Abstract
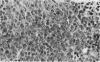
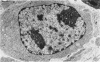
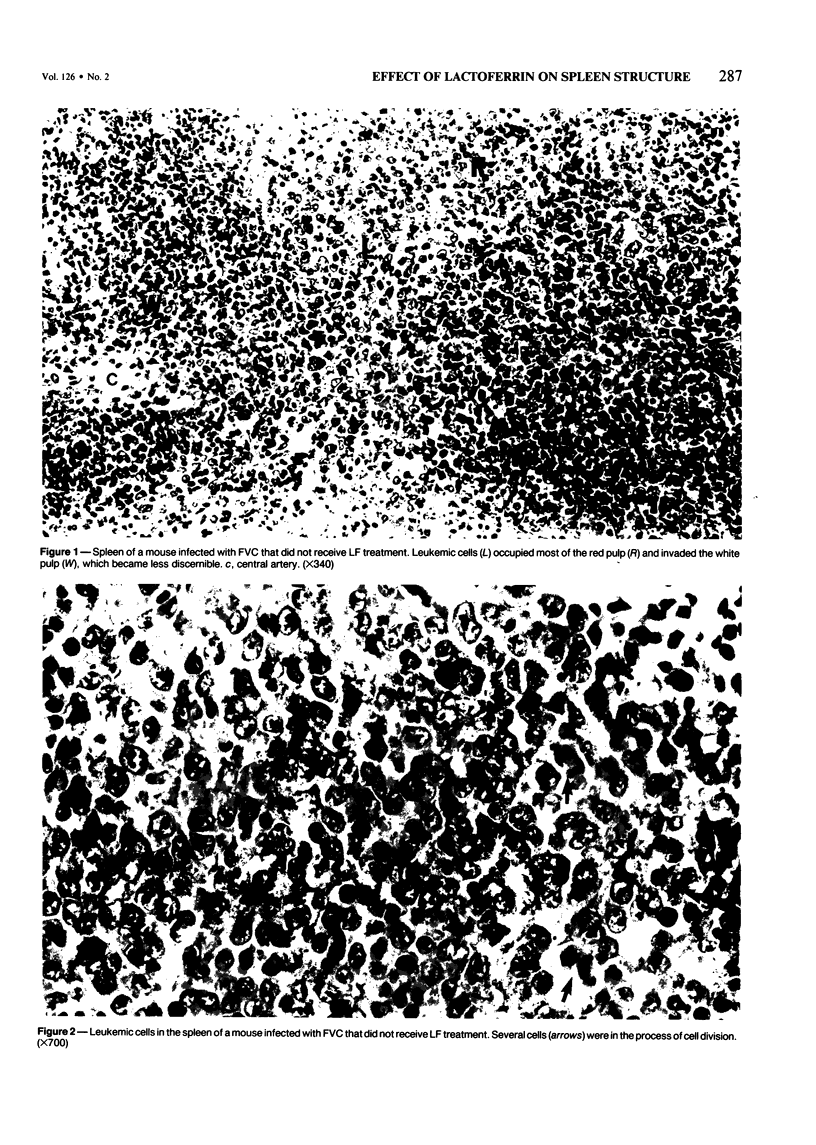
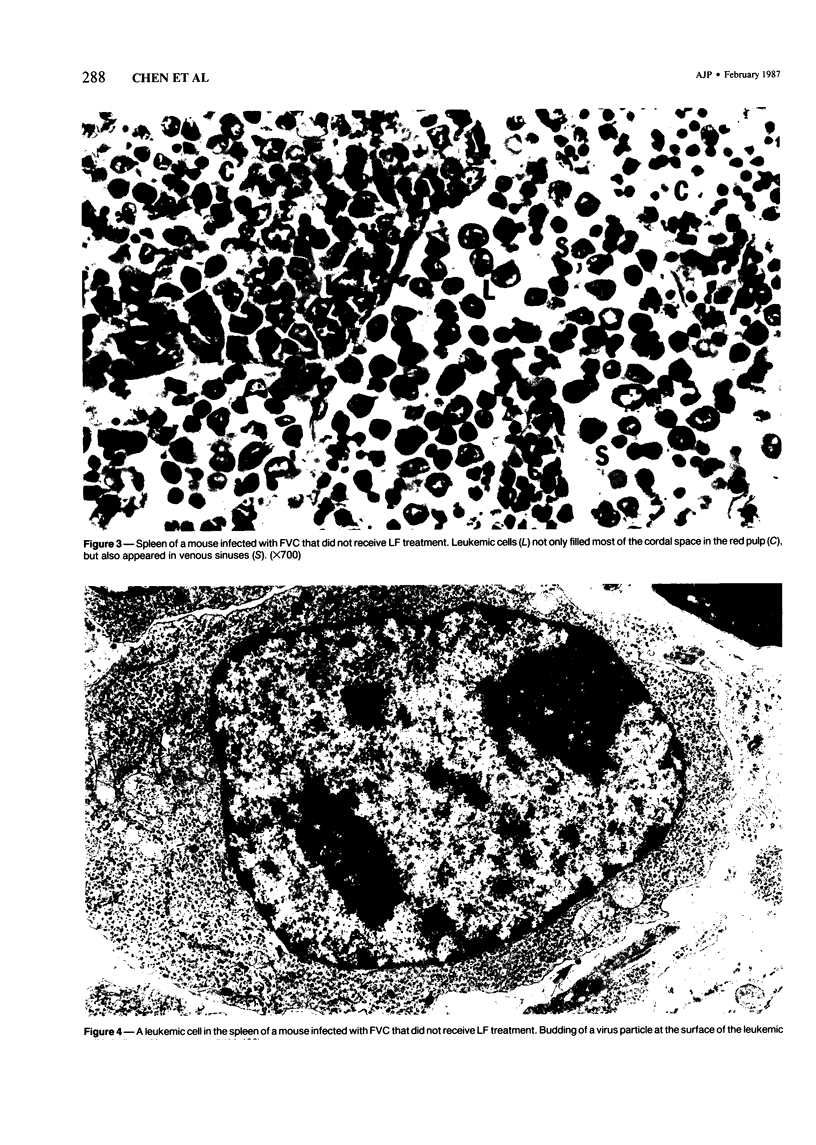
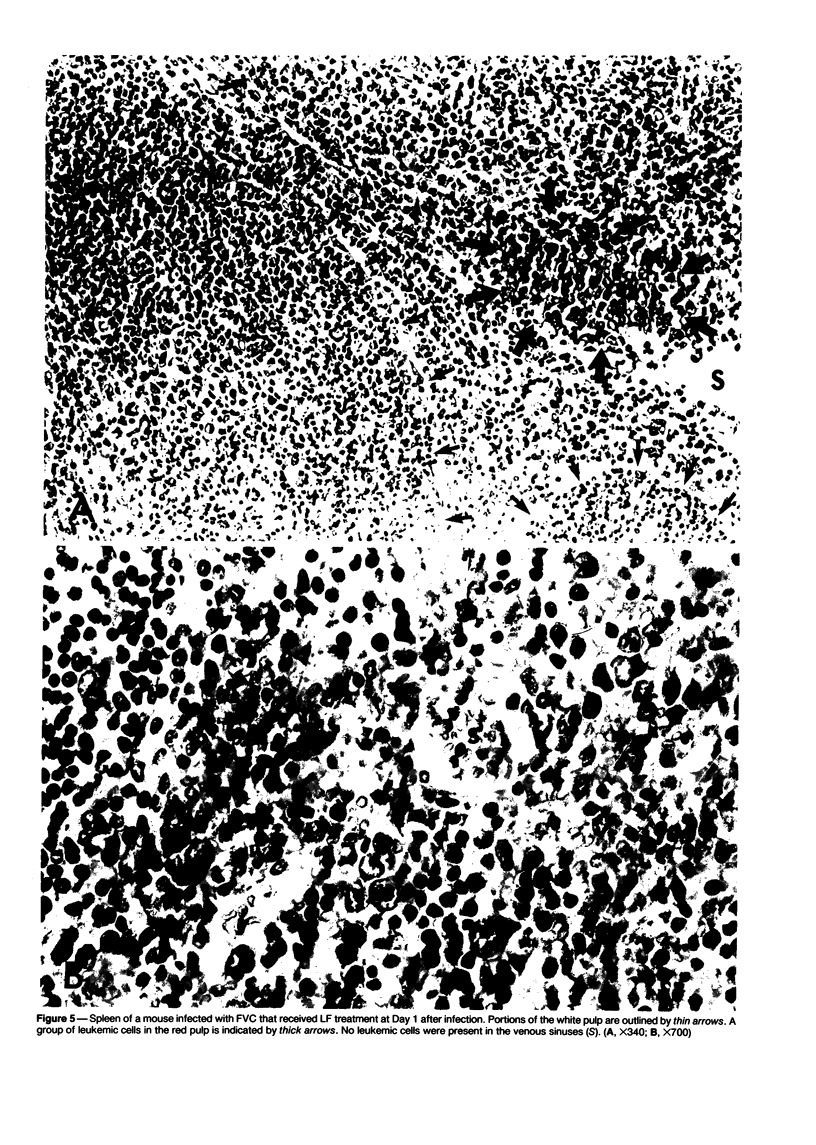
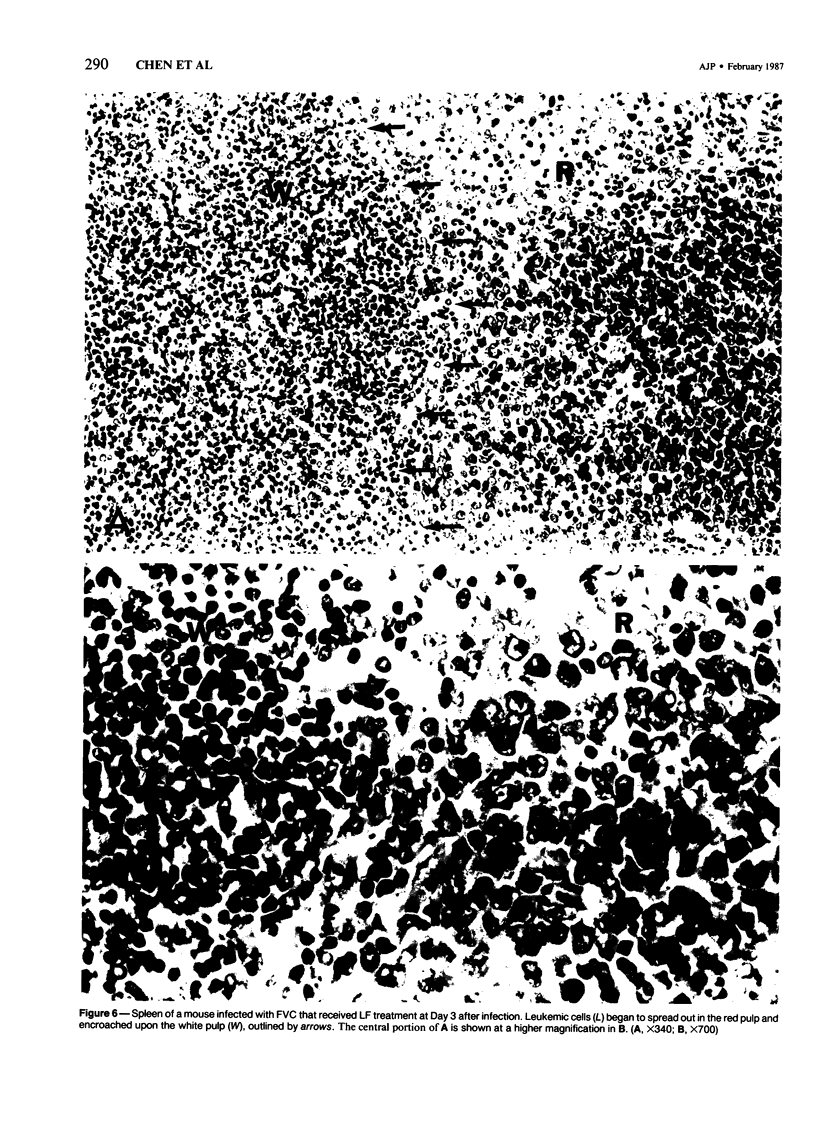
The present report describes effects of lactoferrin treatment on the development of erythroleukemia in the spleen of mice infected with Friend virus complex (FVC). Lactoferrin (LF) treatment was carried out in mice for up to 2 weeks at a total dose of 200 micrograms per mouse. The treatment was started at Days 7 and 14 prior to viral infection and Days 0, 1, 3, 7, and 11 after viral infection. Spleens were analyzed 14 days after viral infection. In mice whose treatment was initiated at Days 0 and 1, few leukemic cells were present in the spleen. Most of them appeared in clumps in the red pulp. No leukemic cells were seen in the white pulp. The white pulp was greatly enlarged. In mice whose treatment was initiated at Day 3, leukemic cells began to spread out in the red pulp and encroached upon the white