Abstract
The multiplication of the human neurotropic polyomavirus JC virus (JCV) is regulated by cell membrane receptors and nuclear transcription factors. Signaling pathways also play a role in determining the extent to which JCV can productively infect cells. These data show that constitutively active MEK1 protein (CA-MEK1), overexpressed in cultures of human glia, supports a substantial increase in late JCV protein (Vp-1) synthesis. The specificity of this pathway was indicated by no significant enhancement of JCV multiplication through activation of other components of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways such as p38, Jun N-terminal protein kinase, and protein kinase A. Further evidence supporting the importance of signaling in JCV infection came from addition of transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), which stimulated a 200% increase of Vp-1 expression. Specific MEK1/2 inhibitors, flavenoid PD98059 and U0126, decreased the basal and TGF-β1-stimulated Vp-1 expression by 95% or more. TGF-β1 is known to phosphorylate/activate Smad DNA binding proteins that could subsequently bind or increase binding to JCV promoter sequences, linking the effects of signaling with JCV transcriptional regulation. The effectiveness with which MEK1/2 inhibitors block JCV multiplication provides insight that may contribute to development of compounds directed against JCV.
Mammalian viruses are known to exploit host cell signaling machinery to regulate replication and host gene responses. The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway appears to facilitate such viral activity through a family of proline-directed serine-threonine proteins which normally function to transduce signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus in response to diverse extracellular stimuli (2, 14). This family of MAPK proteins consist of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1 and ERK2, respectively [ERK1/2]), p38 MAPK (p38), c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and cyclin-dependent kinases (9).
The ERK pathway is the most thoroughly studied of cytoplasmic signaling pathways (4, 5). ERK1 (also known as p44 MAPK) and ERK2 (also known as p42 MAPK) play a central role in mediating cellular responses to a variety of signaling molecules (15). The activity states of ERK1/2 are regulated by the upstream proteins MAPK kinases 1 and 2 (MEK1/2). The activity states of MEK1/2 are, in turn, regulated by MAPK kinase kinases. MEK1/2 activate ERK1/2 by phosphorylating regulatory threonine and tyrosine residues. The activated ERK1/2 then translocate into the nucleus to participate in transcriptional regulation of target genes (4). Recently, regulatory roles for the ERK pathway have been implicated in regard to gene expression and replication of human cytomegalovirus (13), simian virus 40 (29), human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) (11, 31), coxsackievirus (17), and influenza virus (24).
The ERK1/2 as well as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Rho family members can be activated by transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), which mediates biological effects through their regulators. TGF-βs mediate biological effects through interactions with at least three main TGF-β receptors, TβR1, TβR2, and TβR3/betaglycan (3, 16, 30). The intracellular signaling triggered by TGF-βs involves, in part, the phosphorylation of Smad-related proteins which, in turn, transduce complex changes in the transcriptional regulation of various target genes.
Enam et al. proposed a hypothesis based on observations of high TGF-β1 levels accompanying HIV-1-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), the fatal JCV-mediated demyelination disease of the central nervous system (CNS) (7). The high levels of TGF-β1 as well as Smad3/4 in JCV-infected oligodendrocytes of the examined PML patient samples were observed by immunohistochemistry. Using chloramphenicol acetyltransferase cell culture assays, Enam et al. also showed activation of the JCV early and late promoters by Smad3/4 and suggested a proactive role for Smad3/4 in viral propagation.
We show here that addition of TGF-β1 to the culture medium of JCV-exposed cells stimulated JCV multiplication to levels higher than those of untreated controls. Also, inhibition of the MEK pathway, using the specific MEK1/2 inhibitors PD98059 (2′-amino-3′-methoxyflavone; C16H13NO3) and U0126 [1,4-diamino-2,3-dicyano-1,4-bis(2-aminophynyltio)butadiene; C18H16N6S2], resulted in significant decreases of JCV multiplication in both TGF-β1-stimulated and nonstimulated cultures. These findings point to stimulation of JCV multiplication by TGF-β1 occurring through the MEK pathway. These data are of interest considering that enhanced expression levels of TGF-βs are reported to accompany immunosuppressive conditions, including AIDS. Therefore, targeting inhibition of the MEK1/2 pathway could be a promising strategy for the development of antiviral drugs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Progenitor and PDA cell cultures.
