Abstract
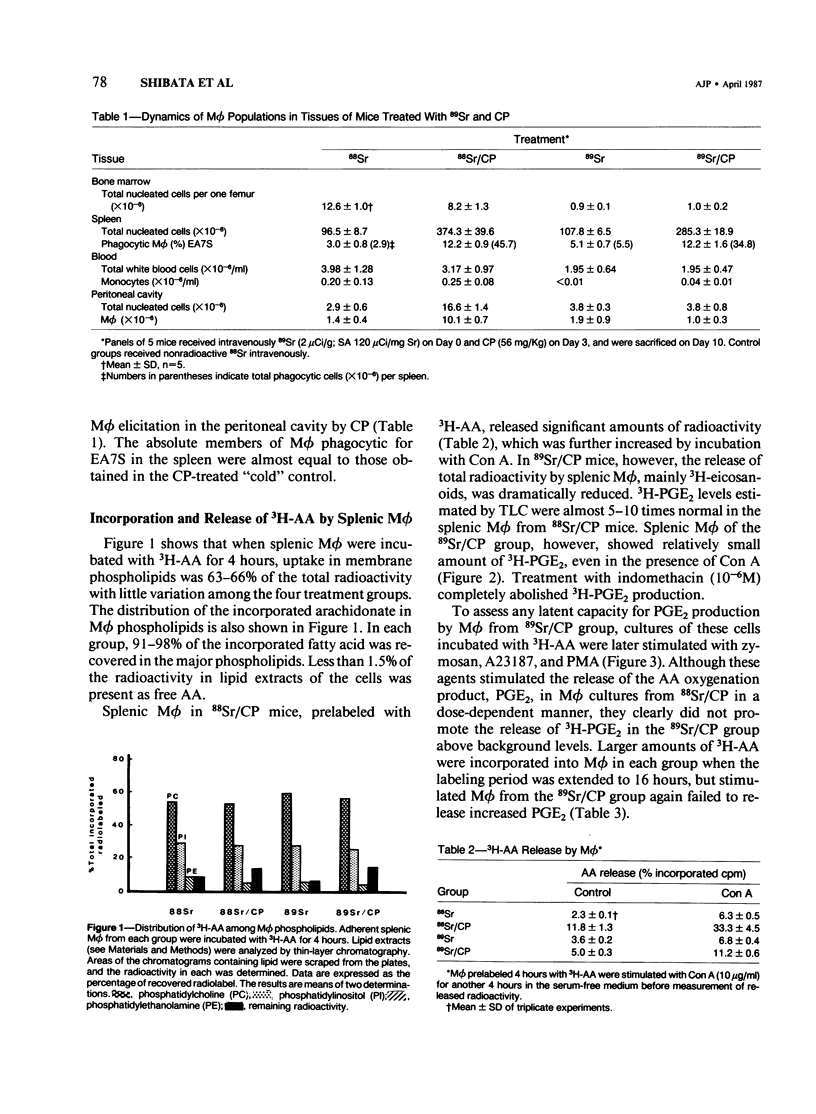
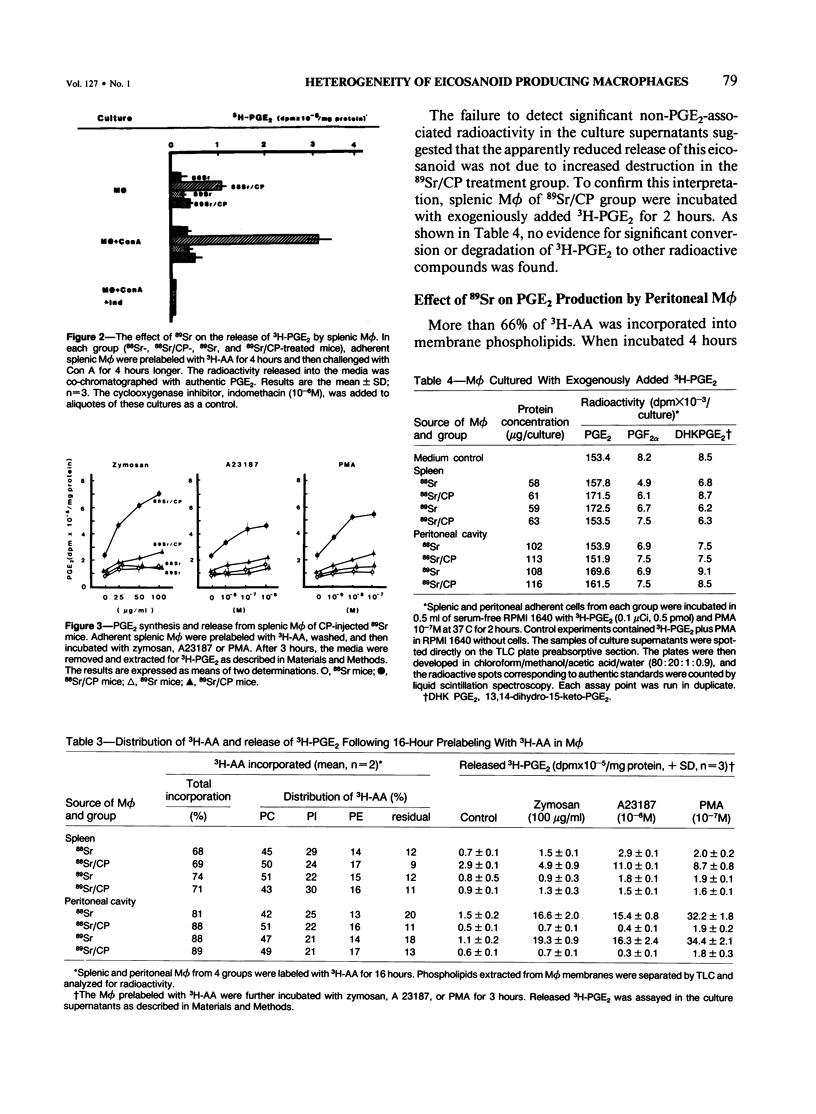
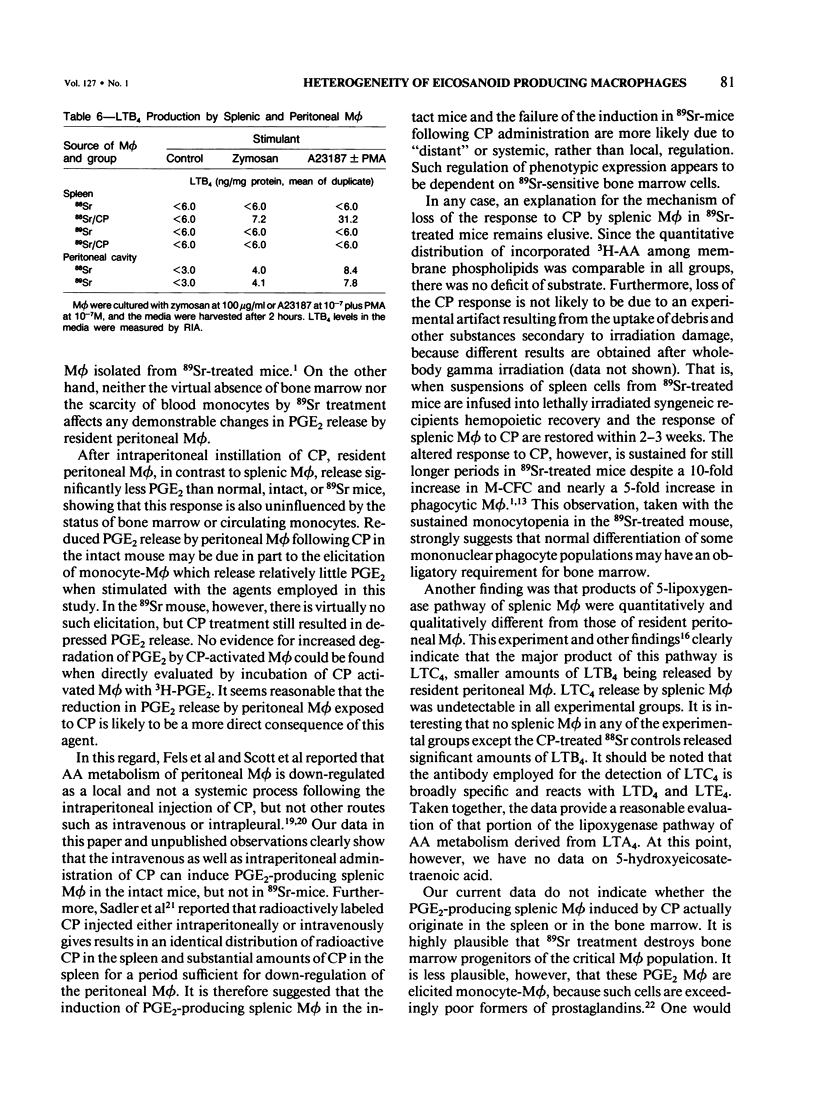
Previous studies showed that the prostaglandin-forming macrophages (M phi) induced in the spleens of CBA/J mice by intraperitoneal administration of Corynebacterium parvum (CP) could not be demonstrated following the depletion of bone marrow and blood monocytes with 89Sr. The present study compares prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), leukotriene C4 (LTC4), and LTB4 release by splenic and resident peritoneal M phi in 89Sr-treated mice and 88Sr controls following in vivo CP and in vitro incubation with zymosan, calcium ionophore A23187, or phorbol ester (PMA). Intraperitoneal administration of CP resulted in the appearance of PGE2- and LTB4-releasing M phi in the spleens of control but not 89Sr mice. The incorporation and quantitative distribution of 3H-arachidonic acid into membrane lipids, however, were comparable in test and control mice. Neither zymosan nor any of the other stimulatory agents was able to effect significant release of PGE2 in vitro. No release of LTC4 by splenic M phi was detectable under experimental or control conditions. In contrast, the capacity of resident peritoneal M phi to release PGE2, LTC4, and LTB4 was apparently unaffected by 89Sr-induced bone marrow and monocyte depletion with virtually no demonstrable elicitation. Resident peritoneal M phi removed after CP in such mice showed a dramatic decrease in PGE2 release when incubated in vitro with zymosan, A23187, or PMA. These results, taken with earlier findings, demonstrate characteristically different phenotypic expression of metabolism of certain eicosanoids by splenic M phi from the spleen and the peritoneal cavity and suggest in addition that the induction of PGE2-synthesizing M phi in the spleen by CP is dependent on either an immigrant cell originating in the bone marrow or a regulatory agent derived from a bone marrow cell.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fels A. O., Pawlowski N. A., Abraham E. L., Cohn Z. A. Compartmentalized regulation of macrophage arachidonic acid metabolism. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):752–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Bankhurst A. D., Messner R. P. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis by prostaglandin. Existence of a prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1719–1734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Burger S., Galavage M., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Wightman P. D., Dahlgren M. E., Davies P., Bonney R. J. The diminished production of arachidonic acid oxygenation products by elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages: possible mechanisms. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2110–2116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Sadowski S., Galavage M., Goldenberg M., Subers E., Bonney R. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr Evidence for two sources of arachidonic acid for oxidative metabolism by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski N. A., Kaplan G., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A., Scott W. A. Arachidonic acid metabolism by human monocytes. Studies with platelet-depleted cultures. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):393–412. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A. Synthesis of leukotriene C and other arachidonic acid metabolites by mouse pulmonary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):720–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A. Synthesis of leukotriene C and other arachidonic acid metabolites by mouse pulmonary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):720–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. E., Cramp W. A., Castro J. E. Radiolabelling of Corynebacterium parvum and its distribution in mice. Br J Cancer. 1977 Mar;35(3):357–368. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Pavlidis N. A., Stylos W. A., Chirigos M. A. Regulation of macrophage tumoricidal function: a role for prostaglandins of the E series. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):320–321. doi: 10.1126/science.694537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Pawlowski N. A., Murray H. W., Andreach M., Zrike J., Cohn Z. A. Regulation of arachidonic acid metabolism by macrophage activation. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1148–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Dempsey W. L., Morahan P. S., Volkman A. Selectively eliminated blood monocytes and splenic suppressor macrophages in mice depleted of bone marrow by strontium 89. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Dec;38(6):659–669. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.6.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Volkman A. The effect of bone marrow depletion on prostaglandin E-producing suppressor macrophages in mouse spleen. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3897–3904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata Y., Volkman A. The effect of hemopoietic microenvironment on splenic suppressor macrophages in congenitally anemic mice of genotype Sl/Sld. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3905–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany B. L., Horowitz M. I. Separation of polar lipids by column chromatography on hydroxylapatite. J Chromatogr. 1970 Jun 24;49(3):455–461. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Lu C. Y., Unanue E. R. Control of macrophage Ia expression in neonatal mice--role of a splenic suppressor cell. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1458–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffet S. M., Russell S. W. Macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing: regulation of expression of cytolytic activity by prostaglandin E. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):424–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp C. S., Mahoney M., Needleman P. Calcium ionophore enables soluble agonists to stimulate macrophage 5-lipoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5895–5898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman A., Chang N. C., Strausbauch P. H., Morahan P. S. Differential effects of chronic monocyte depletion on macrophage populations. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C., Kristensen F., Bettens F., deWeck A. L. Lymphokine regulation of activated (G1) lymphocytes. I. Prostaglandin E2-induced inhibition of interleukin 2 production. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1770–1773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