pulp. The white pulp was enlarged and clearly visible. In mice whose treatment was initiated at Days 7 and 11, many leukemic cells were present in the red pulp. The white pulp was infiltrated by leukemic cells and became less discernible. The morphologic features of the spleen in mice whose treatment was initiated at Day 7 or 14 prior to viral infection were similar to those of untreated groups. Leukemic cells not only filled most of the cordal space in the red pulp but also invaded the white pulp. Many leukemic cells were seen in venous sinuses. When infected mice responded to LF treatment, the general architecture of the red pulp remained intact and the white pulp was enlarged but not infiltrated by leukemic cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broxmeyer H. E., DeSousa M., Smithyman A., Ralph P., Hamilton J., Kurland J. I., Bognacki J. Specificity and modulation of the action of lactoferrin, a negative feedback regulator of myelopoiesis. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):324–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Lu L., Bognacki J. Transferrin, derived from an OKT8-positive subpopulation of T lymphocytes, suppresses the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulatory factors from mitogen-activated T lymphocytes. Blood. 1983 Jul;62(1):37–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentile P., Broxmeyer H. E. Suppression of mouse myelopoiesis by administration of human lactoferrin in vivo and the comparative action of human transferrin. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):982–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa Y., Sugano H. Spleen focus in Friend's disease: an electron microscopic study. Gan. 1967 Apr;58(2):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Broxmeyer H. E., Moore M. A., Sheridan A. P., Gentile P. Abnormalities in myelopoietic regulatory interactions with acidic isoferritins and lactoferrin in mice infected with Friend virus complex: association with altered expression of Ia antigens on effector and responding cells. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- METCALF D., FURTH J., BUFFETT R. F. Pathogenesis of mouse leukemia caused by Friend virus. Cancer Res. 1959 Jan;19(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smadja-Joffe F., Jasmin C., Malaise E. P., Bournoutian C. Study of the cellular proliferation kinetics of Friend leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1973 Mar 15;11(2):300–313. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smadja-Joffe F., Klein B., Kerdiles C., Feinendegen L., Jasmin C. Study of cell death in Friend leukaemia. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Mar;9(2):131–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambourin P. E., Wendling F., Jasmin C., Smadja-Joffe F. The physiopathology of Friend leukemia. Leuk Res. 1979;3(3):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Parks W. P., Vass W. C., Scolnick E. M. Isolation of a fibroblast nonproducer cell line containing the Friend strain of the spleen focus-forming virus. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):602–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]