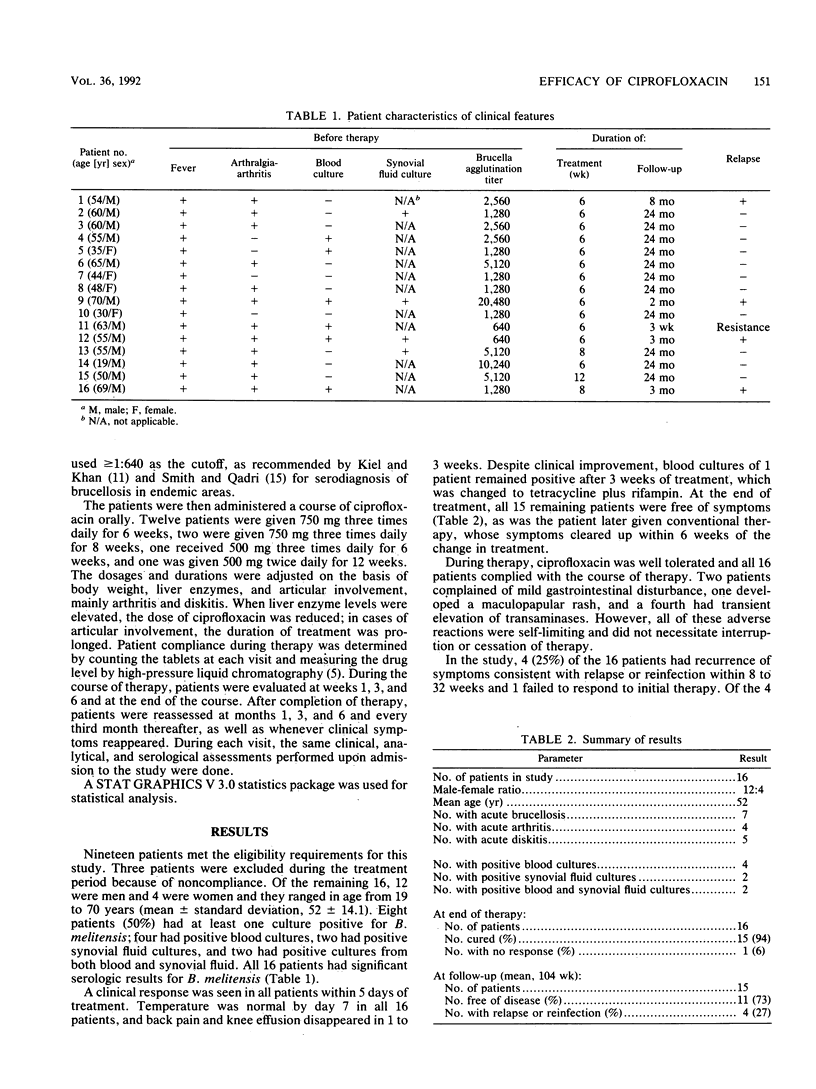
Abstract
The effectiveness of treatment of human brucellosis caused by Brucella melitensis with ciprofloxacin alone was investigated in a prospective nonrandomized study. Subjects with central nervous system involvement, endocarditis, or severe renal dysfunction; children under 16 years of age; and pregnant women were excluded from the study. Of 19 patients, 16 completed the study; 7 were diagnosed as having acute systemic brucellosis, and 9 had acute brucella arthritis-diskitis. A rapid response to ciprofloxacin was seen in all 16 patients, but the blood cultures of 1 patient remained positive and the treatment was changed. During a 104-week follow-up period, 4 of the 15 responding patients relapsed or were reinfected within 8 to 32 weeks after completion of therapy. We conclude that treatment with ciprofloxacin alone, although effective for the acute symptoms, is associated with an appreciable rate of relapse; therefore, it should be given with other agents for treatment of brucellosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acocella G., Bertrand A., Beytout J., Durrande J. B., Garcia Rodriguez J. A., Kosmidis J., Micoud M., Rey M., Rodriguez Zapata M., Roux J. Comparison of three different regimens in the treatment of acute brucellosis: a multicenter multinational study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Mar;23(3):433–439. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J., Liñares J., López de Goicoechea M. J., Ariza J., Cisnal M. C., Martin R. In-vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone and five other antimicrobial agents against 95 strains of Brucella melitensis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):459–461. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Crane J. P., Blowers A. Effect of ciprofloxacin on intracellular organisms: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):43–48. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobernado M., Cantón E., Santos M. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin against Brucella melitensis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):371–371. doi: 10.1007/BF01977500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. H., Manion R. E. In vitro susceptibility of Brucella to various antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):600–604. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.600-604.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. H. Modern chemotherapy for brucellosis in humans. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Nov-Dec;12(6):1060–1099. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.6.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson S. J., Ingham H. R., Snow M. H. Treatment of Salmonella typhi carrier state with ciprofloxacin. Lancet. 1985 May 4;1(8436):1047–1047. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91649-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiel F. W., Khan M. Y. Analysis of 506 consecutive positive serologic tests for brucellosis in Saudi Arabia. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1384–1387. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1384-1387.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R., Raz R., Sacks T., Shapiro M. Failure of prolonged treatment with ciprofloxacin in acute infections due to Brucella melitensis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Dec;26(6):841–846. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.6.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin: an overview and prospective appraisal. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):395–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri S. M., Akhtar M., Ueno Y., al-Sibai M. B. Susceptibility of Brucella melitensis to fluoroquinolones. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1989;15(10):483–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Sibai M. B., Qadri S. M. Development of ciprofloxacin resistance in Brucella melitensis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Feb;25(2):302–303. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.2.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



