Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (122.4 KB).
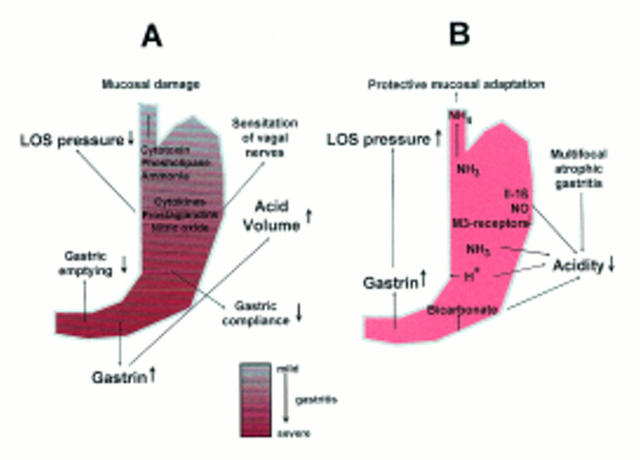
Figure 1 .
: Proposed mechanisms by which H pylori infection could aggravate (A), or protect against (B), GORD. In condition A the gastritis is antrum predominant (antrum > corpus). In condition B the gastritis involves all regions of the stomach to the same degree (corpus ⩾ antrum). It is of note that the cardia is always inflamed.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allescher H. D., Stoschus B., Wünsch E., Schusdziarra V., Classen M. Effect of human gastrin-17 with and without acid suppression on human esophageal motility. Z Gastroenterol. 1995 Jul;33(7):385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayerdörffer E., Neubauer A., Rudolph B., Thiede C., Lehn N., Eidt S., Stolte M. Regression of primary gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection. MALT Lymphoma Study Group. Lancet. 1995 Jun 24;345(8965):1591–1594. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil W., Birkholz C., Wagner S., Sewing K. F. Interaction of Helicobacter pylori and its fatty acids with parietal cells and gastric H+/K(+)-ATPase. Gut. 1994 Sep;35(9):1176–1180. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.9.1176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell N. J., Burget D., Howden C. W., Wilkinson J., Hunt R. H. Appropriate acid suppression for the management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 1992;51 (Suppl 1):59–67. doi: 10.1159/000200917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulant J., Fioramonti J., Dapoigny M., Bommelaer G., Bueno L. Cholecystokinin and nitric oxide in transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation to gastric distention in dogs. Gastroenterology. 1994 Oct;107(4):1059–1066. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd E. J. The prevalence of esophagitis in patients with duodenal ulcer or ulcer-like dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Aug;91(8):1539–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell D. O. Obesity and gastro-oesophageal reflux: is there a relationship? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Jul;8(7):625–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave D. R., Vargas M. Effect of a Campylobacter pylori protein on acid secretion by parietal cells. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):187–189. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90372-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederberg C., Röhss K., Lundborg P., Olbe L. Effect of once daily intravenous and oral omeprazole on 24-hour intragastric acidity in healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;28(2):179–184. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederberg C., Thomson A. B., Mahachai V., Westin J. A., Kirdeikis P., Fisher D., Zuk L., Marriage B. Effect of intravenous and oral omeprazole on 24-hour intragastric acidity in duodenal ulcer patients. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):913–918. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90025-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen M. J., Lewis J. H., Benjamin S. B. Gastric acid hypersecretion in refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1990 Mar;98(3):654–661. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent J., Holloway R. H., Toouli J., Dodds W. J. Mechanisms of lower oesophageal sphincter incompetence in patients with symptomatic gastrooesophageal reflux. Gut. 1988 Aug;29(8):1020–1028. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.8.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esplugues J. V., Barrachina M. D., Calatayud S., Pique J. M., Whittle B. J. Nitric oxide mediates the inhibition by interleukin-1 beta of pentagastrin-stimulated rat gastric acid secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):9–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink S. M., Barwick K. W., DeLuca V., Sanders F. J., Kandathil M., McCallum R. W. The association of histologic gastritis with gastroesophageal reflux and delayed gastric emptying. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1984 Aug;6(4):301–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman D. Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;215:48–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galmiche J. P., Janssens J. The pathophysiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: an overview. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1995;211:7–18. doi: 10.3109/00365529509090286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Huberman R. M., Graham D. Y. The gastric cardia in Helicobacter pylori infection. Hum Pathol. 1994 Sep;25(9):915–919. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Malaty H. M., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Klein P. D., Adam E. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori in an asymptomatic population in the United States. Effect of age, race, and socioeconomic status. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jun;100(6):1495–1501. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90644-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley M. N., Walker S. J., Mackie C. R. Abnormal gastric adaptive relaxation in patients with gastrooesophageal reflux. Gut. 1990 May;31(5):500–503. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.5.