Abstract
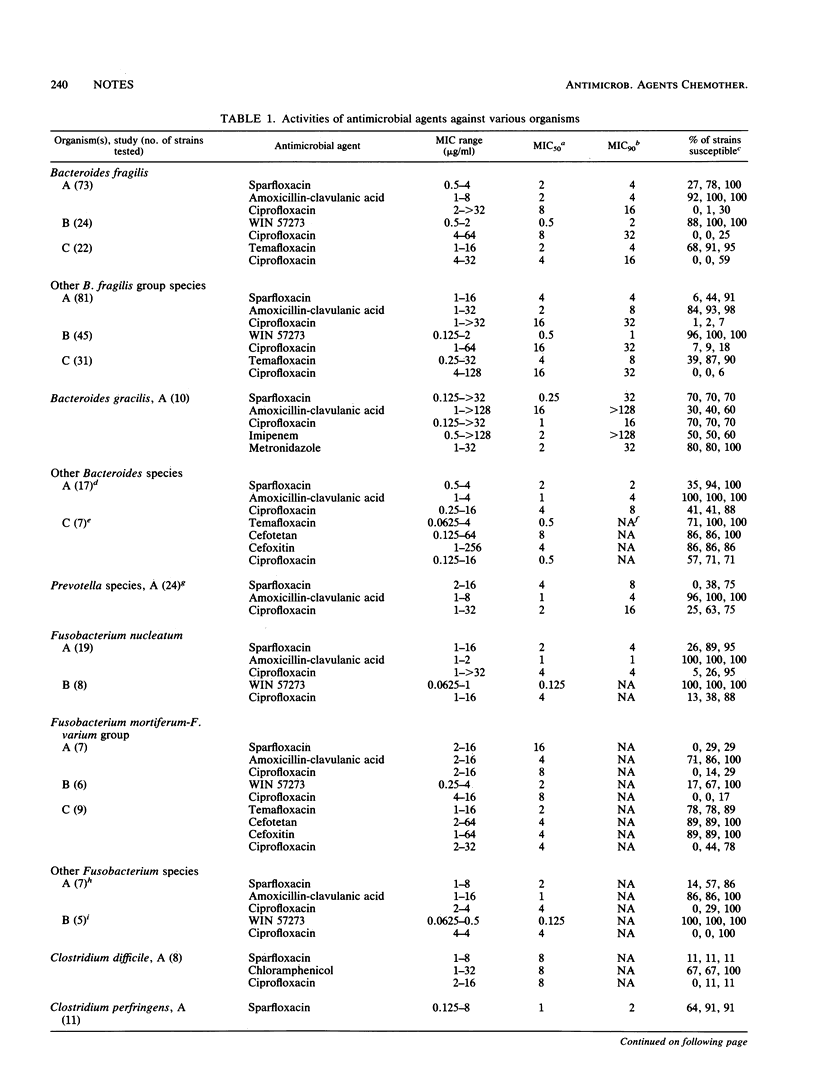
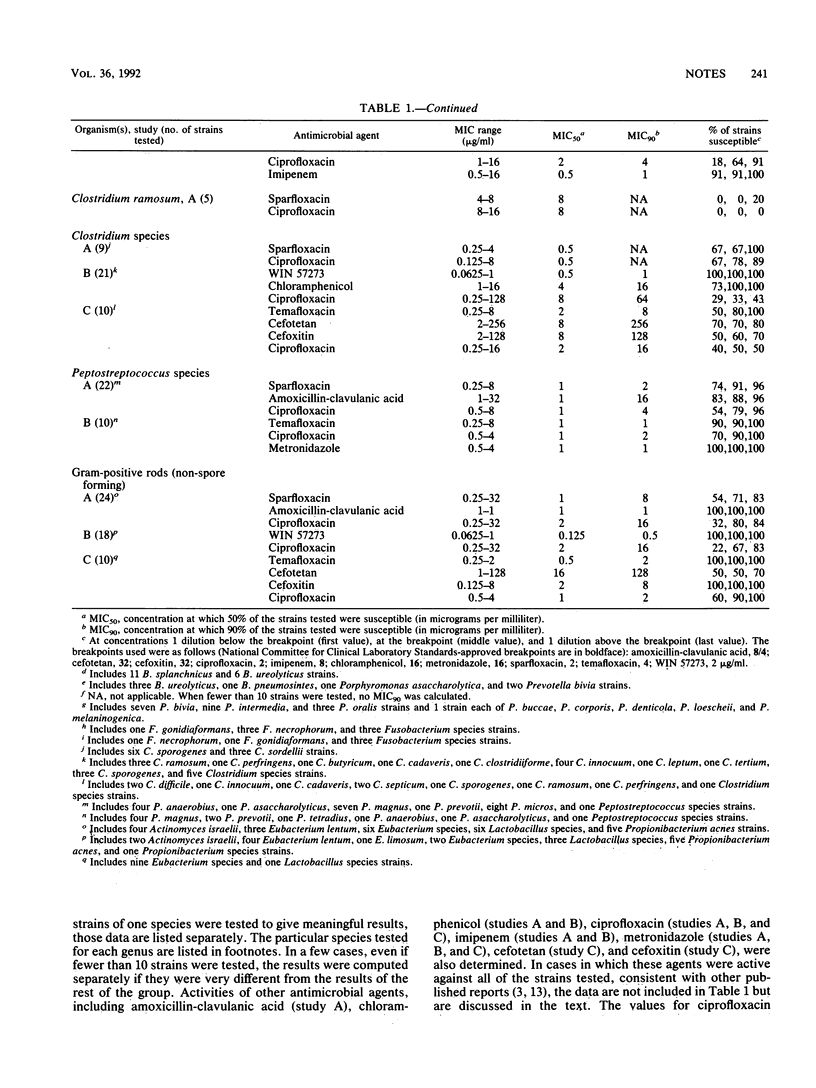
The antimicrobial activities of three new quinolone compounds, sparfloxacin, temafloxacin, and WIN 57273, against anaerobic bacteria were determined in three separate studies. The Wadsworth agar dilution technique using brucella-laked blood agar was used throughout. The activities of other antimicrobial agents, including ciprofloxacin, imipenem, chloramphenicol, metronidazole, cefotetan, cefoxitin, and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, were also determined. The breakpoints of the new quinolones were 2 micrograms/ml for sparfloxacin and WIN 57273 and 4 micrograms/ml for temafloxacin. WIN 57273 displayed very good activity against anaerobes, inhibiting all strains of Bacteroides fragilis group species at 2 micrograms/ml. Only two strains of Fusobacterium species were resistant (MIC, 4 micrograms/ml). Sparfloxacin inhibited 78% of B. fragilis strains and 44% of other B. fragilis group isolates at 2 micrograms/ml. At 2 micrograms/ml, the percentages of other anaerobic species susceptible were as follows: B. gracilis, 70%; other Bacteroides species, 61%; Clostridium species, 50%; Fusobacterium species, 70%; Peptostreptococcus species, 91%; non-spore-forming gram-positive rods, 71%. Temafloxacin inhibited 91% of B. fragilis strains and 87% of other B. fragilis group species at 4 micrograms/ml. All strains of other Bacteroides species, 78% of Fusobacterium species, 80% of Clostridium species, and 90% of Peptostreptococcus species were inhibited at 4 micrograms of temafloxacin per ml.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke A. M., Zemcov S. J. Comparative in vitro activity of lomefloxacin, a new difluoroquinolone. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;8(2):164–168. doi: 10.1007/BF01963905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Shipkowitz N., Bower R. R., Jarvis K. P., Weisz J., Chu D. T. In-vitro and in-vivo potency of five new fluoroquinolones against anaerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Dec;18(6):693–701. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.6.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. R., Phillips I. The antibiotic sensitivity of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United Kingdom. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Oct;20(4):477–488. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Citron D. M. Comparative activity of the quinolones against anaerobic bacteria isolated at community hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):657–659. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. M., Geary I., Lee M. E., Duerden B. I. Activity of pefloxacin and thirteen other antimicrobial agents in vitro against isolates from hospital and genitourinary infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jun;17(6):739–746. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.6.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Phillips I. The comparative in-vitro activity of eight newer quinolones and nalidixic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):1–20. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y. Y., Bulkacz J. Comparative activity of ciprofloxacin against anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):427–428. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt B., Brown F. V. Is ciprofloxacin active against clinically important anaerobes? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 May;17(5):605–613. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. M., Finegold S. M. Antimicrobial resistance in Bacteroides. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Feb;19(2):143–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. M. Susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria: myth, magic, or method? Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Oct;4(4):470–484. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting J. L., Cheng N., Chow A. W. Interactions of ciprofloxacin with clindamycin, metronidazole, cefoxitin, cefotaxime, and mezlocillin against gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1379–1382. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