Human brain-derived progenitor cells (progenitors) from the telencephalon of an 8-week gestational fetal brain were obtained in accordance with NIH guidelines as previously described (20). Progenitor cultures grown at 10 to 40% confluence were at least 98% positive for nestin staining and did not express glial fibrillary acidic protein. Differentiation of progenitors into an astrocytic lineage (progenitor-derived astrocytes [PDA]) was initiated by culture medium substitution as described earlier (21).
Treatments with stimulants/inhibitors of signal transduction pathways on JCV-exposed cultures.
Progenitor or PDA cultures were exposed to JCV (Mad-4 variant) at 100 hemagglutination units (HAU)/5 × 105 cells in a minimal covering of appropriate serum-free medium. After overnight JCV exposure, cultures were washed and replenished with appropriate cell-specific growth medium. The PDA were treated with various signal transduction pathway stimulants/inhibitors in a minimum of serum-free Eagle's minimum essential medium for 2 h, after which JCV was added for overnight incubation. The JCV medium was then removed, and cultures were replenished with Eagle's minimum essential medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, as well as stimulants/inhibitors at concentrations identical to those in the original cultures. For induction of TGF-β1 signaling, culture media were supplemented with 5 ng/ml of recombinant TGF-β1 protein (R & D Systems). All JCV-exposed (controls) and JCV-exposed stimulant/inhibitor-treated cultures were processed 4 days post-JCV exposure as described in “Immunostaining” and “Nuclear extract and whole-cell extract preparation” below.
Immunostaining.
Four days after treatments with signal transduction pathway stimulants/inhibitors, cells grown on chamber slides were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline for 20 min at room temperature and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton in phosphate-buffered saline for 10 min at room temperature (RT). To block nonspecific binding of the antibodies used, fixed cells were incubated in TBS-T (Tris-buffered saline [TBS; 25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl] with 0.1% Tween 20) containing 5% goat serum and 5% bovine serum albumin for 2 h at RT. Cells were incubated with anti-Vp-1 (polyclonal) and antinestin (monoclonal) antibodies in TBS-T containing 5% bovine serum albumin for 2 h at RT (20, 27). After three 15-min TBS-T washes, fluorescence-conjugated anti-mouse and/or rhodamine-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (Jackson Immunoresearch) were incubated for 1 h at RT, followed by three 15-min TBS-T washes and one 15-min TBS wash. Cells were placed on coverslips and fixed with Vectashield mounting medium (Vector Laboratories) containing 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) to stain nuclei blue. Fluorescent staining was examined using a Zeiss Axiovert microscope, and images were captured with Axiovision software. Comparative counts of total versus Vp-1-stained cells were determined using ImageJ software (an open-source program distributed by the National Institutes of Health at http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/).
Nuclear extract and whole-cell extract preparation.
Four days after treatments with signal transduction pathway stimulants/inhibitors, nuclear fractions and whole-cell extracts were separated as previously described (27). Protein concentrations were determined with the Bio-Rad DC protein assay kit according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Western blots.
Ten to 15 μg of protein per lane from the nuclear extracts or whole-cell lysates above was resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 4 to 12% Bis-Tris NuPage gels (Invitrogen) and electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore). The transblotted membranes were blocked with TBS-TM (TBS-T containing 5% nonfat dry milk) for 2 h at RT and probed with appropriate primary antibodies (anti-Vp-1 [developed in our laboratory], anti-simian virus 40 T antigen [Oncogene], anti-MEK1 [Abcam], anti-β-actin [Sigma], anti-Smad2/3, and anti-Smad4 [Cell Signaling]) in TBS-TM. Western blot assays utilizing anti-MAPK antibodies (anti-p44/42 and anti-phospho-p44/42 [Cell Signaling]) were performed as described above, with the exception of TBS-TA (TBS-T containing 5% bovine serum albumin) being used throughout in place of TBS-TM. Bound primary antibodies were detected using either an anti-rabbit or an anti-mouse horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody included with the SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent substrate kit (Pierce), according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Transfection experiments.
