Abstract
Background—Wasting is a major complication of HIV infection. The role of malabsorption in wasting is controversial. Aims—To assess oral intake and malabsorption in a cohort of weight losing HIV infected patients, with or without chronic diarrhoea. Methods—A prospective study using a predefined protocol for HIV infected patients was performed in a gastroenterology and nutrition unit in a university hospital. A retrospective comparison was made with HIV negative patients with malabsorption due either to small bowel disease or resection. Body weight and height, serum albumin, oral intake of macronutrients, faecal weight, and faecal fat were measured. Results—Seventy nine weight losing HIV infected patients were studied. Among the 66 patients with more than 5% lipid malabsorption, wasting was significantly greater in patients with cryptosporidiosis (n=22) than in patients with microsporidiosis (n=18) who exhibited significantly more wasting than patients with no identified enteropathogen (n=26) (body mass index 16.8 (14.0-20.7), 18.9 (16.5-21.3), 19.7(15.9-23), respectively). When controlling for the level of lipid malabsorption, HIV infected patients had a significantly lower energy intake than HIV negative patients with chronic malabsorption. In HIV infected patients, but not in other categories of malabsorbers, body mass index correlated significantly with energy intake (r=0.33, 95% confidence intervals 0.12 to 0.51). Conclusion—In weight losing HIV infected patients, reduced energy intake is superimposed on malabsorption and significantly contributes to wasting.
Keywords: HIV; malabsorption; macronutrient intake
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (120.6 KB).
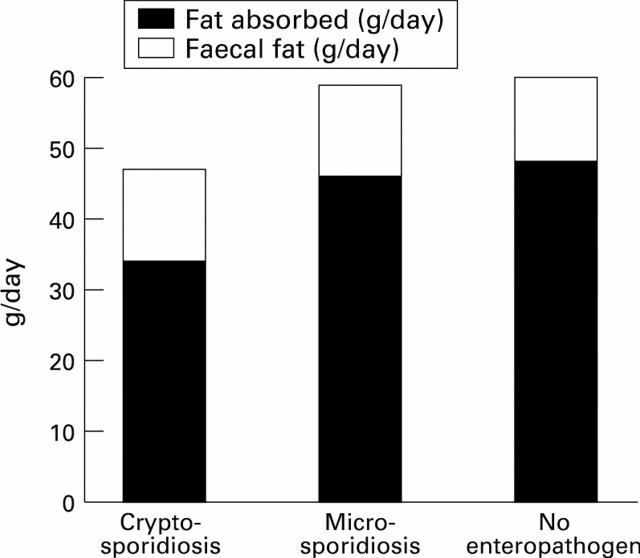
Figure 1 .
: Median values for ingested and apparently absorbed lipids in patients with lipid malabsorption (more than 5% of intake) associated with HIV infection, either due to cryptosporidiosis (n=22), microsporidiosis (n=18), or without detectable enteropathogen (n=26).
Figure 2 .
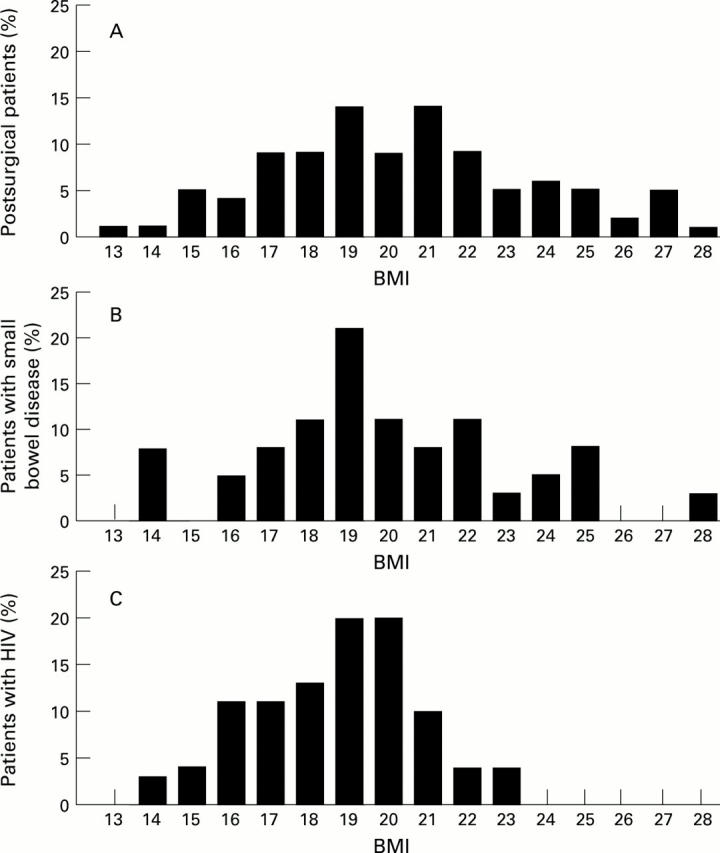
: Distribution of BMI in postsurgical patients (A), small bowel disease (B), or HIV infection (C).
