Abstract
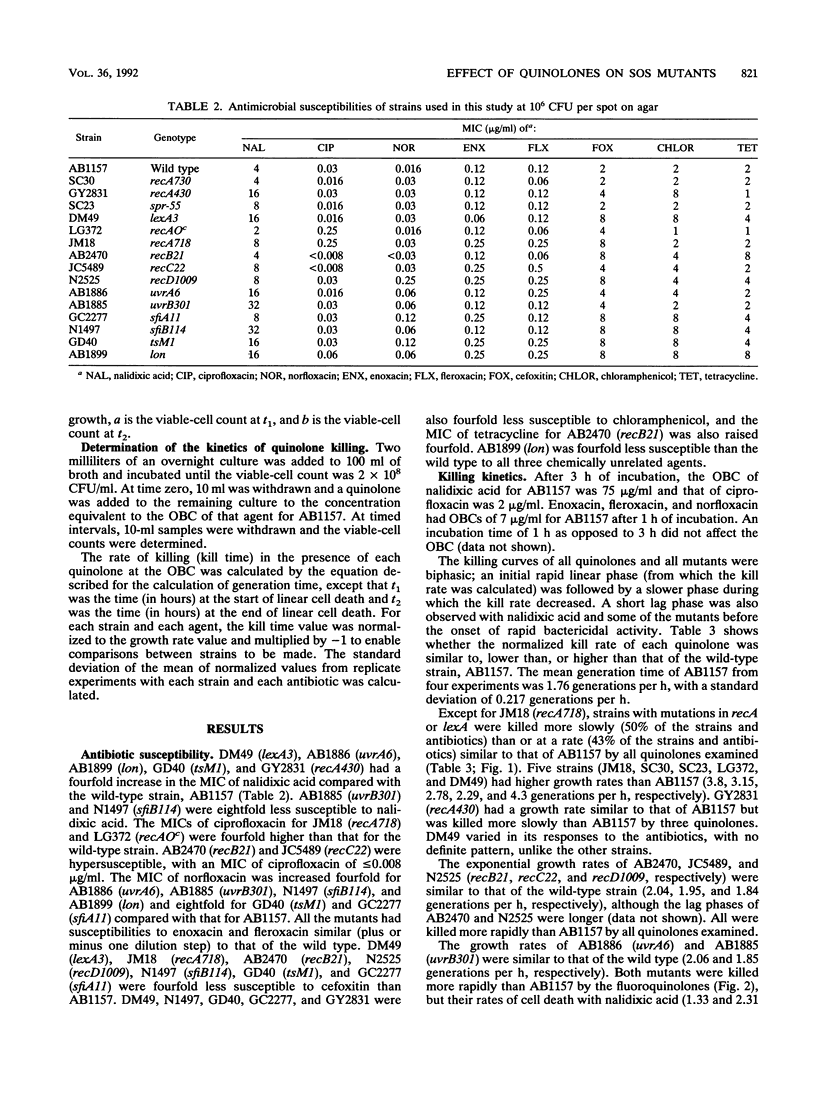
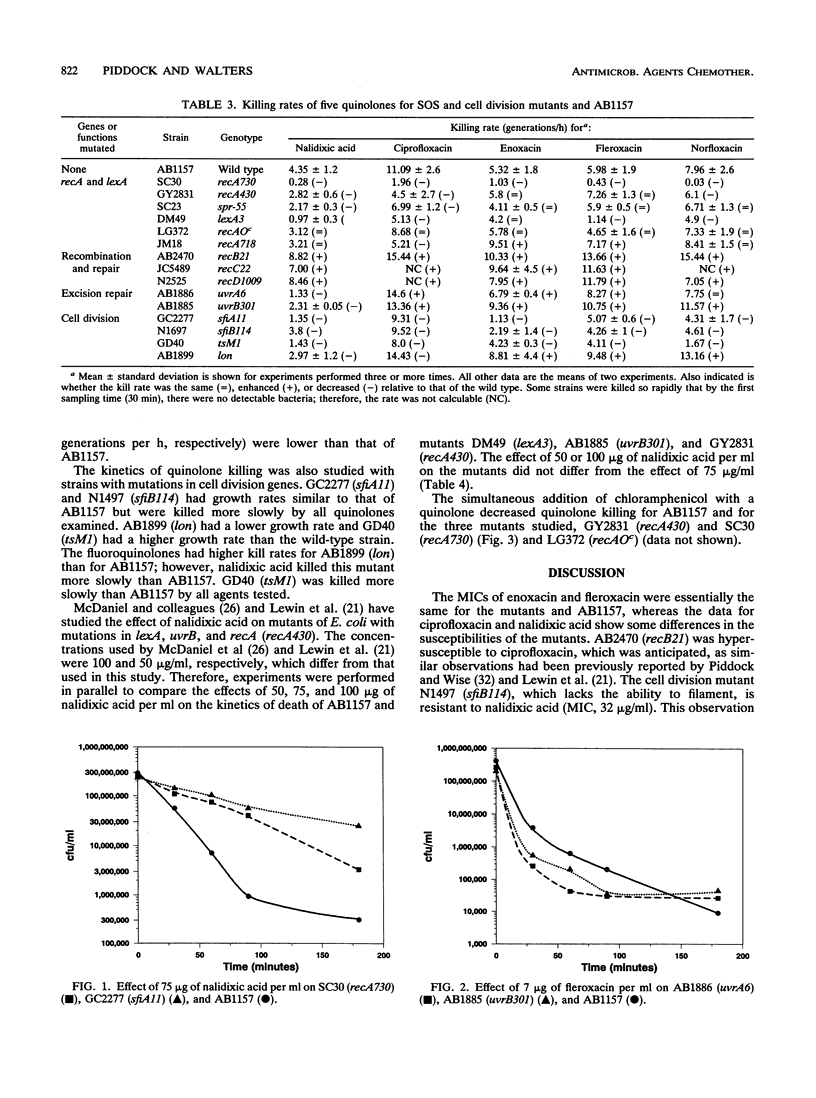
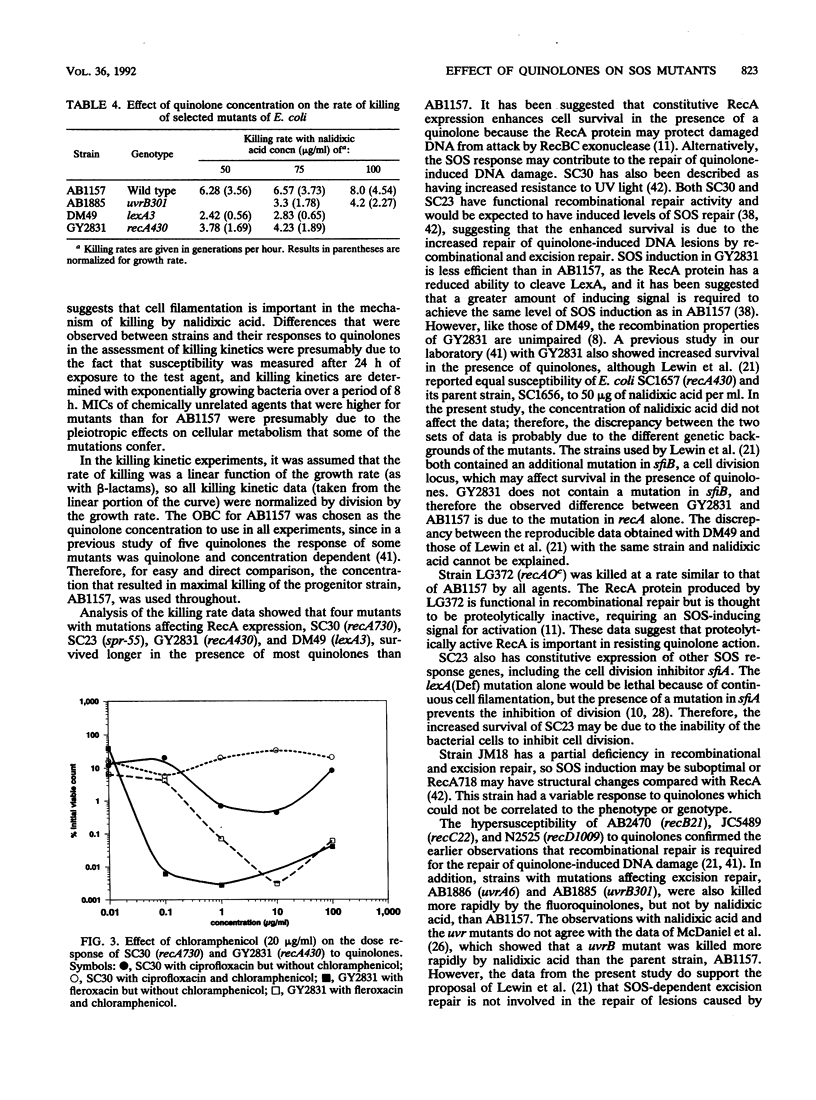
The bactericidal effects of five quinolones (at the optimum bactericidal concentration for strain AB1157) on 15 strains of Escherichia coli with mutations in genes for the SOS response or cell division was studied by a viable-count method. The kill rate data were normalized for growth rate and compared to those for the wild type, AB1157. Similar MICs of enoxacin and fleroxacin were obtained for all mutants; however, different mutants had differing susceptibilities to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and nalidixic acid. Killing kinetic studies showed that mutants with constitutive RecA expression (recA730 and spr-55 mutants) survived longer than AB1157 with all quinolones. Mutants deficient in SOS induction, e.g., recA430 and lexA3 mutants, also survived longer, suggesting that induction of the SOS response by quinolones is harmful to wild-type cells. Recombination repair-deficient mutants (recB21, recC22, and recD1009 mutants) were killed more rapidly than AB1157, as were excision repair mutants, except with nalidixic acid. Mutants which were unable to filament (sfiA11 and sfiB114 mutants) survived longer than AB1157 with all agents, but a mutant defective in the Lon protease was killed more quickly. It was concluded that (i) recombination and excision repair were involved in the repair of quinolone-damaged DNA and (ii) continuous induction (in response to exposure to quinolones) of the SOS response, and hence induction of the cell division inhibitor SfiA, causes cell filamentation and thereby contributes to the bactericidal activity of quinolones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagg A., Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. Inducibility of a gene product required for UV and chemical mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belhumeur P., Drapeau G. R. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: properties of new ftsZ mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):254–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00330971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks K., Clark A. J. Behavior of lambda bacteriophage in a recombination deficienct strain of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):283–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.283-293.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow R. T., Dougherty T. J., Fraimow H. S., Bellin E. Y., Miller M. H. Association between early inhibition of DNA synthesis and the MICs and MBCs of carboxyquinolone antimicrobial agents for wild-type and mutant [gyrA nfxB(ompF) acrA] Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1113–1118. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G. R., Gariépy F., Boulé M. Regulation and SOS induction of division inhibition in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):453–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00382083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K., Engle E. C., Manes S. H. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: possibility of two levels of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6879–6883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. The muc genes of pKM101 are induced by DNA damage. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1306–1315. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1306-1315.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J., Castellazzi M., Buttin G. Prophage induction and cell division in E. coli. III. Mutations sfiA and sfiB restore division in tif and lon strains and permit the expression of mutator properties of tif. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Oct 22;140(4):309–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Edmiston S. H., Harper J., Mount D. W. Isolation and characterization of an operator-constitutive mutation in the recA gene of E. coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(1):4–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. DNA synthesis inhibition and the induction of protein X in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 15;101(4):459–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J., Pardee A. B. Model for regulation of Escherichia coli DNA repair functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland I. B., Jones C. The role of the FtsZ protein (SfiB) in UV-induced division inhibition and in the normal Escherichia coli cell division cycle. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136A(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Apr 30;290(5809):797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., D'Ari R., George J. Further characterization of sfiA and sfiB mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.185-191.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Pardee A. B. Changes of membrane proteins and their relation to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and cell division of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5813–5819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. Expression of the E. coli uvrA gene is inducible. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):808–810. doi: 10.1038/289808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Escherichia coli mutants thermosensitive for deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase subunit A: effects on deoxyribonucleic acid replication, transcription, and bacteriophage growth. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):424–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.424-435.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin C. S., Howard B. M., Ratcliffe N. T., Smith J. T. 4-quinolones and the SOS response. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Jun;29(2):139–144. doi: 10.1099/00222615-29-2-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Porton M. C., Buckman C. Effect of recF, recJ, recN, recO and ruv mutations on ultraviolet survival and genetic recombination in a recD strain of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 May;212(2):317–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00334702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. F. Coupling of DNA replication and cell division: sulB is an allele of ftsZ. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1339–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1339-1346.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguin E., Lutkenhaus J., D'Ari R. Reversibility of SOS-associated division inhibition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.733-738.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham B. E., Little J. W., Mount D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the lexA gene of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4149–4161. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Rogers L. H., Hill W. E. Survival of recombination-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli during incubation with nalidixic acid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1195–1198. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1195-1198.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Gottesman S. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli: the lon gene controls the stability of sulA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W. A mutant of Escherichia coli showing constitutive expression of the lysogenic induction and error-prone DNA repair pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Higgins N. P., Kreuzer K. N., Morrison A., Brown P. O., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Structure and activities of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):41–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Culebras E., Moreno F., Baquero F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):631–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker J. M., Gayda R. C., Markovitz A. Regulation of cell division in Escherichia coli: SOS induction and cellular location of the sulA protein, a key to lon-associated filamentation and death. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):551–561. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.551-561.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., Tocher J., Edwards D. I. Electrochemical characteristics of five quinolone drugs and their effect on DNA damage and repair in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 May;25(5):733–744. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.5.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters R. N., Piddock L. J., Wise R. The effect of mutations in the SOS response on the kinetics of quinolone killing. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Dec;24(6):863–873. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M., McCall J. O., Volkert M. R., Wermundsen I. E. Constitutive expression of SOS functions and modulation of mutagenesis resulting from resolution of genetic instability at or near the recA locus of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00333788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


