Abstract
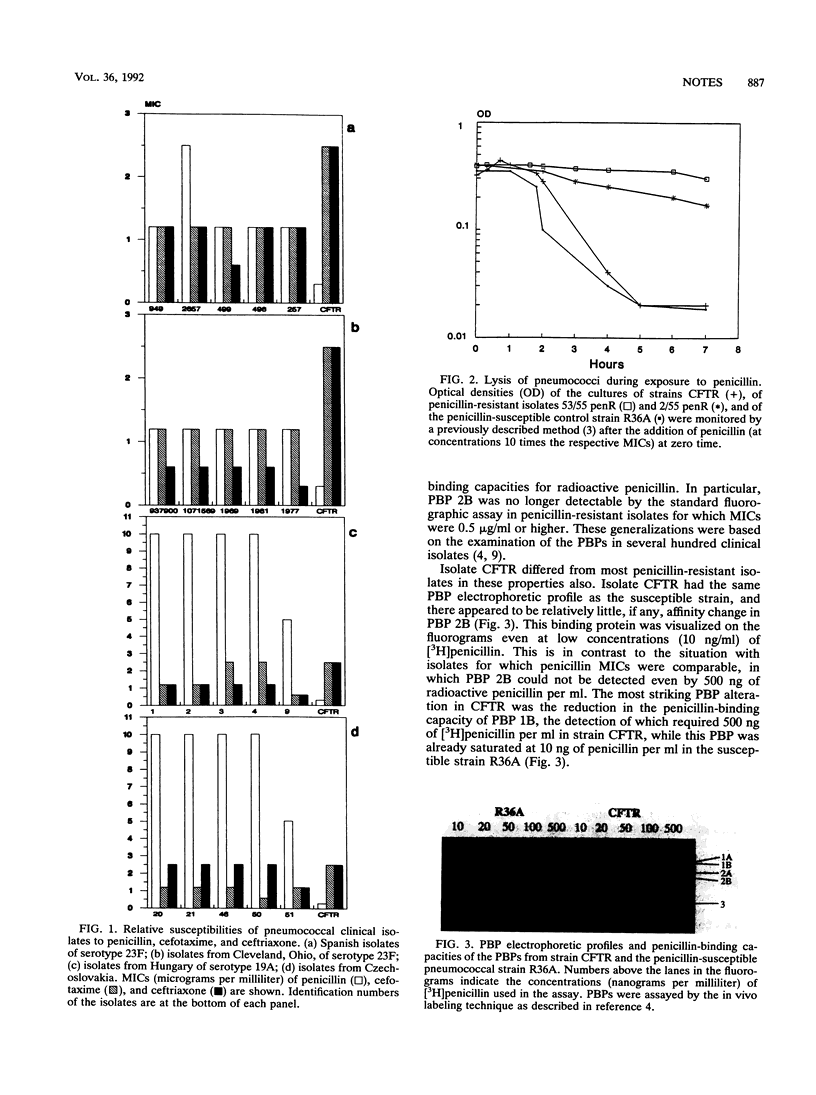
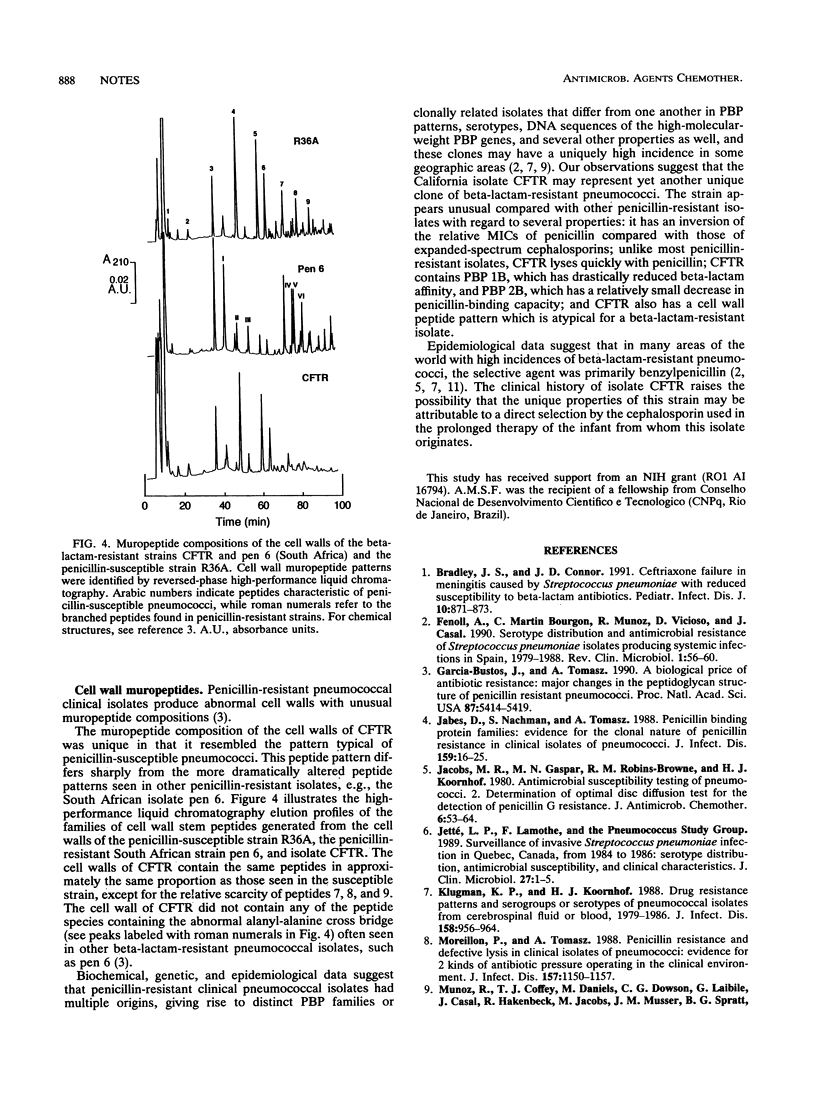
A beta-lactam-resistant serotype 23F Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolate from the cerebrospinal fluid of a pediatric patient from California is unusual in that the MICs of cefotaxime and ceftriaxone (2.5 micrograms/ml each) are higher than that of benzylpenicillin (0.3 micrograms/ml); the isolate also has patterns of penicillin-binding proteins and of cell wall peptides which are atypical compared with those of previously examined penicillin-resistant pneumococci.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley J. S., Connor J. D. Ceftriaxone failure in meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with reduced susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Nov;10(11):871–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Tomasz A. A biological price of antibiotic resistance: major changes in the peptidoglycan structure of penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5415–5419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabes D., Nachman S., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding protein families: evidence for the clonal nature of penicillin resistance in clinical isolates of pneumococci. J Infect Dis. 1989 Jan;159(1):16–25. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. R., Gaspar M. N., Robins-Browne R. M., Koornhof H. J. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of pneumococci. 2. Determination of optimal disc diffusion test for detection of penicillin G resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Jan;6(1):53–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugman K. P., Koornhof H. J. Drug resistance patterns and serogroups or serotypes of pneumococcal isolates from cerebrospinal fluid or blood, 1979-1986. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):956–964. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreillon P., Tomasz A. Penicillin resistance and defective lysis in clinical isolates of pneumococci: evidence for two kinds of antibiotic pressure operating in the clinical environment. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1150–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viladrich P. F., Gudiol F., Liñares J., Rufi G., Ariza J., Pallares R. Characteristics and antibiotic therapy of adult meningitis due to penicillin-resistant pneumococci. Am J Med. 1988 May;84(5):839–846. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. I., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of pneumococci to 14 beta-lactam agents: comparison of strains resistant, intermediate-resistant, and susceptible to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Aug;20(2):204–207. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




