Abstract
Background—Helicobacter pylori strains possessing the cagA gene are thought to induce interleukin 8 (IL-8) in gastric mucosa. However, it is still unclear whether a relation exists between the cagA gene and the expression patterns of cytokines other than IL-8. Aims—To investigate the relation between the cagA gene and the production of various cytokine proteins using an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Patients and methods—In 184 patients, the cagA gene was detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and levels of production of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, and tumour necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in antral biopsy specimens were measured by ELISA. Results—Mucosal levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α were significantly higher in H pylori positive than in H pylori negative patients. Furthermore, the mucosal levels of IL-1β and IL-8 were significantly higher in specimens infected with cagA positive strains than in those infected with cagA negative strains. In H pylori positive patients, the mucosal level of IL-8 was closely correlated with that of IL-1β (p<0.0001), and the mucosal level of IL-6 was closely correlated with that of TNF-α (p<0.0001). Conclusion—These findings suggest that the ability to induce cytokines differs among the strains; cagA+ strains induce various kinds of cytokines and may cause severe inflammation, whereas cagA strains induce IL-8 and IL-1β only weakly and may cause only mild inflammation. However, as most patients infected with the cagA+ strains have gastritis, these strains may not be equivalent to ulcerogenic strains.
Keywords: cytokines; Helicobacter pylori; cagA gene; interleukin 8; interleukin 1β
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (234.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
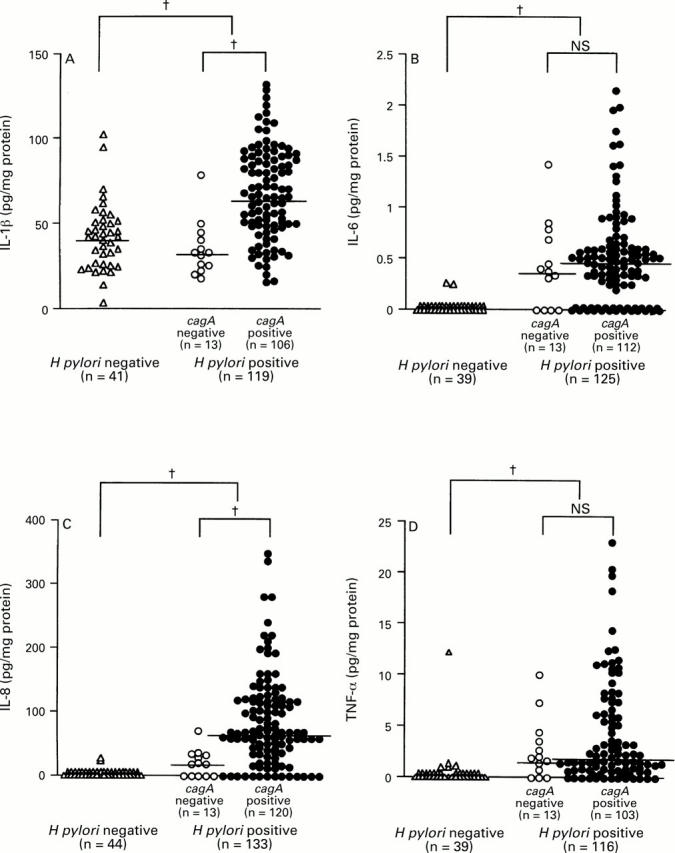
: Production of (A) IL-1β, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, and (D) TNF-α and H pylori infection. Large brackets indicate the comparison between H pylori positive and negative specimens and small brackets the comparison between cagA+ and cagA- specimens. Bars indicate median values for each group. †p<0.0001 by Mann-Whitney U test.
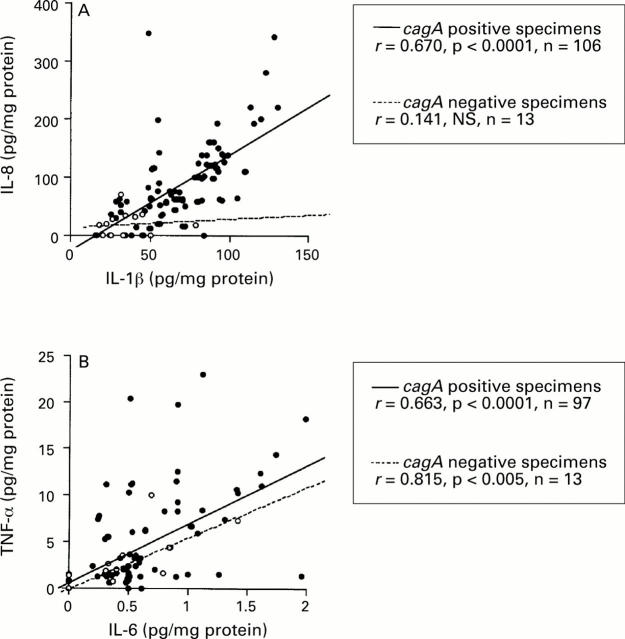
Figure 2 .
