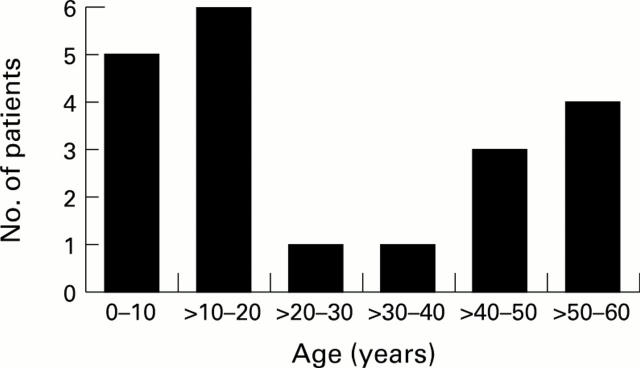Abstract
Background—Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, a syndrome of ineffectual motility due to a primary disorder of enteric nerve or muscle, is rare. Aims—To determine the clinical spectrum, underlying pathologies, response to treatments, and prognosis in a consecutive unselected group of patients. Methods—Cross sectional study of all patients with clinical and radiological features of intestinal obstruction in the absence of organic obstruction, associated with dilated small intestine (with or without dilated large intestine), being actively managed in one tertiary referral centre at one time. Results—Twenty patients (11 men and nine women, median age 43 years, range 22-67) fulfilled the diganostic criteria. Median age at onset of symptoms was 17 years (range two weeks to 59 years). Two patients had an autosomally dominant inherited visceral myopathy. Major presenting symptoms were pain (80%), vomiting (75%), constipation (40%), and diarrhoea (20%). Eighteen patients required abdominal surgery, and a further patient had a full thickness rectal biopsy. The mean time interval from symptom onset to first operation was 5.8 years. Histology showed visceral myopathy in 13, visceral neuropathy in three, and was indeterminate in three. In the one other patient small bowel motility studies were suggestive of neuropathy. Two patients died within two years of symptom onset, one from generalised thrombosis and the other from an inflammatory myopathy. Of the remaining 18 patients, eight were nutritionally independent of supplements, two had gastrostomy or jejunostomy feeds, and eight were receiving home parenteral nutrition. Five patients were opiate dependent, only one patient had benefited from prokinetic drug therapy, and five patients required formal psychological intervention and support. Conclusions—In a referral setting visceral myopathy is the most common diagnosis in this heterogeneous syndrome, the course of the illness is usually prolonged, and prokinetic drug therapies are not usually helpful. Ongoing management problems include pain relief and nutritional support.
Keywords: adult; intestinal; pseudo-obstruction; myopathy; neuropathy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (130.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
: Spectrum of age of onset of symptoms.
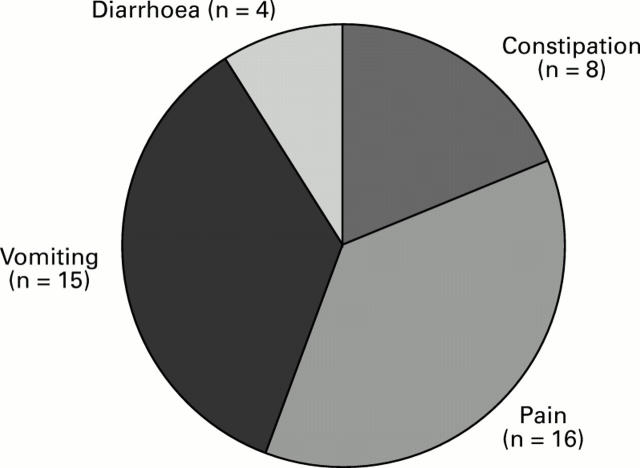
Figure 2 .
: Major symptoms at presentation.
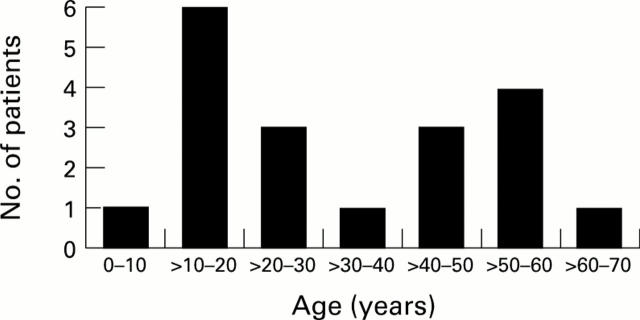
Figure 3 .
