Abstract
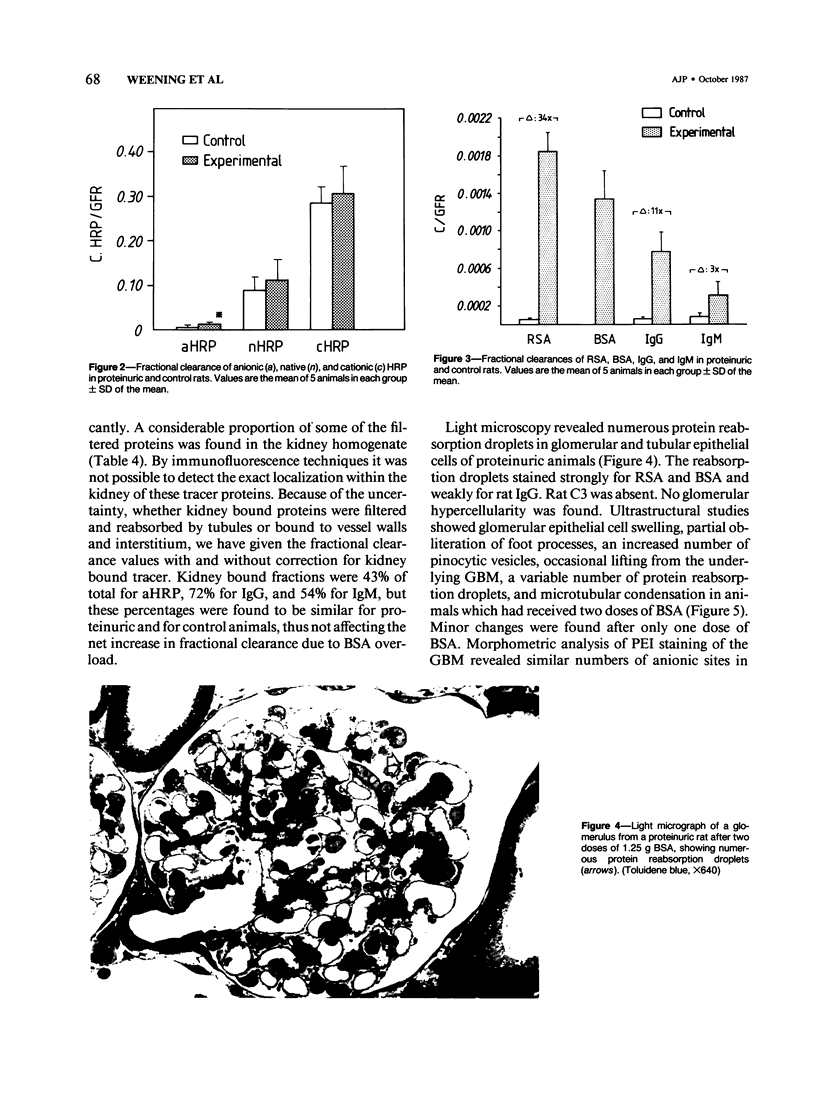
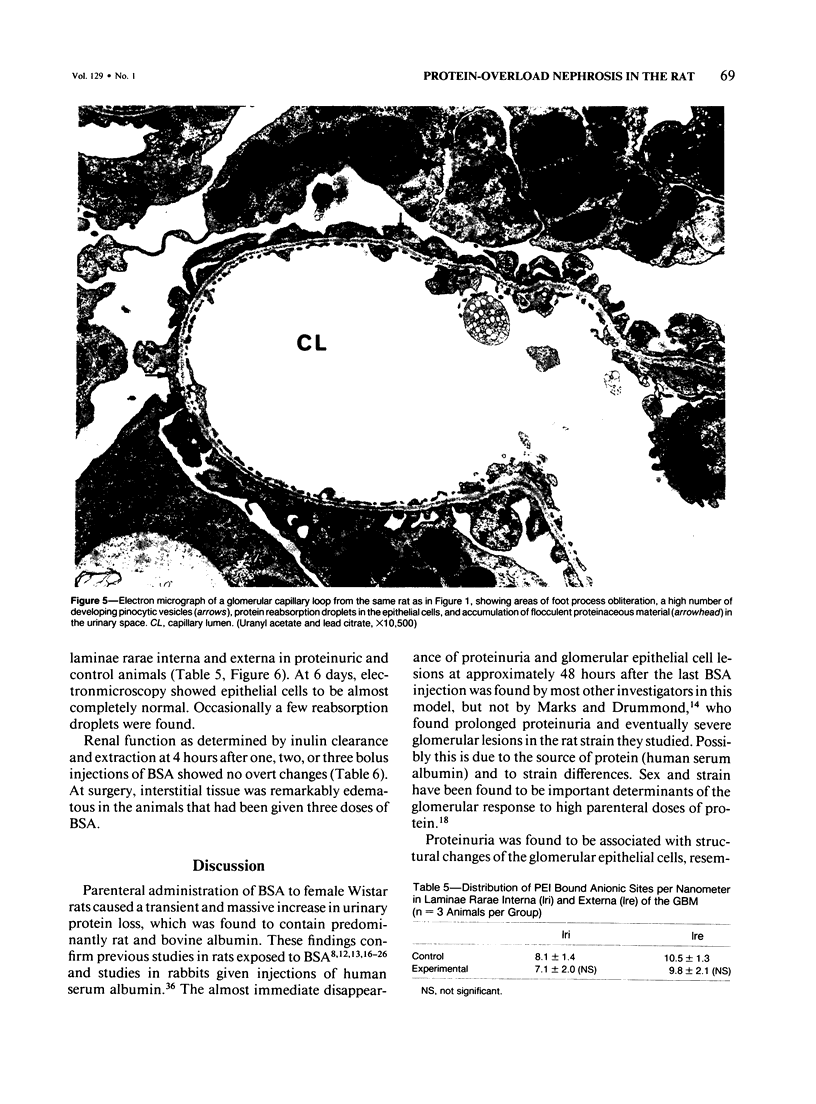
Alterations in glomerular function and structure were studied in protein-overload nephrosis in the rat induced by intraperitoneal administration of bovine serum albumin (BSA). Fractional clearance (C/GFR) studies using inulin and tracer proteins of different molecular size and charge revealed in proteinuric rats 1) unchanged glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow; 2) a 34-fold increase in C/GFR of rat serum albumin, reaching values similar to BSA; 3) a 2-fold increase in C/GFR for anionic horse radish peroxidase (HRP), but normal values for neutral and cationic HRP, and 4) an 11- and 3-fold increase for heterologous IgG and IgM, respectively. Glomerular epithelial cells showed degenerative changes, but the distribution of anionic sites in the glomerular basement membrane was found to be unaltered, as determined by polyethyleneimine binding studies. In summary, an elevation of serum albumin concentration resulted in an increased transcapillary albumin transport. This was found to lead to degenerative changes of glomerular epithelial cells with development of large pore defects, which were completely reversible.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON M. S., RECANT L. Fine structural alterations in the rat kidney following intraperitoneal bovine albumin. Am J Pathol. 1962 May;40:555–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASHWORTH C. T., JAMES J. A. Glomerular excretion of macromolecular substances. Electron microscopic study of rat kidney after administration of human serum albumin. Am J Pathol. 1961 Sep;39:307–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Addis T. The Mechanism of Proteinuria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1949 Apr;35(4):194–198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.35.4.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. M. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic comparison of puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephrosis to hyperalbuminemia-induced proteinuria with emphasis on kidney podocyte pedicel loss. Lab Invest. 1977 Feb;36(2):183–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. L., Radnik R. A., Gilchrist E. P., Venkatachalam M. A. Size and charge selective permeability defects induced in glomerular basement membrane by a polycation. Kidney Int. 1984 Jan;25(1):11–19. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertani T., Poggi A., Pozzoni R., Delaini F., Sacchi G., Thoua Y., Mecca G., Remuzzi G., Donati M. B. Adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in rats: sequence of pathologic events. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss D. J., Brewer D. B. Glomerular lysozyme binding in protein-overload proteinuria. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1985;48(4):351–359. doi: 10.1007/BF02890141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss D. J., Brewer D. B. Increased albumin and normal dextran clearances in protein-overload proteinuria in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Sep;69(3):321–326. doi: 10.1042/cs0690321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss D. J., Brewer D. B. Ultrastructural localization of anionic and cationic ferritin in the rat glomerular basement membrane in protein-overload proteinuria. J Pathol. 