Abstract
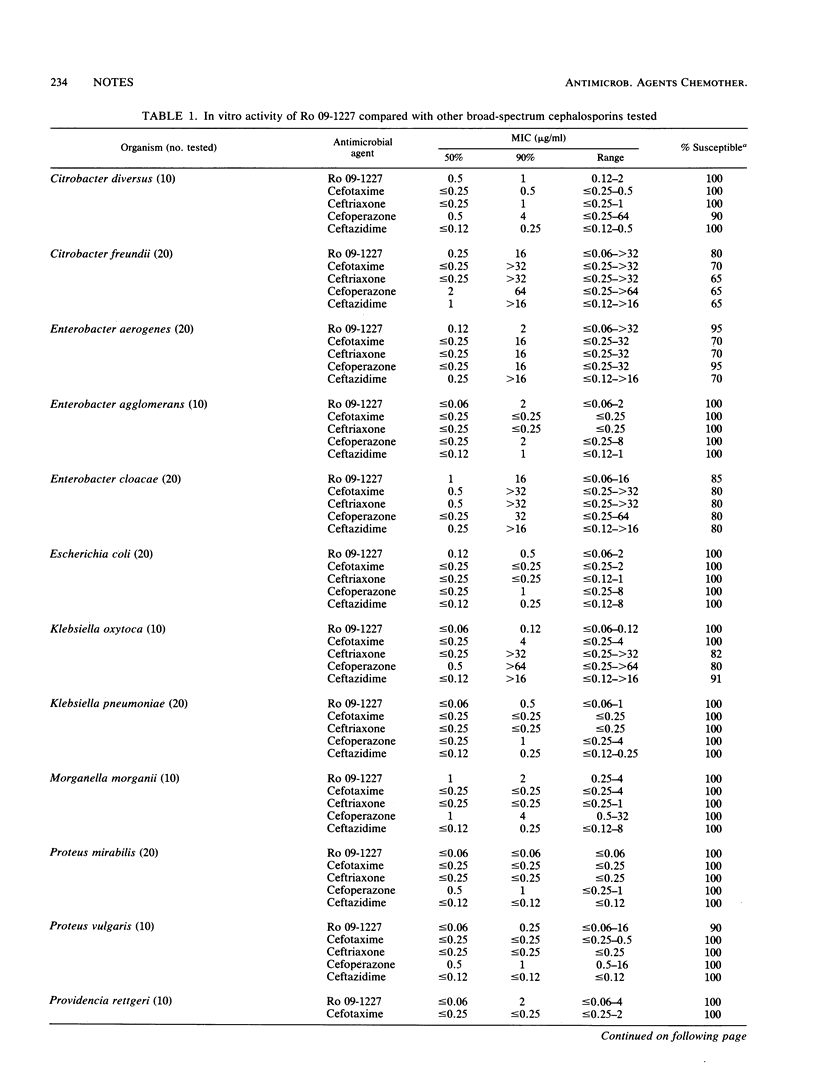
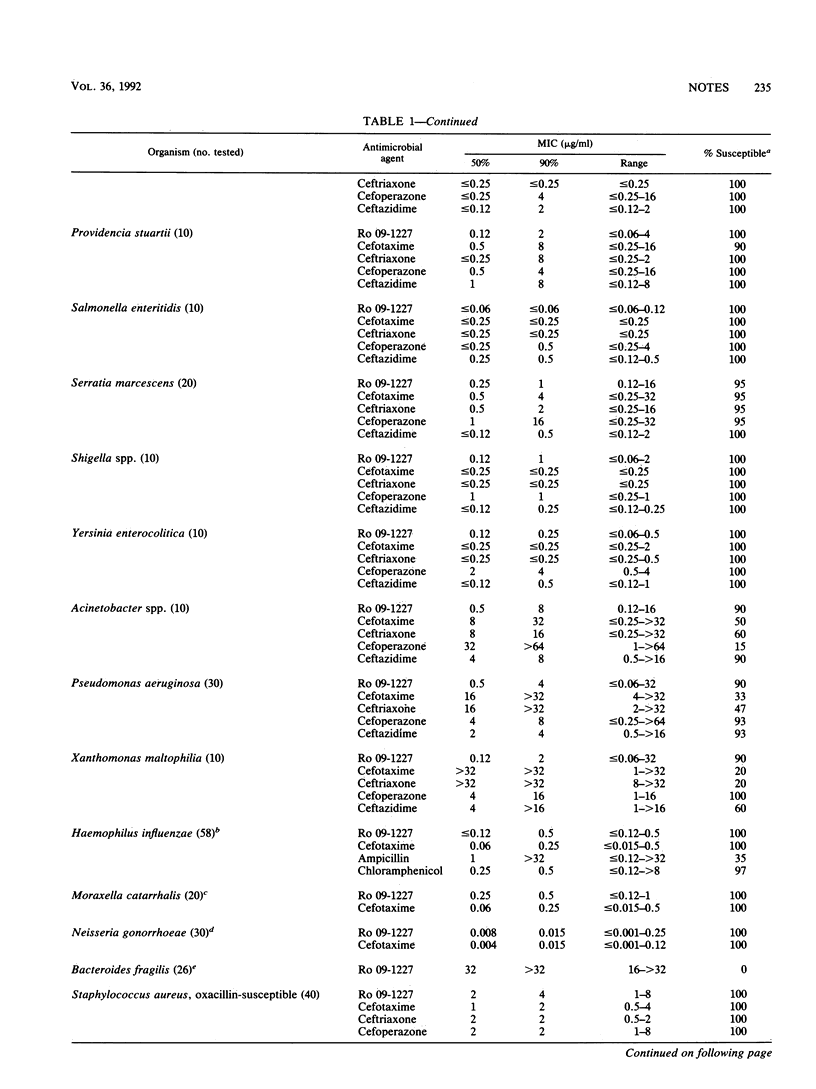
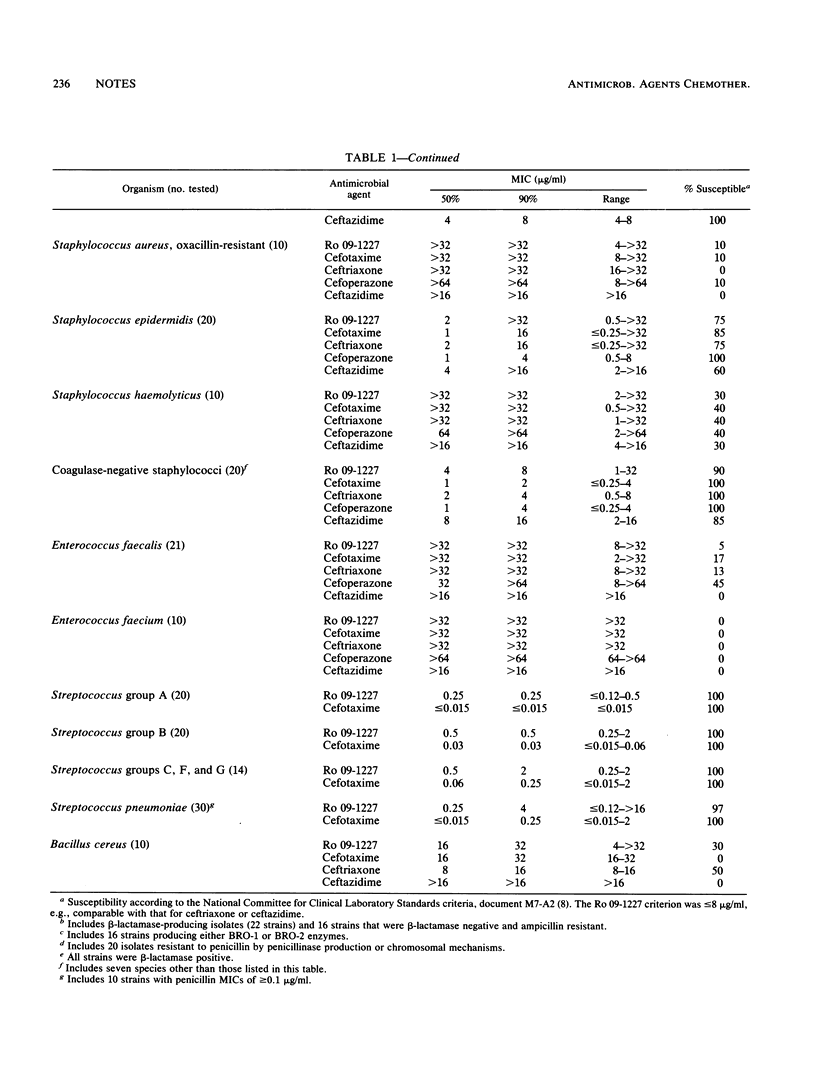
Ro 09-1227 is a novel 7-position catechol-substituted parenteral cephalosporin that also has a 3-position radical similar to previously described cephems. The Ro 09-1227 spectrum was slightly wider than that of ceftazidime against members of the family Enterobacteriaceae tested, principally because of greater activity against species producing Richmond-Sykes type I beta-lactamases. Ro 09-1227 was also more active than ceftazidime against some strains producing extended-spectrum plasmid-encoded beta-lactamases, such as TEM-3, -4, -5, -6, -7, and -9, SHV-2 and -3, and CAZ-2. Most strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Xanthomonas maltophilia, and Acinetobacter spp. were also more susceptible to Ro 09-1227 than cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefoperazone, and ceftazidime. Haemophilus influenzae (MIC for 90% of strains tested [MIC90], 0.5 micrograms/ml), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (MIC90, 0.015 micrograms/ml), and Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis (MIC90, 0.5 micrograms/ml) were also Ro 09-1227 susceptible. Ro 09-1227 activity against important gram-positive cocci was most comparable to that of ceftazidime. Bacteroides