: Spectrum of age at first operation.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alstead E. M., Murphy M. N., Flanagan A. M., Bishop A. E., Hodgson H. J. Familial autonomic visceral myopathy with degeneration of muscularis mucosae. J Clin Pathol. 1988 Apr;41(4):424–429. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuras S., Crane S. A., Faulk D. L., Hubel K. A. Intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1318–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuras S., Mitros F. A., Milano A., Kuminsky R., Decanio R., Green J. B. A familial visceral myopathy with dilatation of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):385–390. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90937-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuras S., Mitros F. A., Nowak T. V., Ionasescu V. V., Gurll N. J., Christensen J., Green J. B. A familial visceral myopathy with external ophthalmoplegia and autosomal recessive transmission. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anuras S., Shirazi S., Faulk D. L., Gardner G. D., Christensen J. Surgical treatment in familial visceral myopathy. Ann Surg. 1979 Mar;189(3):306–310. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197903000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonsib S. M., Fallon B., Mitros F. A., Anuras S. Urological manifestations of patients with visceral myopathy. J Urol. 1984 Dec;132(6):1112–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)50054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Brown M. L., Malagelada J. R. Impaired transit of chyme in chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Correction by cisapride. Gastroenterology. 1986 Sep;91(3):619–626. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90631-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Carbone L. D., Schuffler M. D. Familial enteric neuropathy with pseudoobstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Aug;36(8):1168–1171. doi: 10.1007/BF01297468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R., Abell T. L., Brown M. L., Hench V., Zinsmeister A. R. Effect of six weeks of treatment with cisapride in gastroparesis and intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):704–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colemont L. J., Camilleri M. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 Jan;64(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDLEY H. A., SINCLAIR I. S., McLAREN I. F., McNAIR T. J., NEWSAM J. E. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1958 Mar;3(3):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski H. S., Kamm M. A., Talbot I. C., Khan G., Kangro H. O., Jeffries D. J. DNA viruses in the pathogenesis of sporadic chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Gut. 1997 Jul;41(1):100–106. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer N. H., Dawson A. M., Smith B. F., Todd I. P. Obstruction of bowel due to lesion in the myenteric plexus. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 15;1(5645):686–689. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5645.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber J., Fich A., Steinberg A., Steiner I., Granot E., Alon I., Rachmilevitz D., Freier S., Gilai A. Familial intestinal pseudoobstruction dominated by a progressive neurologic disease at a young age. Gastroenterology. 1987 Mar;92(3):786–790. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk D. L., Anuras S., Christensen J. Chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):922–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk D. L., Anuras S., Gardner G. D., Mitros F. A., Summers R. W., Christensen J. A familial visceral myopathy. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):600–606. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-5-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbons P. L., Chandrasoma P. T. Familial visceral myopathy. Evidence of diffuse involvement of intestinal smooth muscle. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987 Nov;11(11):846–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greydanus M. P., Camilleri M., Colemont L. J., Phillips S. F., Brown M. L., Thomforde G. M. Ileocolonic transfer of solid chyme in small intestinal neuropathies and myopathies. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jul;99(1):158–164. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91243-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higman D., Peters P., Stewart M. Familial hollow visceral myopathy with varying urological manifestations. Br J Urol. 1992 Oct;70(4):435–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1992.tb15804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson R., Griffiths C. Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction: a pharmacological approach. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1992 Sep;74(5):364–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionasescu V. V., Thompson H. S., Aschenbrener C., Anuras S., Risk W. S. Late-onset oculogastrointestinal muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;18(4):781–788. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionasescu V. Oculogastrointestinal muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Genet. 1983 May;15(1):103–112. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E., Ardichvili D., Perissino A., Gottignies P., Hanssens J. F. A case of familial visceral myopathy with atrophy and fibrosis of the longitudinal muscle layer of the entire small bowel. Gastroenterology. 1979 Oct;77(4 Pt 1):745–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. C., Dixon M. F., Lintott D. J., Axon A. T. Familial visceral myopathy. A family with involvement of four generations. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Mar;37(3):464–469. doi: 10.1007/BF01307744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy S., Heng Y., Schuffler M. D. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction in infants and children caused by diverse abnormalities of the myenteric plexus. Gastroenterology. 1993 May;104(5):1398–1408. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90348-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy S., Schuffler M. D. Pathology of neuromuscular disorders of the small intestine and colon. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):610–639. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90926-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon S. H., Schuffler M. D., Kettler M., Rohrmann C. A. Chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction as a complication of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):455–459. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90948-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis T. D., Daniel E. E., Sarna S. K., Waterfall W. E., Marzio L. Idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Report of a case, with intraluminal studies of mechanical and electrical activity, and response to drugs. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jan;74(1):107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton A. B., Knauer C. M. Pseudo-obstruction of the bowel. Therapeutic trial of metoclopramide. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Mar;22(3):263–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01072287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado J. E., Gregg J. A., Green P. A., Brown A. L., Jr Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Med. 1970 Aug;49(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E. A., Schuffler M. D., Rotter J. I., Hanna P., Mogard M. Familial visceral neuropathy with autosomal dominant transmission. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1528–1535. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald G. B., Schuffler M. D., Kadin M. E., Tytgat G. N. Intestinal pseudoobstruction caused by diffuse lymphoid infiltration of the small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):882–889. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90587-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre A. S., Thompson D. G., Day S., Burnham W. R., Walker E. R. Modulation of human upper intestinal nutrient transit by a beta adrenoreceptor mediated pathway. Gut. 1992 Aug;33(8):1062–1070. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.8.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mughal M. M., Irving M. H. Treatment of end stage chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction by subtotal enterectomy and home parenteral nutrition. Gut. 1988 Nov;29(11):1613–1617. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.11.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murr M. M., Sarr M. G., Camilleri M. The surgeon's role in the treatment of chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995 Dec;90(12):2147–2151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Sonsino E., Boige N., Nabarra B., Ferkadji L., Mashako L. M., Cezard J. P. Visceral neuropathies responsible for chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndrome in pediatric practice: analysis of 26 cases. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1990 Aug;11(2):179–195. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199008000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton W. T. Radical enterectomy for hereditary megaduodenum. Arch Surg. 1968 Apr;96(4):549–553. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330220065012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezelof C., Vivien E., Bigel P., Nihoul-Fekete C., Arnaud-Battandier F., Bresson J. L., Arhan P., Ricour C. La myosite idiopathique de l'intestin grêle. Une cause exceptionnelle de pseudo-obstruction intestinale chronique chez l'enfant. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1985 Dec;42(10):823–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues C. A., Shepherd N. A., Lennard-Jones J. E., Hawley P. R., Thompson H. H. Familial visceral myopathy: a family with at least six involved members. Gut. 1989 Sep;30(9):1285–1292. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.9.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. D., Bharucha H., Nevin N. C., Odling-Smee G. W. Idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: a familial visceral neuropathy. Clin Genet. 1980 Oct;18(4):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Bird T. D., Sumi S. M., Cook A. A familial neuronal disease presenting as intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):889–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction syndromes. Med Clin North Am. 1981 Nov;65(6):1331–1358. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Leon S. H., Krishnamurthy S. Intestinal pseudoobstruction caused by a new form of visceral neuropathy: palliation by radical small bowel resection. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1152–1156. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Lowe M. C., Bill A. H. Studies of idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. I. Hereditary hollow visceral myopathy: clinical and pathological studies. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):327–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Pope C. E., 2nd Esophageal motor dysfunction in idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT1):677–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Pope C. E., 2nd Studies of idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. II. Hereditary hollow visceral myopathy: family studies. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuffler M. D., Rohrmann C. A., Chaffee R. G., Brand D. L., Delaney J. H., Young J. H. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. A report of 27 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):173–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A., Shaffer H., Teja K., Kelly T., Grogan E., Bruni C. A perspective for pediatric surgeons: chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Pediatr Surg. 1979 Dec;14(6):719–727. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(79)80253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith V. V., Lake B. D., Kamm M. A., Nicholls R. J. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction with deficient smooth muscle alpha-actin. Histopathology. 1992 Dec;21(6):535–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1992.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smout A. J., De Wilde K., Kooyman C. D., Ten Thije O. J. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. Coexistence of smooth muscle and neuronal abnormalities. Dig Dis Sci. 1985 Mar;30(3):282–287. doi: 10.1007/BF01347898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanghellini V., Camilleri M., Malagelada J. R. Chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical and intestinal manometric findings. Gut. 1987 Jan;28(1):5–12. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Snape W. J., Jr, Matarazzo S. A., Petrokubi R. J., Jeffries G., Cohen S. Gastrointestinal myoelectrical activity in idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 4;297(5):233–238. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708042970501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verne G. N., Eaker E. Y., Hardy E., Sninsky C. A. Effect of octreotide and erythromycin on idiopathic and scleroderma-associated intestinal pseudoobstruction. Dig Dis Sci. 1995 Sep;40(9):1892–1901. doi: 10.1007/BF02208652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verne G. N., Sninsky C. A. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Dig Dis. 1995 May-Jun;13(3):163–181. doi: 10.1159/000171499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]