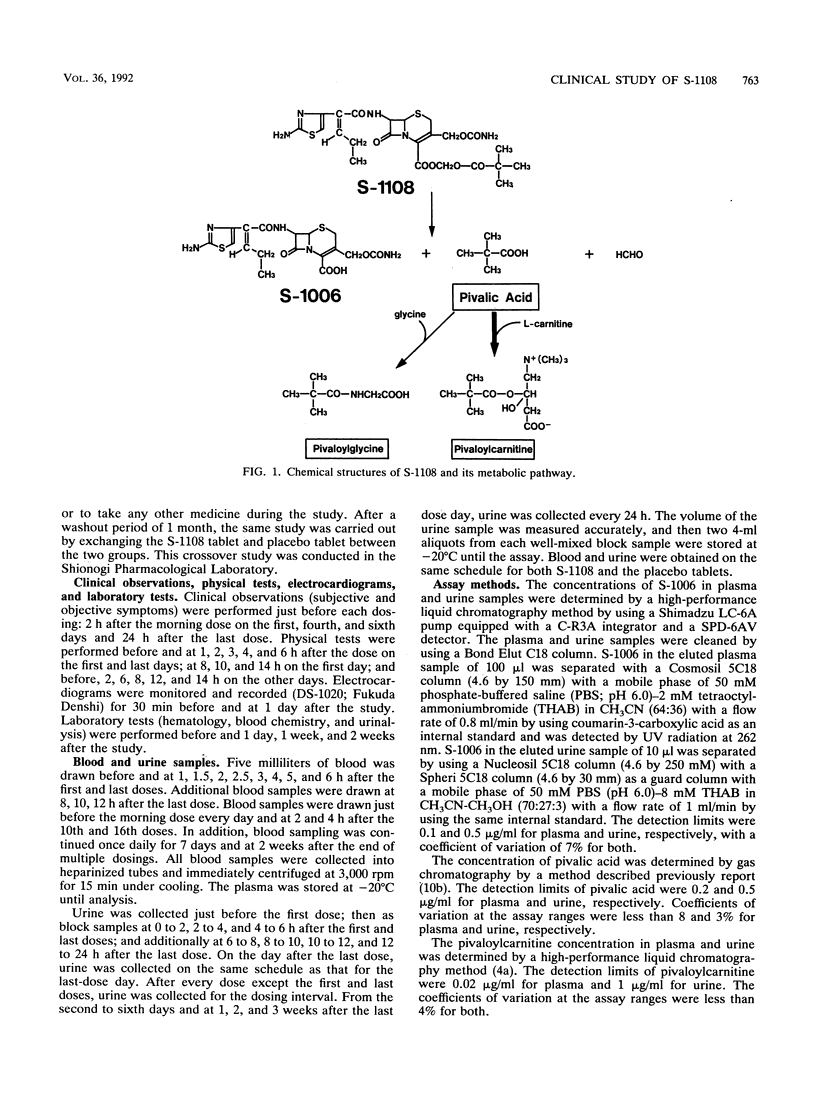
Abstract
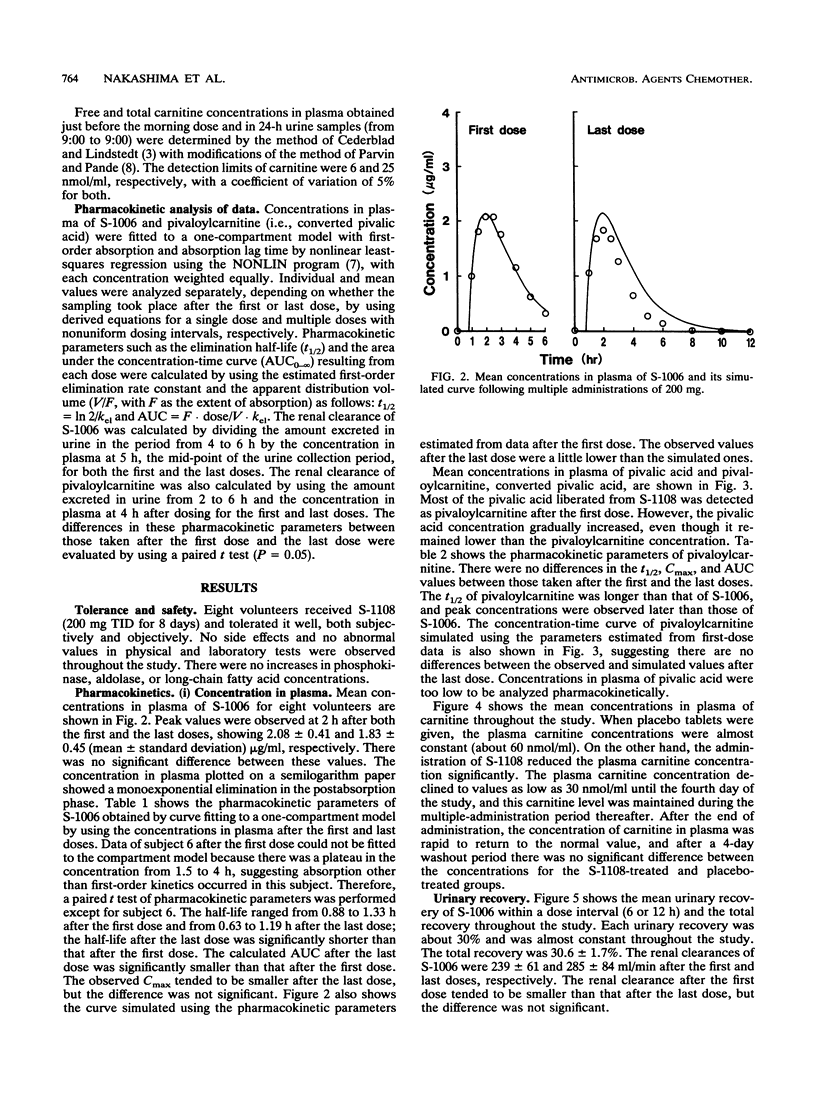
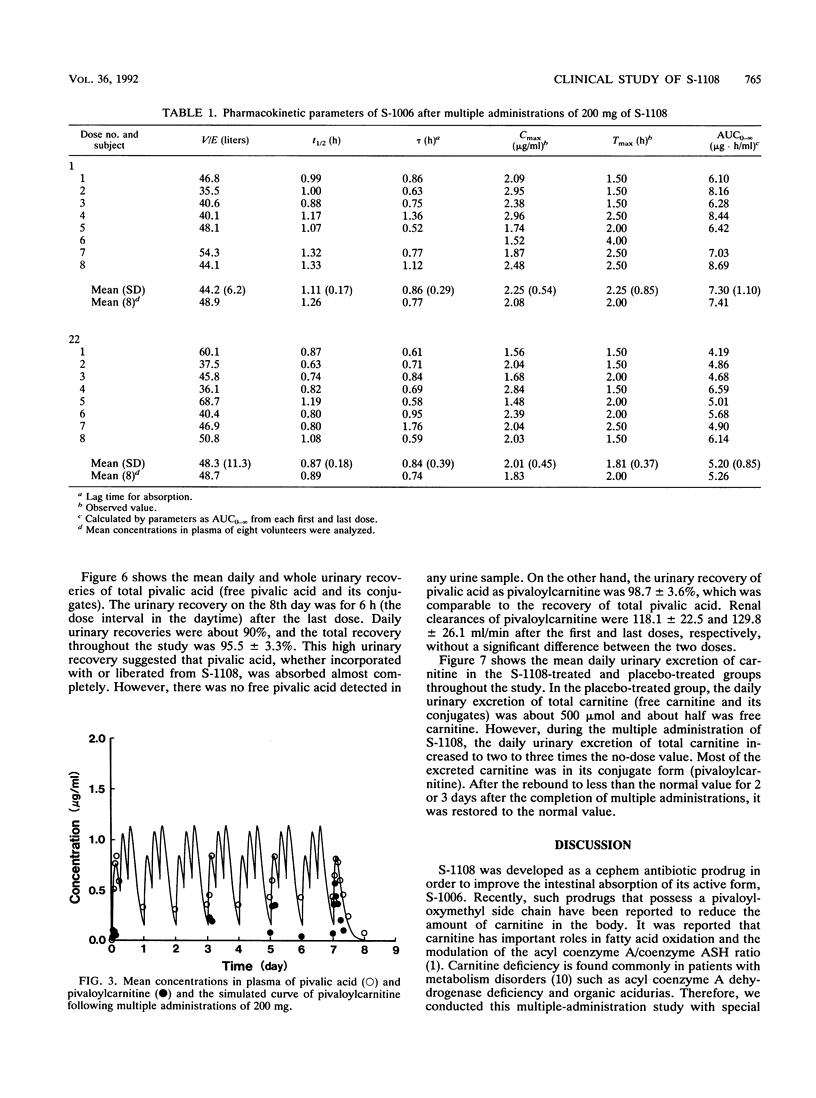
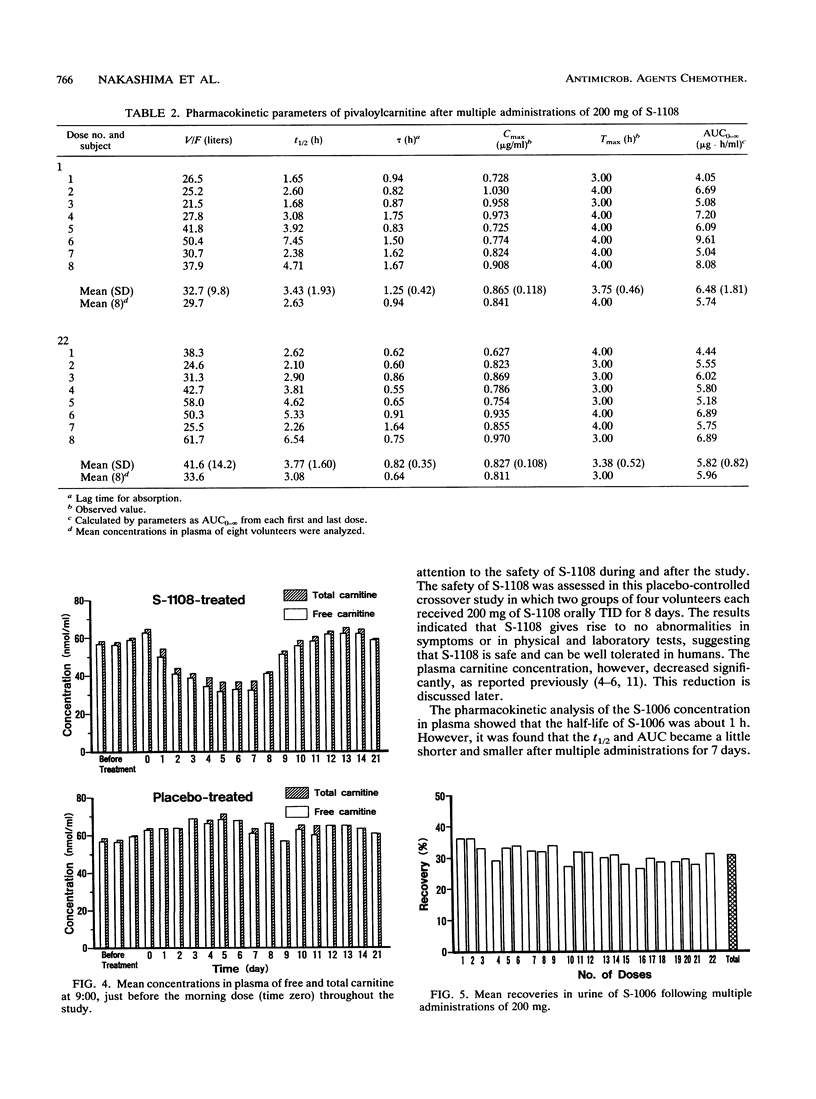
S-1108, the prodrug of S-1006, was given to healthy volunteers three times a day (TID) for 8 days in a dose of 200 mg in a crossover placebo-controlled study. The safety of S-1108 and the pharmacokinetics of S-1006 and pivalic acid liberated from pivaloyloxymethyl ester of S-1108 were investigated. There were no abnormal symptoms or signs, as observed by physical and laboratory tests. The half-life and area under the concentration-time curve of S-1006 was reduced from 1.11 +/- 0.17 h at the first dose to 0.87 +/- 0.18 h at the last dose and from 7.30 +/- 1.10 to 5.20 +/- 0.85 micrograms.h/ml, respectively. However, there was no significant difference in the peak concentration between the two doses. Pivalic acid was found to be completely detoxified by conjugation with carnitine. The total urinary recovery of pivalic acid as pivaloylcarnitine was 98.7 +/- 3.6%, resulting in an increase