Figure 6.
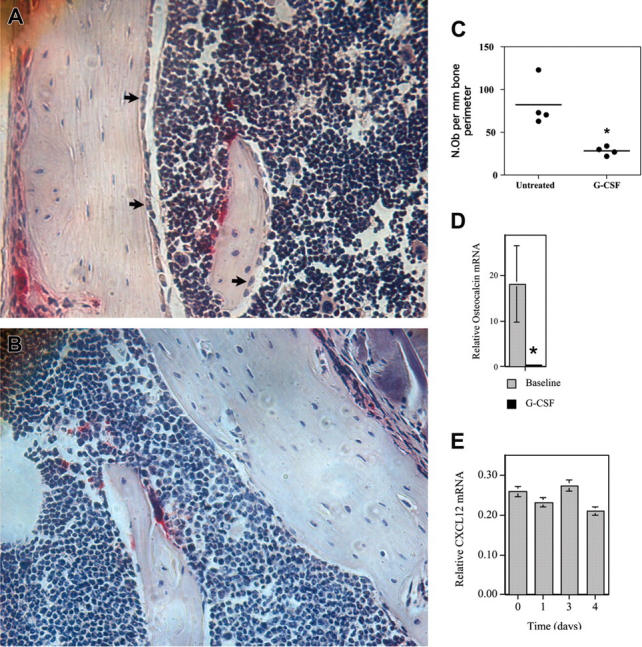
G-CSF inhibits osteoblast activity in the bone marrow. (A-D) WT mice were treated with G-CSF (125 μg/kg twice daily for 5 days) and osteoblast activity assessed. (A-B) Representative photomicrographs show endosteal osteoblasts (arrows) in untreated (A) or G-CSF–treated mice (B); original magnification × 400. (C) Quantification of osteoblast number by histomorphometry. The number of osteoblasts (N.Ob) per millimeter of bone perimeter is shown. (D) Bone marrow osteocalcin mRNA expression. Total bone marrow RNA was obtained by directly flushing femurs with TRIzol. The expression of osteocalcin mRNA relative to β-actin mRNA is shown. (E) Primary osteoblasts were cultured in the presence of 100 ng/mL G-CSF for the indicated time and CXCL12 mRNA quantified. Data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < .05. All images were obtained with a Nikon Eclipse E600 microscope using a Nikon PlanApo 20 ×/0.45 NA objective (Nikon, Melville, NY). The microscope was equipped with a Sony DXC S500 digital camera (Sony Electronics, Park Ridge, NJ), and images were captured using Kodak Imaging for Windows software (Eastman Software, Billerica, MA).
