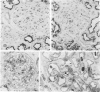
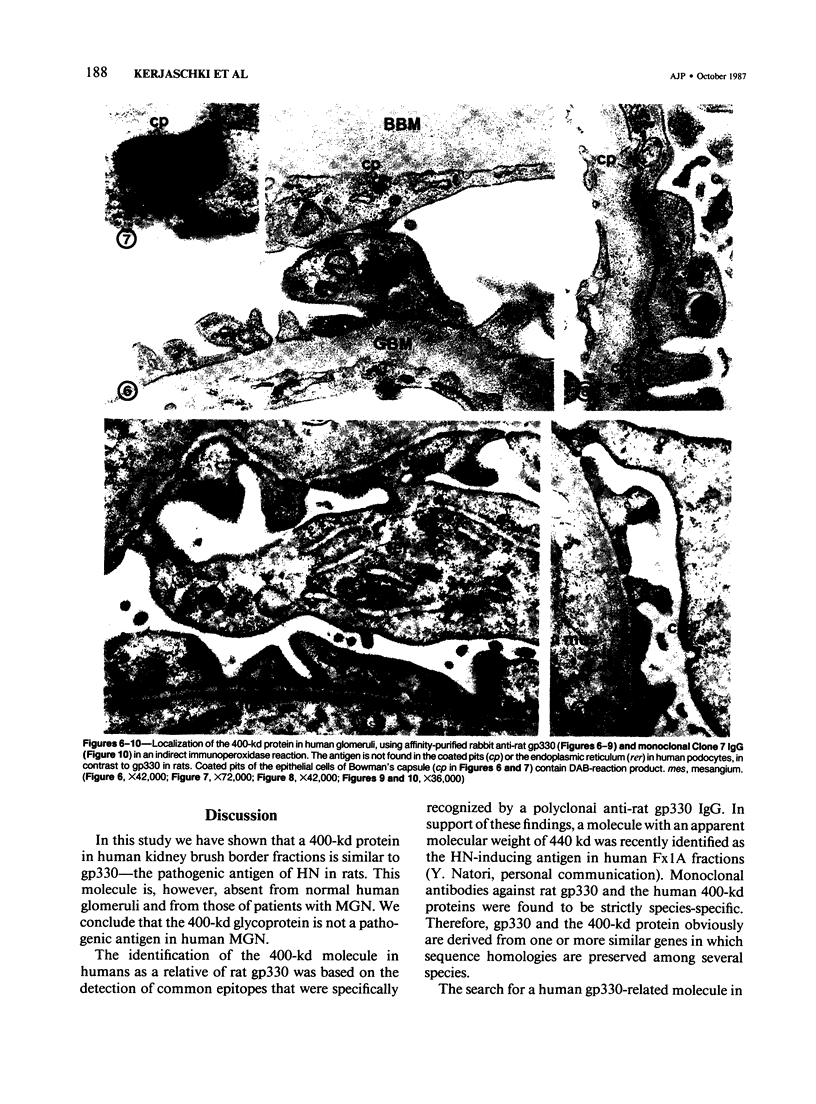
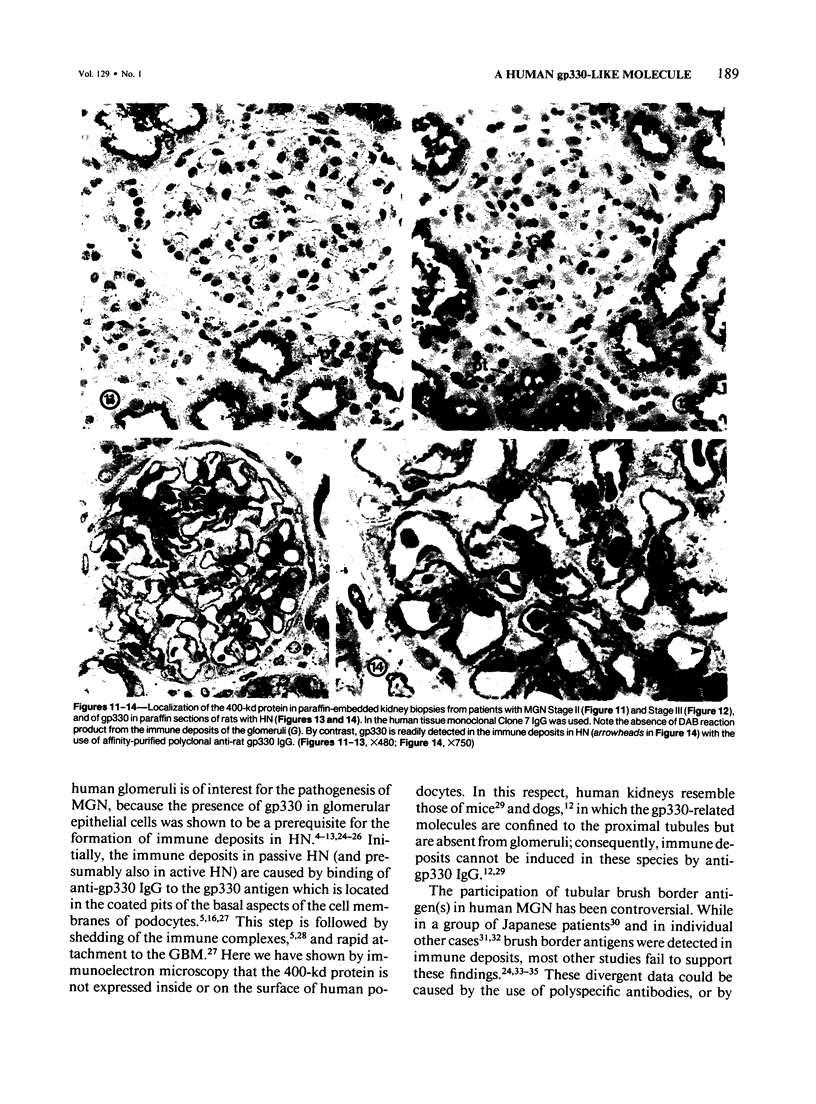
Abstract
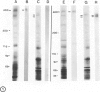
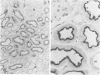
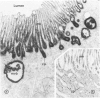
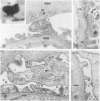
The nephritogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis (HN)--a well-studied experimental rat model disease of human membranous glomerulonephritis (MGN)--was recently shown to be a 330-kd glycoprotein (gp330) which is present in the membranes of both the rat tubular brush borders and of podocytes. Because the pathogenic antigen(s) of MGN are unknown, the authors have searched for a gp330-like molecule in human kidney and for its role in MGN. The authors here report that a membrane protein (apparent molecular weight 400 kd) is present in human kidney which is immunologically cross-reactive with rat gp330. By immunoelectron microscopy (using rabbit anti-rat gp330 IgG or a monoclonal anti-400-kd IgG) this molecule is similarly localized in human proximal tubules, but it is absent from the podocytes of human glomeruli. The 400-kd molecule is not detected in the glomerular immune deposits of 30 biopsies of MGN. It is proposed that this is due to the lack of the 400-kd protein in human glomeruli which prevents the formation of initial 400-kd anti-400-kd IgG immune complexes in situ.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assmann K. J., Ronco P., Tangelder M. M., Lange W. P., Verroust P., Koene R. A. Comparison of antigenic targets involved in antibody-mediated membranous glomerulonephritis in the mouse and rat. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):112–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar M., Katz A., Silverman M. Biochemical investigation of the pathogenesis of Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1986 Jul;30(1):9–15. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Schneeberger E. E., Baird L. G., Collins A. B., Kamata K., Bradford D., Erikson M. E., McCluskey R. T. Studies with monoclonal antibodies against brush border antigens in Heymann nephritis. Lab Invest. 1985 Oct;53(4):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Noble B., Kerjaschki D., Malavasi F., Roholt O. A., Farquhar M. G., Andres G. Antibody-induced redistribution of Heymann antigen on the surface of cultured glomerular visceral epithelial cells: possible role in the pathogenesis of Heymann glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2409–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelet F., Brianti E., Ronco P., Roland J., Verroust P. Ultrastructural localization by monoclonal antibodies of brush border antigens expressed by glomeruli. I. Renal distribution. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):500–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. B., Andres G. A., McCluskey R. T. Lack of evidence for a role of renal tubular antigen in human membranous glomerulonephritis. Nephron. 