenal medulla. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Aug;109(4):345–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Aborg C. H. The ability of ATP-free granule material from bovine adrenal medulla to bind inorganic cations and biogenic amines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Apr;99(4):476–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Parker T. R., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00214536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M., Steinbusch H. W., Joosten H. W. Appearance of tyrosine hydroxylase, aromatic amino-acid decarboxylase, dopamine beta-hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase during the ontogenesis of the adrenal medulla: an immunohistochemical study in the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Aug 3;200(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00236882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Lloyd R. V. Detection of chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells with a monoclonal antibody. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):458–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman R. J., Axelrod J., Vesell E. S., Ross G. T. Species differences in inducibility of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. Endocrinology. 1968 Mar;82(3):584–590. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-3-584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]