Abstract
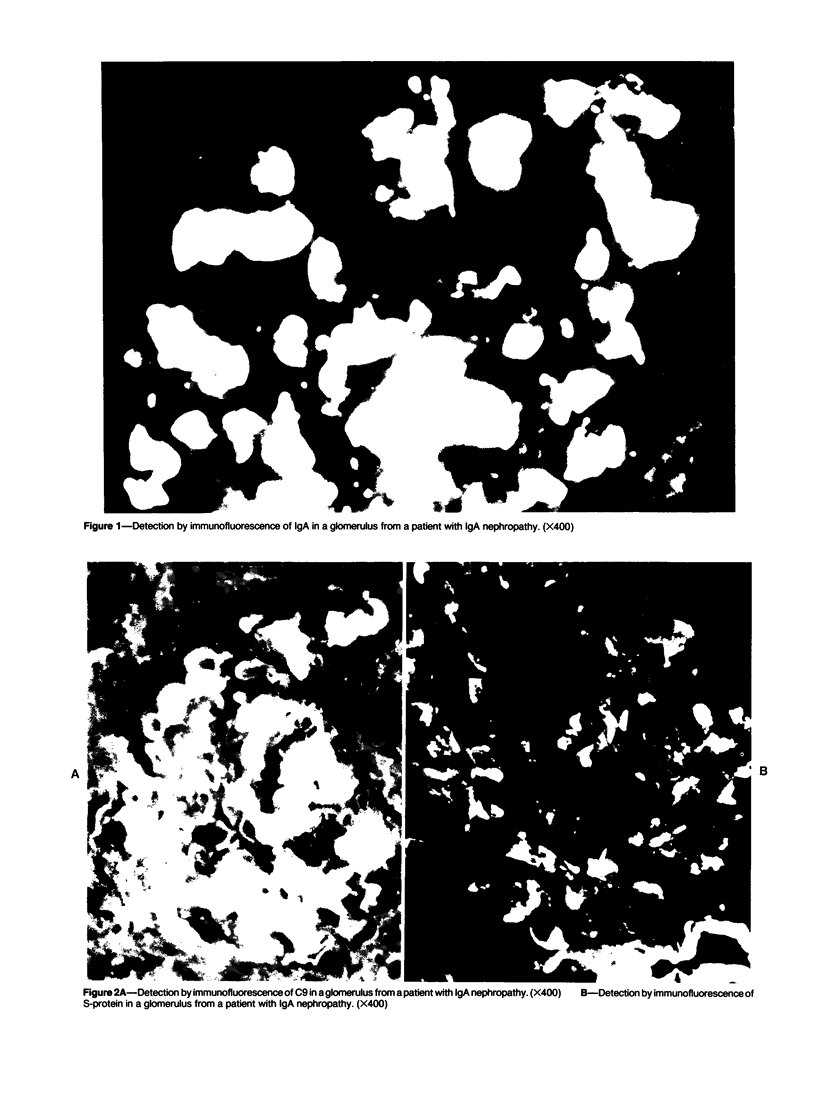
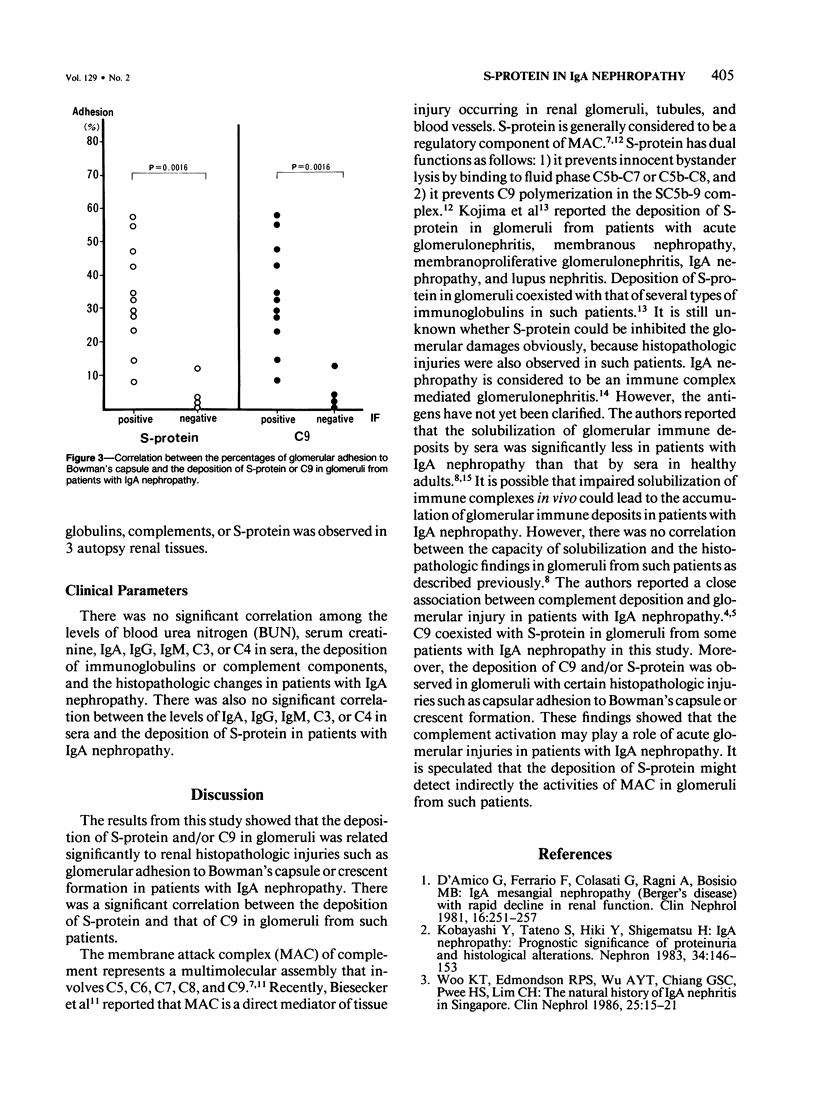
Detection of S-protein, which is a regulatory component of the membrane attack complex (MAC), and of C9 in glomeruli by immunofluorescence in 11 of 15 patients with IgA nephropathy is described. The study showed that glomerular injuries such as glomerular adhesion to Bowman's capsule and crescent formation were more marked in glomeruli with S-protein and/or C9 in patients with IgA nephropathy. S-protein co-existed with C9 in glomeruli from such patients. It is suggested that the deposition of S-protein might reflect certain types of histopathologic injuries in glomeruli from patients with IgA nephropathy. It is concluded that activation of terminal components of complement may be one of the exacerbating factors in patients with IgA nephropathy.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J. IgA glomerular deposits in renal disease. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Katz S., Koffler D. Renal localization of the membrane attack complex in systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1779–1794. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Baker P. J., Adler S. Complement and the direct mediation of immune glomerular injury: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):879–890. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amico G., Ferrario F., Colasanti G., Ragni A., Bestetti Bosisio M. IgA-mesangial nephropathy (Berger's disease) with rapid decline in renal function. Clin Nephrol. 1981 Nov;16(5):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Tateno S., Hiki Y., Shigematsu H. IgA nephropathy: prognostic significance of proteinuria and histological alterations. Nephron. 1983;34(3):146–153. doi: 10.1159/000183000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima H., Ohi H., Seki M., Hatano M. [Function of terminal complement complex and control protein in renal disease (renal localization and serum levels of S protein, and detection of the SC5b-9 complex)]. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1986 Nov;28(11):1449–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Tschopp J. Membrane attack by complement. Mol Immunol. 1984 Jul;21(7):589–603. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Tomino Y., Sato M., Yoshiki T., Itoh T. IgA nephropathy: clinicopathology and immunopathology. Contrib Nephrol. 1978;9:88–100. doi: 10.1159/000401436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y. Complement system in IgA nephropathy. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1980 Jan;5(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Endoh M., Nomoto Y., Sakai H. Activation of complement by renal tissues from patients with IgA nephropathy. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jan;34(1):35–40. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomino Y., Sakai H., Suga T., Miura M., Kaneshige H., Endoh M., Nomoto Y. Impaired solubilization of glomerular immune deposits by sera from patients with IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1983 Jul;3(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(83)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo K. T., Edmondson R. P., Wu A. Y., Chiang G. S., Pwee H. S., Lim C. H. The natural history of IgA nephritis in Singapore. Clin Nephrol. 1986 Jan;25(1):15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]