: Correlation between (A) IL-1β and IL-8, and (B) IL-6, and TNF-α production. Filled circles, cagA+ specimens; open circles, cagA specimens. Correlation coefficients were calculated with the Spearman rank test.
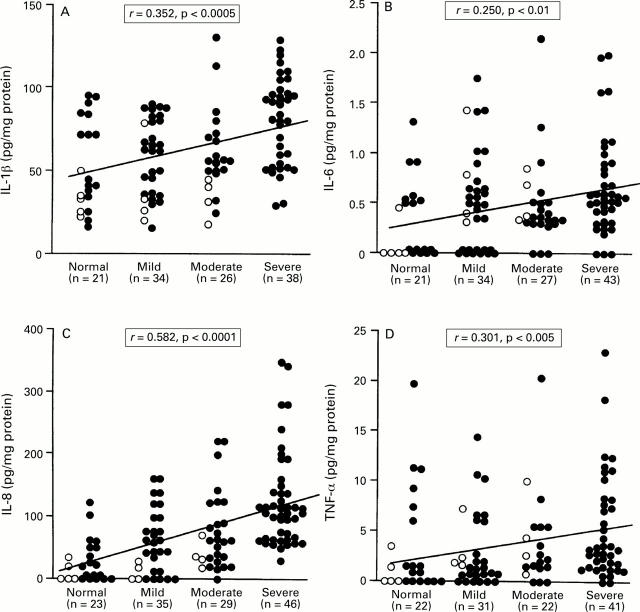
Figure 3 .
: Relation between the production of (A) IL-1β, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, and (D) TNF-α and MNC infiltration in patients with H pylori infection. Filled circles, cagA+ specimens; open circles, cagA specimens. Correlation coefficients were calculated with the Spearman rank test.
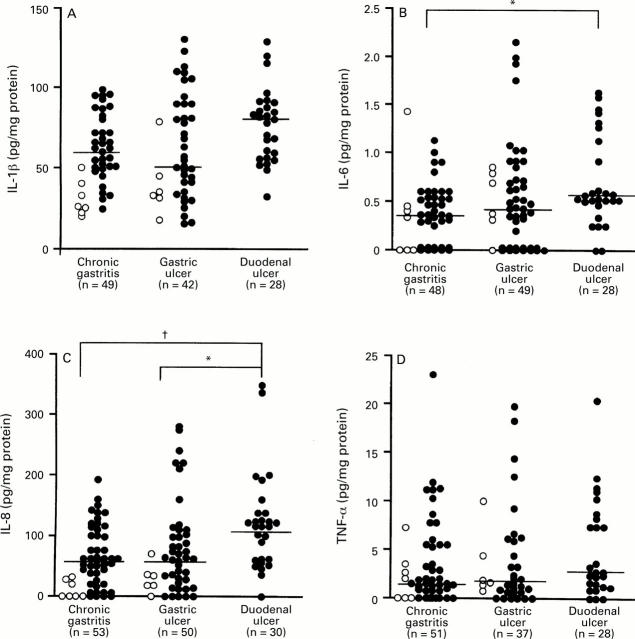
Figure 4 .
: Relation between the production of (A) IL-1β, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, and (D) TNF-α and PMN infiltration in patients with H pylori infection. Filled circles, cagA+ specimens; open circles, cagA specimens. Correlation coefficients were calculated with the Spearman rank test.
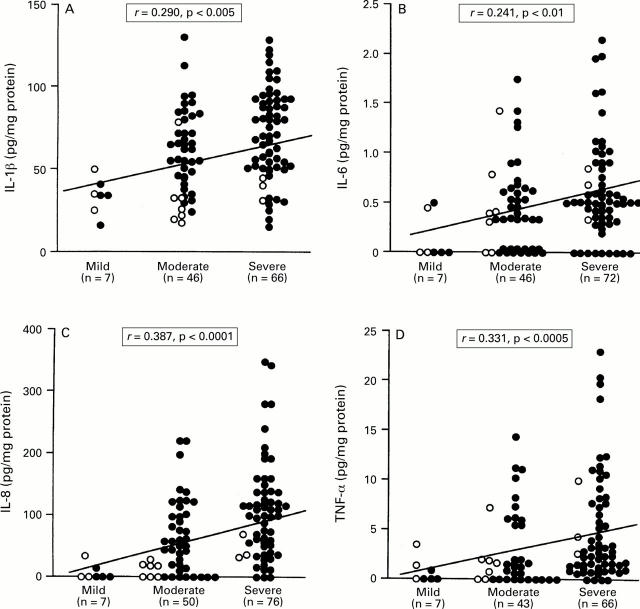
Figure 5 .