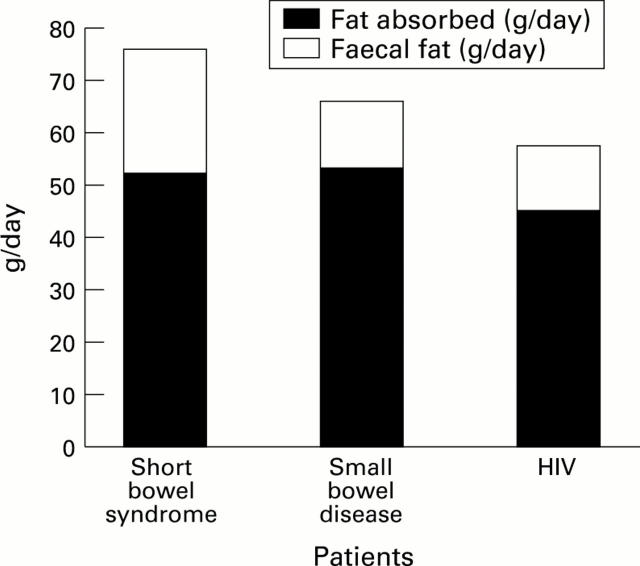
Figure 3 .
: Median values for ingested and apparently absorbed lipids in patients with lipid malabsorption (>5% of intake) associated with short bowel syndrome (n=75), small bowel disease (n=29), or HIV infection (n=66).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R., Maini B. S., Schlamm H. T., Smith M. F. Nutritional and metabolic assessment of the hospitalized patient. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1977;1(1):11–22. doi: 10.1177/014860717700100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanshard C., Francis N., Gazzard B. G. Investigation of chronic diarrhoea in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective study of 155 patients. Gut. 1996 Dec;39(6):824–832. doi: 10.1136/gut.39.6.824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonnel F., Lémann M., Rambaud J. C., Mundler O., Jian R. Effect of the energy density of a solid-liquid meal on gastric emptying and satiety. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Sep;60(3):307–311. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/60.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosnes J., Lamy P., Beaugerie L., Le Quintrec M., Gendre J. P., Le Quintrec Y. Adaptive hyperphagia in patients with postsurgical malabsorption. Gastroenterology. 1990 Dec;99(6):1814–1819. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90492-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich D. T., Lew E. A., Kotler D. P., Poles M. A., Orenstein J. M. Treatment with albendazole for intestinal disease due to Enterocytozoon bieneusi in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1994 Jan;169(1):178–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.1.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Endres S., Meydani S. N., Meydani M., Hellerstein M. K. Interleukin-1, anorexia, and dietary fatty acids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;587:332–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb00174.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro-Luzzi A., Sette S., Franklin M., James W. P. A simplified approach of assessing adult chronic energy deficiency. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1992 Mar;46(3):173–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin J. S., Shike M., Alcock N., Urmacher C., Krown S., Kurtz R. C., Lightdale C. J., Winawer S. J. Malabsorption and mucosal abnormalities of the small intestine in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985 May;102(5):619–622. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-5-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenson J. K., Belitsos P. C., Yardley J. H., Bartlett J. G. AIDS enteropathy: occult enteric infections and duodenal mucosal alterations in chronic diarrhea. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Mar 1;114(5):366–372. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-5-366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Pang M., Shimizu L., Shigenaga J. K., Jensen P., Feingold K. R. Resting energy expenditure, caloric intake, and short-term weight change in human immunodeficiency virus infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992 Feb;55(2):455–460. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/55.2.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenter P., Muurahainen N., Simons G., Kosok A., Cohan G. R., Rudenstein R., Turner J. L. Relationships among nutritional status, disease progression, and survival in HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Oct;6(10):1130–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerstein M. K., Meydani S. N., Meydani M., Wu K., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1-induced anorexia in the rat. Influence of prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):228–235. doi: 10.1172/JCI114145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating J., Bjarnason I., Somasundaram S., Macpherson A., Francis N., Price A. B., Sharpstone D., Smithson J., Menzies I. S., Gazzard B. G. Intestinal absorptive capacity, intestinal permeability and jejunal histology in HIV and their relation to diarrhoea. Gut. 1995 Nov;37(5):623–629. doi: 10.1136/gut.37.5.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Francisco A., Clayton F., Scholes J. V., Orenstein J. M. Small intestinal injury and parasitic diseases in AIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Sep 15;113(6):444–449. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-6-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Tierney A. R., Brenner S. K., Couture S., Wang J., Pierson R. N., Jr Preservation of short-term energy balance in clinically stable patients with AIDS. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990 Jan;51(1):7–13. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/51.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibel R. L., Rosenbaum M., Hirsch J. Changes in energy expenditure resulting from altered body weight. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 9;332(10):621–628. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503093321001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck D. P., Bennett C. L., Mazonson P. D., Fifer S. K., Fries J. F. Quality of life and health service use among HIV-infected patients with chronic diarrhea. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 May;6(5):478–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macallan D. C., Noble C., Baldwin C., Foskett M., McManus T., Griffin G. E. Prospective analysis of patterns of weight change in stage IV human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993 Sep;58(3):417–424. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/58.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macallan D. C., Noble C., Baldwin C., Jebb S. A., Prentice A. M., Coward W. A., Sawyer M. B., McManus T. J., Griffin G. E. Energy expenditure and wasting in human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 13;333(2):83–88. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507133330202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan I., Radford-Smith G., Jewell D. P. Cytokine gene expression in HIV-infected intestinal mucosa. AIDS. 1994 Nov;8(11):1569–1575. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior J. C., Chastang C., Gelas P., Carbonnel F., Zazzo J. F., Boulier A., Cosnes J., Boulétreau P., Messing B. Efficacy of 2-month total parenteral nutrition in AIDS patients: a controlled randomized prospective trial. The French Multicenter Total Parenteral Nutrition Cooperative Group Study. AIDS. 1996 Apr;10(4):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior J. C., Salmon D., Rigaud D., Leport C., Bouvet E., Detruchis P., Vildé J. L., Vachon F., Coulaud J. P., Apfelbaum M. Resting energy expenditure is increased in stable, malnourished HIV-infected patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Feb;53(2):437–441. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.2.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing B., Pigot F., Rongier M., Morin M. C., Ndeïndoum U., Rambaud J. C. Intestinal absorption of free oral hyperalimentation in the very short bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jun;100(6):1502–1508. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Orav E. J., Martin S. R., Cooper E. R., McIntosh K., Winter H. S. Malnutrition and carbohydrate malabsorption in children with vertically transmitted human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection. Gastroenterology. 1991 May;100(5 Pt 1):1296–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice A. M., Goldberg G. R., Jebb S. A., Black A. E., Murgatroyd P. R., Diaz E. O. Physiological responses to slimming. Proc Nutr Soc. 1991 Aug;50(2):441–458. doi: 10.1079/pns19910055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przemioslo R. T., Kontakou M., Nobili V., Ciclitira P. J. Raised pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha in coeliac disease mucosa detected by immunohistochemistry. Gut. 1994 Oct;35(10):1398–1403. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.10.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Lombard P., Modoux C., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Purified blood monocytes from HIV 1-infected patients produce high levels of TNF alpha and IL-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Mar;50(3):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P., Rothkopf M. M., Kvetan V., Kirvelä O., Gaare J., Askanazi J. Risks and benefits of home parenteral nutrition in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1991 Jan-Feb;15(1):75–79. doi: 10.1177/014860719101500175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. C., Jr, Chappell C. L., Hayat C. S., Kimball K. T., Flanigan T. P., Goodgame R. W. Paromomycin for cryptosporidiosis in AIDS: a prospective, double-blind trial. J Infect Dis. 1994 Aug;170(2):419–424. doi: 10.1093/infdis/170.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]