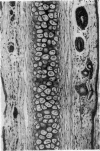
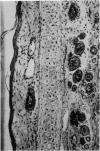
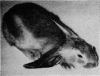
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER W. R., BREMNER J. M., DUTHIE J. J. Incidence of the anti-nuclear factor in human sera. Ann Rheum Dis. 1960 Dec;19:338–350. doi: 10.1136/ard.19.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPPELL J. W., EBERT R. H., BARCLAY W. R. The effects of cortisone on the cutaneous histamine response of rabbits using Evans blue dye as an indicator. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Jun;39(6):896–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER W. D., LORING H. S. The purine and pyrimidine composition of the tobacco mosaic virus and the Holmes masked strain. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):505–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A., FELL H. B. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 1. Effect of excess of vitamin A on the metabolism and composition of embryonic chick-limb cartilage grown in organ culture. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj0790497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T., LUCY J. A., FELL H. B. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 1. Effect of excess of vitamin A on the metabolism and composition of embryonic chick-limb cartilage grown in organ culture. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj0790497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINGLE J. T. Studies on the mode of action of excess of vitamin A. 3. Release of a bound protease by the action of vitamin A. Biochem J. 1961 Jun;79:509–512. doi: 10.1042/bj0790509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELL H. B., MELLANBY E. The effect of hypervitaminosis A on embryonic limb bones cultivated in vitro. J Physiol. 1952 Mar;116(3):320–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELL H. B., THOMAS L. Comparison of the effects of papain and vitamin A on cartilage. II. The effects on organ cultures of embryonic skeletal tissue. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:719–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACK C. H., ANDERSON A. J., ALISY Action of plasmin on cartilage matrix in vivo. Nature. 1961 Sep 30;191:1402–1403. doi: 10.1038/1911402a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELLETT P. G., WALTER J. B., HOUGHTON L. E. The mechanism of inhibition of acute x-ray damage to guinea-pig skin by cortisone. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Jun;42:212–221. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR H. The nature of the link between protein and carbohydrate of a chondroitin sulphate complex from hyaline cartilage. Biochem J. 1958 Jun;69(2):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj0690195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F. The chemistry of connective tissues. 4. The presence of a non-collagenous protein in cartilage. Biochem J. 1958 Feb;68(2):298–305. doi: 10.1042/bj0680298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. L., DUTHIE J. J. Effects of environmental temperature upon capillary resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other individuals. Ann Rheum Dis. 1961 Jun;20:144–148. doi: 10.1136/ard.20.2.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. L., McCLUSKEY R. T., WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. The removal of cartilage matrix by papain. Factors affecting the distribution of crystalline papain in vivo. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. L. On papain and flop-eared rabbits. Arthritis Rheum. 1961 Aug;4:389–399. doi: 10.1002/art.1780040408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER J. L., WIGZELL F. W. Capillary resistance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Sep;16(3):357–364. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., McCLUSKEY R. T., POTTER J. L., WEISSMANN G. Comparison of the effects of papain n vitamin A on cartilage. I. The effects in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:705–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. Reversible collapse of rabbit ears after intravenous papain, and prevention of recovery by cortisone. J Exp Med. 1956 Aug 1;104(2):245–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. Reversible collapse of rabbit ears after intravenous papain, and prevention of recovery by cortisone. J Exp Med. 1956 Aug 1;104(2):245–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. Reversible collapse of rabbit ears after intravenous papain, and prevention of recovery by cortisone. J Exp Med. 1956 Aug 1;104(2):245–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., DINGLE J. Release of lysosomal protease by ultraviolet irradiation and inhibition by hydrocortisone. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Oct;25:207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILHELM D. L., MASON B. Vascular permeability changes in inflammation: the role of endogenous permeability factors in mild thermal injury. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Oct;41:487–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr, BOUCEK R. J. Connective tissue development in subcutaneously implanted polyvinyl sponge. II. Enzymic changes during development. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Apr;93:95–109. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]