: Production of (A) IL-1β, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, and (D) TNF-α and endoscopic findings in patients with H pylori infection. Filled circles, cagA+ specimens; open circles, cagA specimens. Bars indicate median values for each group. *p<0.05; †p<0.005 by Mann-Whitney U test.
Figure 6 .
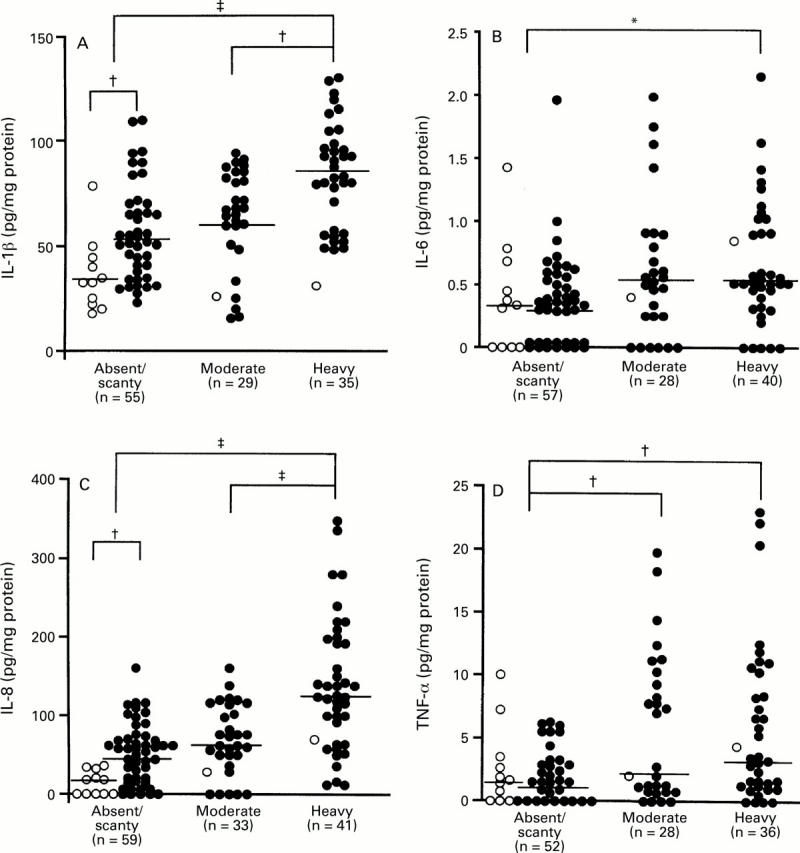
: Production of (A) IL-1β, (B) IL-6, (C) IL-8, and (D) TNF-α and the density of H pylori colonisation. Filled circles, cagA+ specimens; open circles, cagA specimens. *p<0.05; †p<0.005; ‡p<0.0001 by Mann-Whitney U test.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson M. R., Tough T. W., Ziegler S. F., Grabstein K. H. Interleukin 7 induces cytokine secretion and tumoricidal activity by human peripheral blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):923–930. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covacci A., Censini S., Bugnoli M., Petracca R., Burroni D., Macchia G., Massone A., Papini E., Xiang Z., Figura N. Molecular characterization of the 128-kDa immunodominant antigen of Helicobacter pylori associated with cytotoxicity and duodenal ulcer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5791–5795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Covacci A., Farmery S. M., Xiang Z., Tompkins D. S., Perry S., Lindley I. J., Rappuoli R. Helicobacter pylori induced interleukin-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jan;48(1):41–45. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Farmery S. M., Lindley I. J., Figura N., Peichl P., Tompkins D. S. CagA/cytotoxic strains of Helicobacter pylori and interleukin-8 in gastric epithelial cell lines. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Oct;47(10):945–950. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.10.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Peichl P., Wyatt J. I., Stachl U., Lindley I. J. Gastric interleukin-8 and IgA IL-8 autoantibodies in Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jan;37(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Shallcross T. M., Heatley R. V., Wyatt J. I. Mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut. 1991 Dec;32(12):1473–1477. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.12.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree J. E., Taylor J. D., Wyatt J. I., Heatley R. V., Shallcross T. M., Tompkins D. S., Rathbone B. J. Mucosal IgA recognition of Helicobacter pylori 120 kDa protein, peptic ulceration, and gastric pathology. Lancet. 1991 Aug 10;338(8763):332–335. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. G., Chua A., Fan X. J., Keeling P. W. Increased gastric production of interleukin-8 and tumour necrosis factor in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Feb;48(2):133–136. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gionchetti P., Vaira D., Campieri M., Holton J., Menegatti M., Belluzzi A., Bertinelli E., Ferretti M., Brignola C., Miglioli M. Enhanced mucosal interleukin-6 and -8 in Helicobacter pylori-positive dyspeptic patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jun;89(6):883–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina S., Kahn S. M., Jiang W., Green P. H., Neu H. C., Chin N., Morotomi M., LoGerfo P., Weinstein I. B. Direct detection and amplification of Helicobacter pylori ribosomal 16S gene segments from gastric endoscopic biopsies. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;13(6):473–479. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(90)90079-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., O'Toole P. W., Doig P., Trust T. J. Stimulation of interleukin-8 production in epithelial cell lines by Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1995 May;63(5):1732–1738. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.5.1732-1738.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 8 and MCAF: novel inflammatory cytokines inducible by IL 1 and TNF. Cytokine. 1989 Nov;1(1):2–13. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(89)91043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S. F., Legon S., Davies J., Calam J. Cytokine gene expression in Helicobacter pylori associated antral gastritis. Gut. 1994 Nov;35(11):1567–1570. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.11.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Yoshimura K., McElvaney N. G., Crystal R. G. Neutrophil elastase in respiratory epithelial lining fluid of individuals with cystic fibrosis induces interleukin-8 gene expression in a human bronchial epithelial cell line. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1478–1484. doi: 10.1172/JCI115738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noach L. A., Bosma N. B., Jansen J., Hoek F. J., van Deventer S. J., Tytgat G. N. Mucosal tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 beta, and interleukin-8 production in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1994 May;29(5):425–429. doi: 10.3109/00365529409096833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peek R. M., Jr, Miller G. G., Tham K. T., Perez-Perez G. I., Zhao X., Atherton J. C., Blaser M. J. Heightened inflammatory response and cytokine expression in vivo to cagA+ Helicobacter pylori strains. Lab Invest. 1995 Dec;73(6):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B. The Sydney System: histological division. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):209–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Langenberg W., Houthoff H. J., Zanen H. C., Tytgat G. N. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. A., Tummuru M. K., Miller G. G., Blaser M. J. Interleukin-8 response of gastric epithelial cell lines to Helicobacter pylori stimulation in vitro. Infect Immun. 1995 May;63(5):1681–1687. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.5.1681-1687.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Miura S., Suematsu M., Fukumura D., Kurose I., Suzuki H., Kai A., Kudoh Y., Ohashi M., Tsuchiya M. Helicobacter pylori-associated ammonia production enhances neutrophil-dependent gastric mucosal cell injury. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G719–G725. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tummuru M. K., Cover T. L., Blaser M. J. Cloning and expression of a high-molecular-mass major antigen of Helicobacter pylori: evidence of linkage to cytotoxin production. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1799–1809. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1799-1809.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tummuru M. K., Sharma S. A., Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori picB, a homologue of the Bordetella pertussis toxin secretion protein, is required for induction of IL-8 in gastric epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Dec;18(5):867–876. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.18050867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weel J. F., van der Hulst R. W., Gerrits Y., Roorda P., Feller M., Dankert J., Tytgat G. N., van der Ende A. The interrelationship between cytotoxin-associated gene A, vacuolating cytotoxin, and Helicobacter pylori-related diseases. J Infect Dis. 1996 May;173(5):1171–1175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/173.5.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka Y., Kita M., Kodama T., Sawai N., Imanishi J. Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1996 Jun;110(6):1744–1752. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8964399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka Y., Kita M., Kodama T., Sawai N., Kashima K., Imanishi J. Expression of cytokine mRNA in gastric mucosa with Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Dec;30(12):1153–1159. doi: 10.3109/00365529509101624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R., Abrams J., Bennett B., Figdor C. G., de Vries J. E. Interleukin 10(IL-10) inhibits cytokine synthesis by human monocytes: an autoregulatory role of IL-10 produced by monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1209–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]