fragilis (MIC90, greater than 32 micrograms/ml) and the enterococci (MIC90, greater than 32 micrograms/ml) were resistant to Ro 09-1227. These in vitro results indicate that this catechol-substituted cephalosporin may be useful as an empiric agent, especially for some isolates resistant to currently available broad-spectrum cephalosporins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arisawa M., Sekine Y., Shimizu S., Takano H., Angehrn P., Then R. L. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of Ro 09-1428, a new parenteral cephalosporin with high antipseudomonal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):653–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullen J. J. The significance of iron in infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1127–1138. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Eisenstadt R. L., East S. J., Cornford R. J., Walker L. A., White A. J. Iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and mechanism of action of catechol-substituted cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1879–1886. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin M. E., Jones R. N., Barrett M. S., Briggs B. M., Johnson D. M. In vitro evaluation of GR69153, a novel catechol-substituted cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):929–937. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Barry A. L. In vitro evaluation of HR810, a new wide-spectrum aminothiazolyl alpha-methoxyimino cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):710–718. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki H., Yamada H., Oikawa Y., Murakami K., Ishiguro J., Kosuzume H., Aizawa N., Mochida E. Bactericidal activity of M14659 enhanced in low-iron environments. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silley P., Griffiths J. W., Monsey D., Harris A. M. Mode of action of GR69153, a novel catechol-substituted cephalosporin, and its interaction with the tonB-dependent iron transport system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1806–1808. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson C. H., Feld R. D., Jaynes P. K. Centrifugal analysis for serum iron and iron-binding capacity using the IL Multistat III Analyzer. Clin Biochem. 1982 Dec;15(6):313–314. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(82)96918-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N. A., Nagasu T., Katsu K., Kitoh K. E-0702, a new cephalosporin, is incorporated into Escherichia coli cells via the tonB-dependent iron transport system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):497–504. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