1984 May;143(1):57–68. doi: 10.1002/path.1711430109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Hostetter T. H., Humes H. D. Glomerular permselectivity: barrier function based on discrimination of molecular size and charge. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):F455–F460. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.6.F455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Hostetter T. H., Humes H. D. Molecular basis of proteinuria of glomerular origin. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 13;298(15):826–833. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804132981507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Farquhar M. G. Loss of anionic sites from the glomerular basement membrane in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1978 Nov;39(5):505–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., Reid J. J., Farquhar M. G. Alterations of the glomerular epithelium in acute aminonucleoside nephrosis. Evidence for formation of occluding junctions and epithelial cell detachment. Lab Invest. 1976 Jan;34(1):43–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. J., Brewer D. B., Hardwicke J. Urinary proteins and glomerular morphometry in protein overload proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1978 Mar;38(3):232–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. J., Messina A., Thumwood C. M., Ryan G. B. Glomerular podocytic injury in protein overload proteinuria. Pathology. 1985 Jul;17(3):412–419. doi: 10.3109/00313028509105494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER E. R., HELLSTROM H. R. Mechanism of proteinuria: Functional and ultrastructural correlation of effects of infusion of homologous and heterologous protein (bovine serum albumin) in the rat. Lab Invest. 1962 Aug;11:617–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V., Fahimi H. D. A new sensitive colorimetric assay for peroxidase using 3,3'-diaminobenzidine as hydrogen donor. Anal Biochem. 1973 Oct;55(2):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F85–F93. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie A. J., Bliss D. J., Brewer D. B. The glomerular ultrastructural distribution of immunoglobulin G in hyperalbuminaemic (protein-overload) proteinuria. J Pathol. 1985 Mar;145(3):213–227. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S. Biophysiology of glomerular filtration and proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):7–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S., Rosenzweig L. J. Altered glomerular permeability as a result of focal detachment of the visceral epithelium. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):565–574. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Vernillo A. T., Farquhar M. G. Reduced sialylation of podocalyxin--the major sialoprotein of the rat kidney glomerulus--in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):343–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPPMAN R. W., UREEN H. J., OLIVER J. Mechanism of proteinuria. III. A comparison of the functional and structural aspects of the effects of certain intraperitoneally administered proteins on hemoglobin excretion in the rat. J Exp Med. 1951 Apr 1;93(4):325–336. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.4.