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh P. J., Clapp R. W., Doos W. G., Spechler S. J. The increasing frequency of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Cancer. 1989 Jul 15;64(2):526–530. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890715)64:2<526::aid-cncr2820640228>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschowitz B. I. A critical analysis, with appropriate controls, of gastric acid and pepsin secretion in clinical esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1991 Nov;101(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90062-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. J., Girardi L. S., Turney E. A. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori eradication and reduced duodenal and gastric ulcer recurrence: a review. Gastroenterology. 1996 Apr;110(4):1244–1252. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson F., Joelsson B., Gudmundsson K., Greiff L. Symptoms and endoscopic findings in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Aug;22(6):714–718. doi: 10.3109/00365528709011148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J. Cigarette smoking and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis. 1992;10(2):61–71. doi: 10.1159/000171345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J., Kern M., Arndorfer R. C., Reece A. Esophageal peristaltic dysfunction in peptic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90692-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. H., Wang S. J., Chen G. H., Yeh S. H. The relationship between Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis or ulcer disease and gastric emptying. Eur J Nucl Med. 1994 Mar;21(3):209–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00188667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. E., Kaye M. D. Induction of gastro-oesophageal reflux by alcohol. Gut. 1978 Apr;19(4):336–338. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.4.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek J. W., Gillessen A., Konturek S. J., Domschke W. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori restores the inhibitory effect of cholecystokinin on postprandial gastrin release in duodenal ulcer patients. Gut. 1995 Oct;37(4):482–487. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.4.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Konturek P. C., Brzozowski T., Stachura J., Zembala M. Gastric mucosal damage and adaptive protection by ammonia and ammonium ion in rats. Digestion. 1996 Nov-Dec;57(6):433–445. doi: 10.1159/000201372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Lee A., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Meuwissen S. G. Review article: the development of atrophic gastritis--Helicobacter pylori and the effects of acid suppressive therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Aug;9(4):331–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Lundell L., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Havu N., Festen H. P., Liedman B., Lamers C. B., Jansen J. B., Dalenback J., Snel P. Atrophic gastritis and Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with reflux esophagitis treated with omeprazole or fundoplication. N Engl J Med. 1996 Apr 18;334(16):1018–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199604183341603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Uyterlinde A. M., Peña A. S., Hazenberg H. J., Bloemena E., Lindeman J., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Meuwissen S. G. Increase of Helicobacter pylori-associated corpus gastritis during acid suppressive therapy: implications for long-term safety. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995 Sep;90(9):1401–1406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers E. J., Uyterlinde A. M., Peña A. S., Roosendaal R., Pals G., Nelis G. F., Festen H. P., Meuwissen S. G. Long-term sequelae of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Lancet. 1995 Jun 17;345(8964):1525–1528. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Blum A. L., Bayerdörffer E., Meining A., Stolte M., Börsch G. Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 1997 May;112(5):1442–1447. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Tillenburg B., Peitz U., Börsch G., Idström J. P., Verdú E., Stolte M., Blum A. L. Efficacy of omeprazole one year after cure of Helicobacter pylori infection in duodenal ulcer patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Apr;92(4):576–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Tillenburg B., Peitz U., Idström J. P., Verdú E. F., Stolte M., Börsch G., Blum A. L. Helicobacter pylori augments the pH-increasing effect of omeprazole in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1996 Mar;110(3):725–732. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8608881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labenz J., Tillenburg B., Peitz U., Verdú E., Stolte M., Börsch G., Blum A. L. Effect of curing Helicobacter pylori infection on intragastric acidity during treatment with ranitidine in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gut. 1997 Jul;41(1):33–36. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine L., Cominelli F., Sloane R., Casini-Raggi V., Marin-Sorensen M., Weinstein W. M. Interaction of NSAIDs and Helicobacter pylori on gastrointestinal injury and prostaglandin production: a controlled double-blind trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Apr;9(2):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loffeld R. J., Ten Tije B. J., Arends J. W. Prevalence and significance of Helicobacter pylori in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Nov;87(11):1598–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löf L., Götell P., Elfberg B. The incidence of reflux oesophagitis. A study of endoscopy reports from a defined catchment area in Sweden. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;28(2):113–118. doi: 10.3109/00365529309096056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. W., Berkowitz D. M., Lerner E. Gastric emptying in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):285–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. W., Walsh J. H. Relationship between lower esophageal sphincter pressure and serum gastrin concentration in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and other clinical settings. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):76–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan C. C., Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and gastric acid: biological and therapeutic implications. Gastroenterology. 1996 Mar;110(3):926–938. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8608904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mearin F., de Ribot X., Balboa A., Salas A., Varas M. J., Cucala M., Bartolomé R., Armengol J. R., Malagelada J. R. Does Helicobacter pylori infection increase gastric sensitivity in functional dyspepsia? Gut. 1995 Jul;37(1):47–51. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Rosberg K., Scott D. R., Rex D., Melchers K., Sachs G. The effect of environmental pH on the proton motive force of Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 1996 Oct;111(4):886–900. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(96)70056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers R. L., Orlando R. C. In vivo bicarbonate secretion by human esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1992 Oct;103(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91501-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. S., Vinayek R., Frucht H., Gardner J. D., Jensen R. T., Maton P. N. Reflux esophagitis in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1990 Feb;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90823-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittal R. K., Holloway R. H., Penagini R., Blackshaw L. A., Dent J. Transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation. Gastroenterology. 1995 Aug;109(2):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. Deleterious effects of prostaglandin E2 in reflux oesophagitis. Med Hypotheses. 1996 Jan;46(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/s0306-9877(96)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay A., Rattan S., Goyal R. K. Effect of prostaglandin E2 on esophageal motility in man. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Sep;39(3):479–481. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noach L. A., Bosma N. B., Jansen J., Hoek F. J., van Deventer S. J., Tytgat G. N. Mucosal tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-8 production in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 May;29(5):425–429. doi: 10.3109/00365529409096833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlando R. C., Powell D. W., Carney C. N. Pathophysiology of acute acid injury in rabbit esophageal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):286–293. doi: 10.1172/JCI110246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Krömer W., Friemann J., Ruge M., Herawi M., Schätzl M., Schwegler U., May B., Schatz H. Muscarinic receptors in gastric mucosa are increased in peptic ulcer disease. Gut. 1995 Jun;36(6):813–818. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.6.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phull P. S., Ryder S. D., Halliday D., Price A. B., Levi A. J., Jacyna M. R. The economic and quality-of-life benefits of Helicobacter pylori eradication in chronic duodenal ulcer disease--a community-based study. Postgrad Med J. 1995 Jul;71(837):413–418. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.71.837.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieramico O., Ditschuneit H., Malfertheiner P. Gastrointestinal motility in patients with non-ulcer dyspepsia: a role for Helicobacter pylori infection? Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Mar;88(3):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. U., Bell G. D., Bolton G. H., Burridge S. M., Bowden A. F., Rameh B., Hart L., Bradley P., Harrison G., Gant P. W. Helicobacter pylori eradication in patients with peptic ulcer disease: clinical consequences and financial implications. Q J Med. 1994 May;87(5):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiksaitis H. G., Tremblay L., Diamant N. E. Nitric oxide mediates inhibitory nerve effects in human esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Apr;39(4):770–775. doi: 10.1007/BF02087422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvist N., Rasmussen L., Axelsson C. K. Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis and dyspepsia. The influence on migrating motor complexes. