Abstract
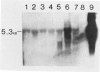
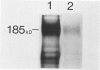
Monotypic cultures of passaged human umbilical vein endothelial cells secrete C3 protein, which is specifically immunoprecipitable from cell lysates and conditioned medium. A transcript migrating at 5.3 kilobases hybridizes with a mouse-derived C3 DNA probe in parallel cultures of endothelial cells, hepatoma cells (HepG2), and freshly isolated human monocytes. Steady-state transcript levels were as follows: HepG2 cells, 1.0; monocytes, 0.05; endothelial cells, 0.01. These data suggest that C3, an indispensible component for activation of complement by both the classical and alternative pathways, is locally synthesized in the vascular bed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Johnson A. M., Birtch A. G., Moore F. D. Human C'3: evidence for the liver as the primary site of synthesis. Science. 1969 Jan 17;163(3864):286–288. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3864.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett T. B., Gajdusek C. M., Schwartz S. M., McDougall J. K., Benditt E. P. Expression of the sis gene by endothelial cells in culture and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6772–6774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. S., Auerbach H. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Tissue-specific pretranslational regulation of complement production in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2610–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Ooi Y. M., Edelson P. J. Synthesis and secretion of complement proteins by macrophages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1979;332:482–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1979.tb47142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., 3rd, Harrison R. A., Lachmann P. J. Physiologic inactivation of fluid phase C3b: isolation and structural analysis of C3c, C3d,g (alpha 2D), and C3g. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1960–1966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton A. O., Jones L., Morrison L., Whaley K. Modulation of monocyte complement synthesis by interferons. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):809–815. doi: 10.1042/bj2420809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Engvall E. C3d fragment of complement interacts with laminin and binds to basement membranes of glomerulus and trophoblast. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):1091–1100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth J. L., Morgan E. L., DiSipio R. G., Hugli T. E. Suppression of T lymphocyte functions by human C3 fragments. I. Inhibition of human T cell proliferative responses by a kallikrein cleavage fragment of human iC3b. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2605–2611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Takami N., Ikehara Y. Biosynthesis and processing of pro-C3, a precursor of the third component of complement in rat hepatocytes: effect of secretion-blocking agents. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80570-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris K. M., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B. Biosynthesis and processing of a human precursor complement protein, pro-C3, in a hepatoma-derived cell line. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):399–400. doi: 10.1126/science.7199205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Hasegawa H., Yoshimura S., Watanabe K. The third (C3) and fourth (C4) components of complement in human liver. Immunocytochemical evidence for hepatocytes as the site of synthesis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1985 Jan;35(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1985.tb02206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. K. LPS stimulation of complement (C3) synthesis by a human monocyte cell line. Complement. 1984;1(2):108–115. doi: 10.1159/000467823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis P., Bonner W. M. Quantitative determination of histone modification. H2A acetylation and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4669–4675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis P., Pelicci P. G., Dalla-Favera R., Antoniades H. N. Synthesis and secretion of proteins resembling platelet-derived growth factor by human glioblastoma and fibrosarcoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2404–2408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Tedesco F., Bitter-Suermann D., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Biosynthesis of the third (C3), eighth (C8), and ninth (C9) complement components by guinea pig hepatocyte primary cultures. Immunobiology. 1985 Sep;170(3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(85)80092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Porter R. R. The proteolytic activation systems of complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:433–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]