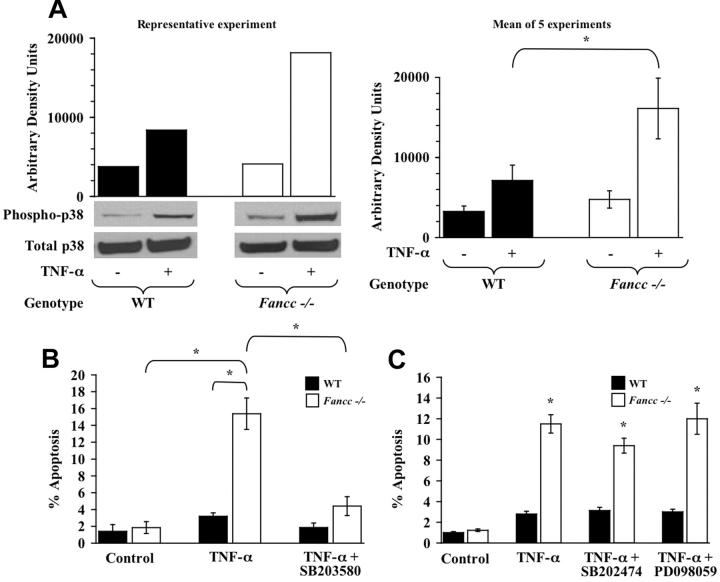
Figure 2.
TNF-α hypersensitivity of Fancc-/- MEFs is p38 dependent. (A) p38 activity. WT and Fancc-/- MEFs were treated with 50 ng/mL TNF-α before assaying p38 activity by Western blot analysis using a phospho-specific p38 antibody. Western blots for phosphorylated p38 and total p38 are shown, as is densitometry analysis of phosphorylated p38. Data in the left panel are representative of 5 independent experiments. The graph on the right depicts the mean arbitrary density units from the 5 experiments (*P < .001). (B) p38 inhibitor and MEF apoptosis assays. WT and Fancc-/- MEFs were grown in normal conditions or were pretreated with the p38 inhibitor SB203580 before 50 ng/mL TNF-α treatment. Apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL as previously described (n = 6; *P ≤ .001). (C) Control inhibitors and MEF apoptosis assays. WT and Fancc-/- MEFs were grown in normal conditions or pretreated with the SB203580 structural analog SB202474 or the MEK inhibitor PD098059 before 50 ng/mL TNF-α exposure for 24 hours. Apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL, as previously described (n = 3; *P ≤ .003), compared with Fancc-/- control. Data shown represent the mean of multiple experiments, and error bars represent the SD.