Abstract
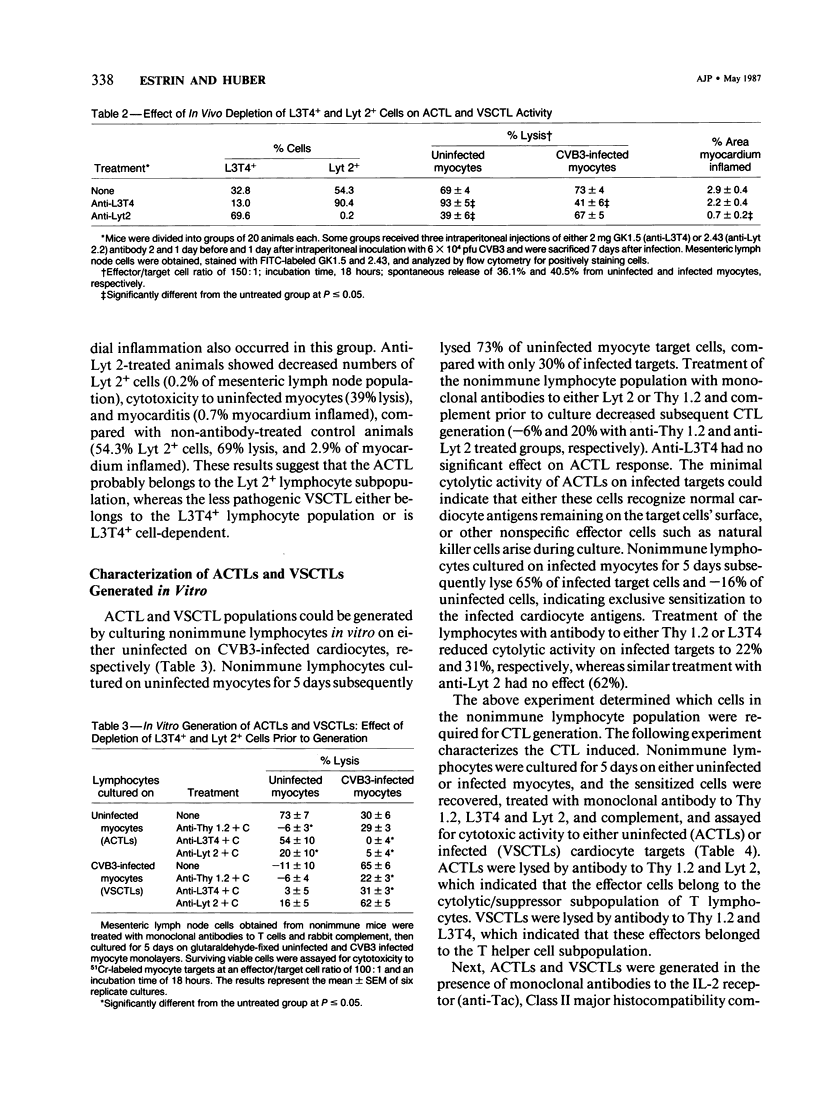
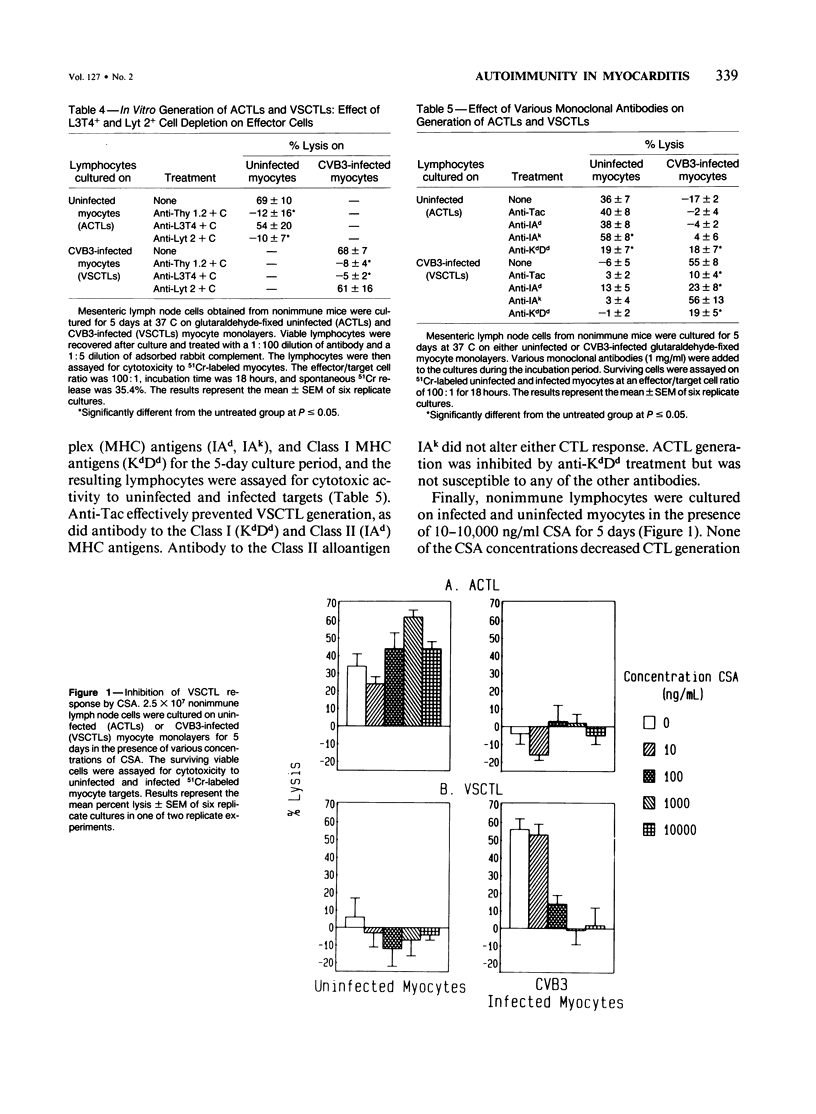
Male BALB/c mice inoculated with 6 X 10(4) plaque-forming units (pfu) coxsackievirus, group B, type 3 (CVB3), develop myocarditis within 7 days. Two cytolytic T lymphocyte (CTL) populations arise in infected animals. One population belongs to the Lyt 2+ T (cytolytic/suppressor) lymphocyte subset and reacts specifically with uninfected heart cells (autoreactive CTLs, ACTLs), whereas the other belongs to the L3T4+ T (helper) lymphocyte subset and reacts with infected targets (virus-specific CTLs, VSCTLs). Although both immune T lymphocyte populations can induce cardiac inflammation in vivo, ACTLs predominantly cause tissue injury. VSCTL generation can be inhibited by either anti-Tac (antibody to the interleukin 2 [IL-2] receptor) or anti-Iad but not by anti-IAk, indicating that this response is probably both IL-2-dependent and Class II (major histocompatibility complex [MHC] antigen restricted. ACTL generation is independent of IL-2, because neither anti-Tac or cyclosporin A inhibit this response.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrus L., Lafferty K. J. Inhibition of T-cell activity by cyclosporin A. Scand J Immunol. 1981 May;15(5):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabant G., Peter H., Becker H., Schwarzrock R., Wonigeit K., Hesch R. D. Cyclosporin in infiltrative eye disease. Lancet. 1984 Mar 3;1(8375):515–516. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92887-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrin M., Smith C., Huber S. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis. T-cell autoimmunity to heart antigens is resistant to cyclosporin-A treatment. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):244–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenoglio J. J., Jr, Ursell P. C., Kellogg C. F., Drusin R. E., Weiss M. B. Diagnosis and classification of myocarditis by endomyocardial biopsy. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 6;308(1):12–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301063080103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garman R. D., Fan D. P. Characterization of helper factors distinct from interleukin 2 necessary for the generation of allospecific cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):756–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie M., Lodge P. A., Huber S. A. Cardiac injury in myocarditis induced by Coxsackievirus group B, type 3 in Balb/c mice is mediated by Lyt 2 + cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):558–567. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett T. A., Lawton N. F., Fells P., Besser G. M. Deterioration of severe Graves' ophthalmopathy during cyclosporin treatment. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1101–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91541-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P. Cellular immune mechanisms in Coxsackievirus group B, type 3 induced myocarditis in Balb/C mice. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1983;161:491–508. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4472-8_29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Job L. P., Woodruff J. F. In vitro culture of coxsackievirus group B, type 3 immune spleen cells on infected endothelial cells and biological activity of the cultured cells in vivo. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.567-573.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Lodge P. A. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis in Balb/c mice. Evidence for autoimmunity to myocyte antigens. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jul;116(1):21–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S. A., Lodge P. A. Coxsackievirus B-3 myocarditis. Identification of different pathogenic mechanisms in DBA/2 and Balb/c mice. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):284–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Daniele R. P., Greene W. C., Nowell P. C. Evidence for an interleukin-independent pathway for human lymphocyte activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3444–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutton C. W., Gudvangen R. J., Nealon T. J., Paque R. E., Gauntt C. J. Cellular immune responses in mice challenged with an amyocarditic variant of Coxsackievirus B3. J Med Virol. 1985 Dec;17(4):345–357. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch B., Bülowius U., Schmier K., Klopf D., Koper D., Sibelis T., Kochsiek K. Immunological cellular regulator and effector mechanisms in myocarditis. Herz. 1985 Feb;10(1):8–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch B., Deeg P., Liebau G., Kochsiek K. Diagnostic relevance of humoral and cytotoxic immune reactions in primary and secondary dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Nov 1;52(8):1072–1078. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor A. M., Beck L., Hall R. Cyclosporin A in management of Graves' disease. J R Soc Med. 1985 Jun;78(6):511–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Ono S., Malek T. R., Singer A. Characterization of two distinct primary T cell populations that secrete interleukin 2 upon recognition of class I or class II major histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):603–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monrad E. S., Matsumori A., Murphy J. C., Fox J. G., Crumpacker C. S., Abelmann W. H. Therapy with cyclosporine in experimental murine myocarditis with encephalomyocarditis virus. Circulation. 1986 May;73(5):1058–1064. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.5.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Palestine A. G., Chan C. C. Cyclosporin A therapy in the treatment of intraocular inflammatory disease resistant to systemic corticosteroids and cytotoxic agents. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Sep;96(3):275–282. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)77814-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell J. B., Reap E. A., Robinson J. A. The effects of cyclosporine on acute murine Coxsackie B3 myocarditis. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):353–359. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller C. R., Dupré J., Gent M., Jenner M. R., Keown P. A., Laupacis A., Martell R., Rodger N. W., von Graffenried B., Wolfe B. M. Effects of cyclosporine immunosuppression in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1362–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.6367043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfgram L. J., Beisel K. W., Herskowitz A., Rose N. R. Variations in the susceptibility to Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis among different strains of mice. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1846–1852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F. Lack of correlation between neutralizing antibody production and suppression of coxsackievirus B-3 replication in target organs: evidence for involvement of mononuclear inflammatory cells in host defense. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. F., Woodruff J. J. Involvement of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of coxsackie virus B3 heart disease. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1726–1734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