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence G. M., Brewer D. B. A biochemical and immunological investigation into the physiological basis of the increased albumin filtration induced in hyperalbuminaemic female Wistar rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 May;62(5):495–502. doi: 10.1042/cs0620495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence G. M., Brewer D. B. Effect of strain and sex on the induction of hyperalbuminaemic proteinuria in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Dec;61(6):751–756. doi: 10.1042/cs0610751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence G. M., Brewer D. B. Studies on the relationship between proteinuria and glomerular ultrastructural change in hyperalbuminaemic female Wistar rats. J Pathol. 1982 Dec;138(4):365–383. doi: 10.1002/path.1711380407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I., Drummond K. N. Nephropathy and persistent proteinuria after albumin administration in the rat. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):416–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaine P. N., Marks M. I., Baliah T., Drummond K. N. Hyperproteinemic proteinuria induced by plasma infusion. Pediatr Res. 1969 Nov;3(6):597–603. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196911000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medlar E. M., Blatherwick N. R. The Pathogenesis of Dietary Nephritis in the Rat. Am J Pathol. 1937 Nov;13(6):881–896.17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Yamashita H., Nakanishi C., Koizumi K., Makino S., Kishimoto Y., Hayashi Y. Proteinuria induced by transplantable rat pituitary tumor MtT SA5. Model for homologous protein-overload proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):636–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A. Alterations in the charge and size selectivity barrier of the glomerular filter in aminonucleoside nephrosis in rats. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):271–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennke H. G., Patel Y., Venkatachalam M. A. Glomerular filtration of proteins: clearance of anionic, neutral, and cationic horseradish peroxidase in the rat. Kidney Int. 1978 Apr;13(4):278–288. doi: 10.1038/ki.1978.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollason T. P., Brewer D. B. A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of glomerular damage in the rat following heterologous serum albumin overload. J Pathol. 1981 May;134(1):39–56. doi: 10.1002/path.1711340106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollason T. P., Brewer D. B. A study of glomerular basement membrane anionic sites and glomerular visceral epithelial cell coat in protein overload proteinuria in the rat. J Pathol. 1984 Apr;142(4):301–316. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. P., Vernier R. L., Michael A. F. Effect of protein-load proteinuria on glomerular polyanion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):870–874. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurer J. W., Kalicharan D., Hoedemaeker P. J., Molenaar I. The use of polyethyleneimine for demonstration of anionic sites in basement membranes and collagen fibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):688–689. doi: 10.1177/26.8.690407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening J. J., Rennke H. G. Glomerular permeability and polyanion in adriamycin nephrosis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1983 Aug;24(2):152–159. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