of daily carnitine urinary excretion two- to threefold the predose value. During the multiple administration of S-1108, the plasma carnitine concentration was reduced to and maintained at 50 to 70% of the control value, suggesting that there might be enough carnitine store in the body to detoxify the pivalic acid in a dose of 200 mg TID. Moreover, the reduced plasma carnitine was rapidly returned to the control value within a few days after the cessation of the administration of 200 mg TID.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieber L. L., Emaus R., Valkner K., Farrell S. Possible functions of short-chain and medium-chain carnitine acyltransferases. Fed Proc. 1982 Oct;41(12):2858–2862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederblad G., Lindstedt S. A method for the determination of carnitine in the picomole range. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Mar;37:235–243. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holme E., Greter J., Jacobson C. E., Lindstedt S., Nordin I., Kristiansson B., Jodal U. Carnitine deficiency induced by pivampicillin and pivmecillinam therapy. Lancet. 1989 Aug 26;2(8661):469–473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melegh B., Kerner J., Bieber L. L. Pivampicillin-promoted excretion of pivaloylcarnitine in humans. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 15;36(20):3405–3409. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melegh B., Kerner J., Jaszai V., Bieber L. L. Differential excretion of xenobiotic acyl-esters of carnitine due to administration of pivampicillin and valproate. Biochem Med Metab Biol. 1990 Feb;43(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0885-4505(90)90005-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin R., Pande S. V. Microdetermination of (-)carnitine and carnitine acetyltransferase activity. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):190–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikawa I., Nakajima Y., Tai M., Sakai H., Demachi K., Kajita T., Hayakawa H., Onoda M., Fukuda H., Sadaki H. [Studies on beta-lactam antibiotics for medicinal purposes. XXII. Studies on the metabolism of pivaloyloxymethyl (6R,7R)-7-[(Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetamido]- 3-[(5-methyl-2H-tetrazol-2-yl)methyl]-3-cephem-4-carboxylate (T-2588) (2)]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1986 Jun;106(6):478–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. A. New genetic defects in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and carnitine deficiency. Adv Pediatr. 1987;34:59–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totsuka K., Shimizu K., Konishi M., Yamamoto S. Metabolism of S-1108, a new oral cephem antibiotic, and metabolic profiles of its metabolites in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):757–761. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers S., Duncan C. A., White S. D., Ramjit H. G., Smith J. L., Walker R. W., Flynn H., Arison B. H. Carnitine and glucuronic acid conjugates of pivalic acid. Xenobiotica. 1985 Jun;15(6):453–458. doi: 10.3109/00498258509045018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



