Abstract
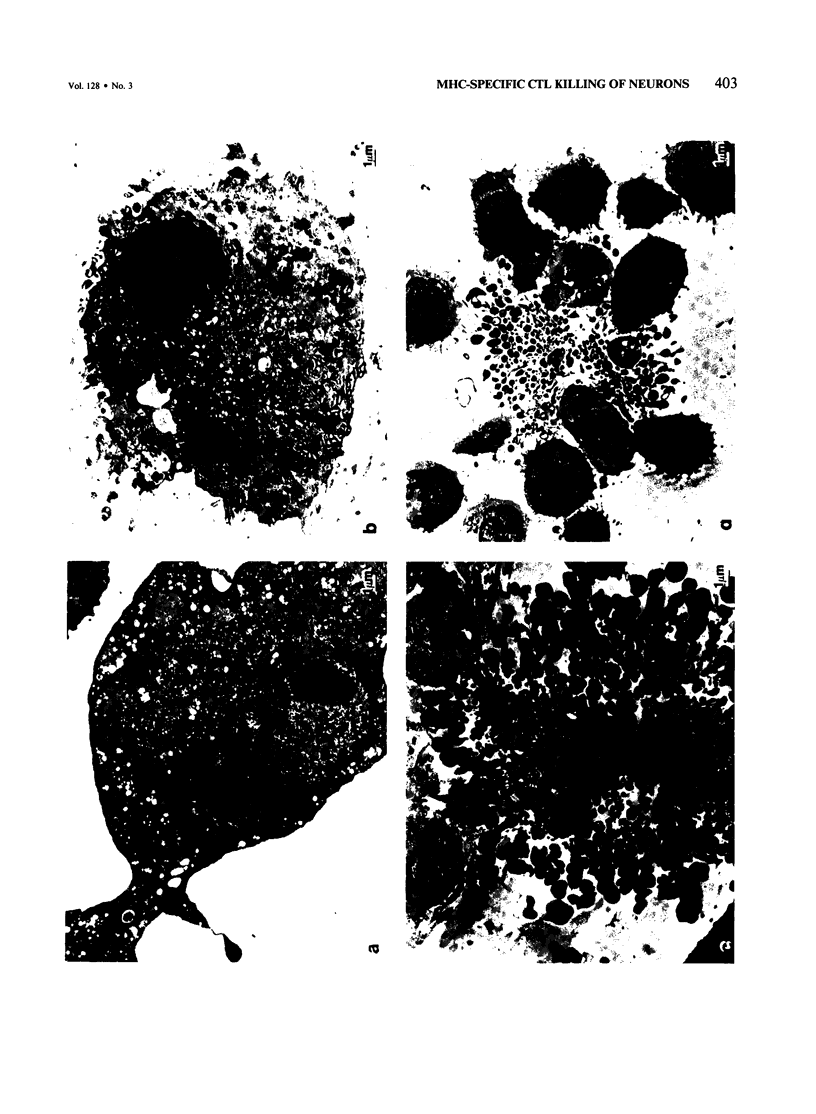
Experiments were conducted to determine whether neurons in culture can serve as targets for immunologic attack mediated by major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) which recognize Class I antigens. Allogeneic C3H/He primary neuronal cultures were quickly destroyed after CTL addition, while syngeneic C57BL/6J neurons were not lysed. Alterations in the distribution of chromatin were the first ultrastructural changes that occurred, followed by loss of nuclear morphology, cytosolic changes, and eventually fragmentation of both the nucleus and cytosol. With Campenot chambers, it was possible to separate the membrane and nuclear lesions. CTLs exposed to neurites, but separated from the cell body by the chamber barrier, caused degeneration of neurites but did not cause lysis and cell death. Neuronal lysis mediated by antibody and complement appeared to be distinct from CTL-mediated lysis. These experiments demonstrate that neurons in culture are targets for MHC-specific CTLs, and therefore probably express functional levels of Class I antigens. The signal for killing by CTLs is not retrogradely transported from the neurite to the cell body, and morphologic events following CTL-neuron interaction resemble those that occur in dividing tumor target cell populations.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G., Fishelson Z. T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: contribution of intracellular components to target cell susceptibility. Transplant Proc. 1977 Mar;9(1):671–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G. Interaction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and target cells. Prog Allergy. 1980;27:69–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campenot R. B. Regeneration of neurites on long-term cultures of sympathetic neurons deprived of nerve growth factor. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):579–581. doi: 10.1126/science.7292000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiaansen J. E., Sears D. W. Lack of lymphocyte-induced DNA fragmentation in human targets during lysis represents a species-specific difference between human and murine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4482–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don M. M., Ablett G., Bishop C. J., Bundesen P. G., Donald K. J., Searle J., Kerr J. F. Death of cells by apoptosis following attachment of specifically allergized lymphocytes in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1977 Aug;55(4):407–417. doi: 10.1038/icb.1977.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekidin M., Henney C. S. The effect of capping H-2 antigens on the susceptibility of target cells to humoral and T cell-mediated lysis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):47–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio246047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming K. A., McMichael A., Morton J. A., Woods J., McGee J. O. Distribution of HLA class 1 antigens in normal human tissue and in mammary cancer. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jul;34(7):779–784. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.7.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG B., GREEN H. The cytotoxic action of immune gamma globulin and complement on Krebs ascites tumor cells. I. Ultrastructural studies. J Exp Med. 1959 May 1;109(5):505–510. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.5.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais A. G. Detection of mouse histocompatibility antigens by immunofluorescence. Transplantation. 1968 Mar;6(2):261–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasebrook A. L., Sarmiento M., Loken M. R., Dialynas D. P., Quintans J., Eisenberg L., Lutz C. T., Wilde D., Fitch F. W. Murine T lymphocyte clones with distinct immunological functions. Immunol Rev. 1981;54:225–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkowski S. H., Brown T. C., Cerutti P. A., Cerottini J. C. DNA of human Raji target cells is damaged upon lymphocyte-mediated lysis. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale A. H., Paulus L. K. Lysis of enucleated tumor cells with allogeneic and syngeneic cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):640–646. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe R. C., Russell J. H. Isolation of alloreactive CTL clones with cyclical changes in lytic activity. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2141–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Fisher C. A., Whelan J. P. Striking paucity of HLA-A, B, C and beta 2-microglobulin on human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2471–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Whelan J. P. Paucity of HLA-A,B,C molecules on human cells of neuronal origin: microscopic analysis of neuroblastoma cell lines and tumor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;420:107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb22194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter A. Microcinematographic and electron microscopic analysis of target cell lysis induced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1979 Feb;36(2):179–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Wilkinson M. M., Wood M., Westwood J. H. Immunohistochemical demonstration of H2 antigens in mouse tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):911–919. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6343482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Dobos C. B. Characterization of a "heteroclitic" cytotoxic lymphocyte clone: heterogeneity of receptors or signals? J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):538–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Dobos C. B. Mechanisms of immune lysis. II. CTL-induced nuclear disintegration of the target begins within minutes of cell contact. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1256–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H. Internal disintegration model of cytotoxic lymphocyte-induced target damage. Immunol Rev. 1983;72:97–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Masakowski V., Rucinsky T., Phillips G. Mechanisms of immune lysis. III. Characterization of the nature and kinetics of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced nuclear lesion in the target. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2087–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Glauert A. M. The mechanism of T-cell mediated cytotoxicity. VI. T-cell projections and their role in target cell killing. Immunology. 1979 Jan;36(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J. The mechanism of T cell mediated cytotoxicity. II. Morphological studies of cell death by time-lapse microcinematography. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Jan 20;192(1107):241–255. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano R. F., Henney C. S. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. X. Enucleated cells as targets for cytotoxic attack. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):186–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakshull E., Johnson M. I., Burton H. Persistence of an amine uptake system in cultured rat sympathetic neurons which use acetylcholine as their transmitter. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):121–131. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., Battye F., Schrader J. W. Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):688–691. doi: 10.1038/310688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces the expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Feb-Mar;7(5-6):255–278. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