1981;27(6):297–301. doi: 10.1159/000182074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Wagonfeld J. B., Spargo B. H., Lewis E. J. Glomerular deposition of tumor antigen in membranous nephropathy associated with colonic carcinoma. Am J Med. 1974 Dec;57(6):962–970. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Syré G., Weirich E. Immunomorphologic methods in routine pathology. Application of immunofluorescence and the unlabeled antibody-enzyme (peroxidase-antiperoxidase) technique to formalin fixed paraffin embedded kidney biopsies. Beitr Pathol. 1977 May;160(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(77)80024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. F., Rabideau D. P., Schwartz M. M., Lewis E. J. Evidence of autologous immune-complex nephritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Nov 26;305(22):1326–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198111263052206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune-complex pathogenesis of experimental allergic glomerulonephritis. Science. 1967 Mar 17;155(3768):1432–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3768.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMANN W., HACKEL D. B., HARWOOD S., WILSON S. G., HUNTER J. L. Production of nephrotic syndrome in rats by Freund's adjuvants and rat kidney suspensions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Apr;100(4):660–664. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat R., Hovorka A., Dekan G., Poczewski H., Kerjaschki D. Endothelial cell membranes contain podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of visceral glomerular epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):484–491. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyoux C., Foidart J., Rigo P., Mahieu P., Geubelle F. Effects of methylprednisolone on the Fc-receptor function of human reticuloendothelial system in vivo. Eur J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;14(1):60–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1984.tb00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata K., Baird L. G., Erikson M. E., Collins A. B., McCluskey R. T. Characterization of antigens and antibody specificities involved in Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2400–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. The pathogenic antigen of Heymann nephritis is a membrane glycoprotein of the renal proximal tubule brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5557–5561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Miettinen A., Farquhar M. G. Initial events in the formation of immune deposits in passive Heymann nephritis. gp330-anti-gp330 immune complexes form in epithelial coated pits and rapidly become attached to the glomerular basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):109–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Noronha-Blob L., Sacktor B., Farquhar M. G. Microdomains of distinctive glycoprotein composition in the kidney proximal tubule brush border. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1505–1513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Poczewski H., Dekan G., Horvat R., Balzar E., Kraft N., Atkins R. C. Identification of a major sialoprotein in the glycocalyx of human visceral glomerular epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1142–1149. doi: 10.1172/JCI112694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Sawada H., Farquhar M. G. Immunoelectron microscopy in kidney research: some contributions and limitations. Kidney Int. 1986 Aug;30(2):229–245. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malathi P., Preiser H., Fairclough P., Mallett P., Crane R. K. A rapid method for the isolation of kidney brush border membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 13;554(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen A., Törnroth T., Tikkanen I., Virtanen I., Linder E. Heymann nephritis induced by kidney brush border glycoproteins. Lab Invest. 1980 Dec;43(6):547–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Allegri L., Melcion C., Pirotsky E., Appay M. D., Bariety J., Pontillon F., Verroust P. A monoclonal antibody to brush border and passive Heymann nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):319–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B., Galceran M., Verroust P. An immunopathologic study of a 330-kD protein defined by monoclonal antibodies and reactive with anti-RTE alpha 5 antibodies and kidney eluates from active Heymann nephritis. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slusarczyk J., Michalak T., Nazarewicz-de Mezer T., Krawczyński K., Nowosławski A. Membranous glomerulopathy associated with hepatitis B core antigen immune complexes in children. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jan;98(1):29–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verroust P., Ronco P. M., Chatelet F. Monoclonal antibodies and identification of glomerular antigens. Kidney Int. 1986 Nov;30(5):649–655. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth J. A., Leibowitz S., Kennedy M. C., Cameron J. S., Evans D. J., Glassock R. J., Schoenfeld L. S. Absence of glomerular renal tubular epithelial antigen in membranous glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 1976 Apr;5(4):159–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zager R. A., Couser W. G., Andrews B. S., Bolton W. K., Pohl M. A. Membranous nephropathy: a radioimmunologic search for anti-renal tubular epithelial antibodies and circulating immune complexes. Nephron. 1979;24(1):10–16. doi: 10.1159/000181675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetti M., Mandet C., Duboust A., Bedrossian J., Bariety J. Demonstration of a passive Heymann nephritis-like mechanism in a human kidney transplant. Clin Nephrol. 1981 May;15(5):272–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]