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Feb;29(2):133–137. doi: 10.3109/00365529409090451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly T. G., Ayres R. C., Poxon V., Walt R. P. Helicobacter pylori eradication in a clinical setting: success rates and the effect on the quality of life in peptic ulcer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1995 Oct;9(5):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1995.tb00410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Olafsson A. S., Lancaster C., Zhang W. R. Interleukin-1 is cytoprotective, antisecretory, stimulates PGE2 synthesis by the stomach, and retards gastric emptying. Life Sci. 1991;48(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90405-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze K., Hentschel E., Dragosics B., Hirschl A. M. Helicobacter pylori reinfection with identical organisms: transmission by the patients' spouses. Gut. 1995 Jun;36(6):831–833. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.6.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. M., Kellow J. E., Shuter B., Cowan H., Corbett A. M., Riley J. W., Lunzer M. R., Eckstein R. P., Höschl R., Lam S. K. Intragastric distribution and gastric emptying of solids and liquids in functional dyspepsia. Lack of influence of symptom subgroups and H. pylori-associated gastritis. Dig Dis Sci. 1993 Dec;38(12):2247–2254. doi: 10.1007/BF01299904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaker R., Kahrilas P. J., Dodds W. J., Hogan W. J. Oesophageal clearance of small amounts of equal or less than one millilitre of acid. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):7–10. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solcia E., Fiocca R., Villani L., Carlsson J., Rudbäck A., Zeijlon L. Effects of permanent eradication or transient clearance of Helicobacter pylori on histology of gastric mucosa using omeprazole with or without antibiotics. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1996;215:105–110. doi: 10.3109/00365529609094545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J. Epidemiology and natural history of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Digestion. 1992;51 (Suppl 1):24–29. doi: 10.1159/000200911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi K., Ohuchi T., Okabe S. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on duodenal alkaline secretory and ulcerogenic responses induced by mepirizole in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Mar;40(3):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF02064389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trespi E., Broglia F., Villani L., Luinetti O., Fiocca R., Solcia E. Distinct profiles of gastritis in dyspepsia subgroups. Their different clinical responses to gastritis healing after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 Oct;29(10):884–888. doi: 10.3109/00365529409094858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucci A., Corinaldesi R., Stanghellini V., Tosetti C., Di Febo G., Paparo G. F., Varoli O., Paganelli G. M., Labate A. M., Masci C. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric function in patients with chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):768–774. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90004-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdú E. F., Armstrong D., Fraser R., Viani F., Idström J. P., Cederberg C., Blum A. L. Effect of Helicobacter pylori status on intragastric pH during treatment with omeprazole. Gut. 1995 Apr;36(4):539–543. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdú E. F., Armstrong D., Idström J. P., Labenz J., Stolte M., Börsch G., Blum A. L. Intragastric pH during treatment with omeprazole: role of Helicobacter pylori and H. pylori-associated gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1996 Dec;31(12):1151–1156. doi: 10.3109/00365529609036903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdú E. F., Armstrong D., Idström J. P., Labenz J., Stolte M., Dorta G., Börsch G., Blum A. L. Effect of curing Helicobacter pylori infection on intragastric pH during treatment with omeprazole. Gut. 1995 Dec;37(6):743–748. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.6.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener M., Börsch G., Schaffstein J., Schulz-Flake C., Mai U., Leverkus F. Are dyspeptic symptoms in patients with Campylobacter pylori-associated type B gastritis linked to delayed gastric emptying? Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jul;83(7):737–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. T., Ramanujam K. S., Mobley H. L., Musselman R. F., James S. P., Meltzer S. J. Helicobacter pylori stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and activity in a murine macrophage cell line. Gastroenterology. 1996 Dec;111(6):1524–1533. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(96)70014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasunaga Y., Shinomura Y., Kanayama S., Yabu M., Nakanishi T., Miyazaki Y., Murayama Y., Bonilla-Palacios J. J., Matsuzawa Y. Improved fold width and increased acid secretion after eradication of the organism in Helicobacter pylori associated enlarged fold gastritis. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1571–1574. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Omar E. M., Penman I. D., Ardill J. E., Chittajallu R. S., Howie C., McColl K. E. Helicobacter pylori infection and abnormalities of acid secretion in patients with duodenal ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1995 Sep;109(3):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]