Either 5 μg of a plasmid which codes for constitutively active mutant MEK1 (CA-MEK1) protein (kindly provided by H. Pant, NINDS) or 5 μg of an empty control plasmid vector (pCDNA3; Invitrogen) was transfected into PDA cultures using astrocyte Nucleofector reagent (Amaxa, Inc.). At 16 h posttransfection, the culture medium was replaced with fresh medium containing JCV at 100 HAU/5 × 105 cells. After 8 h of JCV exposure, viral medium was aspirated, cells were washed once, and fresh medium was added. Four days after the transfection (3 days after JCV exposure), whole-cell lysates were prepared for use in Western blot experiments.
Because variants of JCV promoter sequence convey different levels of viral activity, two JCV genomic plasmids, which contain distinct viral promoter sequences, were assayed in comparative immunoblotting experiments for levels of JCV Vp-1 protein synthesis expressed by transfected PDA. pM1TC (6) has the relatively robust Mad-1, type I repeat (I-R) promoter sequence while pJC-CY (29) has the less-active Archetype, type II singular (II-S) promoter sequence (12). The PDA nuclear extracts used for these Western blot experiments were prepared 7 days posttransfection.
Anchored transcriptional promoter assay (ATPA).
The Archetype and Mad-1 JCV promoters were PCR amplified from pJC-CY (32) and pM1TC (8), respectively, using a modified forward primer (JCV Mad-1 nucleotides 4992 to 5011) having a biotin group linked to the 5′ end and a normal reverse primer (JCV Mad-1 nucleotides 447 to 427) as previously described to generate ATP-Arche and ATP-Mad-1, respectively (27). Also, an anchored coding region (ACR-NF-1A1.1) used for preclearing cellular extracts was amplified as previously described (27).
In an approach similar to antibody-based immunoprecipitations, ATP-Arche and ATP-Mad-1 slurries were used to test the affinity of DNA binding proteins from aliquots of PDA nuclear extracts. Briefly, nuclear extracts from nontreated or TGF-β1-treated PDA nuclear extracts were added to an equal volume of protein binding buffer (TBS, pH 7.4, 1% Triton X-100, 1% glycerol, and protease inhibitors) containing 10% ACR-NF-1A1.1 and gently rotated overnight at 4°C. After centrifugation to pellet ACR-NF-1A1.1, the supernatants (precleared nuclear extracts) were added to equal volumes of protein binding buffer containing 10% ATP-Arche or ATP-Mad-1. After 2 h at 4°C with gentle rotation, the ATP-Arche and ATP-Mad-1 were pelleted by centrifugation and washed three times with ATPA wash buffer (TBS, pH 7.4, 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.5% glycerol, and protease inhibitors) and once with TBS containing protease inhibitors. Proteins that bound were eluted by boiling the washed ATP-Arche and ATP-Mad-1 for 3 min in Laemmli protein loading buffer and then resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Smad2/3 and anti-Smad4 polyclonal antibodies.
RESULTS
To facilitate examination of the molecular factors that affect JCV multiplication in human neural cell types, we previously developed a culture model system based on multipotential human CNS progenitor cells (progenitors) which can be selectively differentiated into either a JCV-susceptible astrocytic (PDA) or a nonsusceptible neuronal (progenitor-derived neurons) lineage (20). These cultures provide nearly pure populations of target cells for infection studies.
Stimulation of JCV multiplication by TGF-β1 through the MEK signaling pathway.
The activation of MAPK, p38 kinase, JNK, or protein kinase A pathways showed no significant stimulatory effect on JCV multiplication (Table 1). However, the addition of TGF-β1 nearly doubled JCV multiplication (approximately 200% of the control). Addition of the MEK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 or U0126 not only abolished basal viral multiplication but also significantly reduced this TGF-β1-stimulated viral multiplication. To test if these inhibitors negatively affect the binding and entry of JCV, PDA cultures were treated either 4 h before or 4 h after JCV exposure and continuing through to the experimental end point (day 4). For each inhibitor, no difference in Vp-1 expression level was observed between times of viral exposure, suggesting that the effects of these inhibitors on JCV permissiveness are intracellular, not cell membrane associated.
TABLE 1.
Effects of various signal transduction stimulants and inhibitors on JCV activity in PDA
| Chemical tested | Final concn | Action | % Vp-1a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control (no treatment) | 0 | None | 100 |
| Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate | 100 ng/ml | Activates protein kinase C | 100 |
| Interleukin-1β | 1 ng/ml | Stimulates inflammatory and immune response | 105 |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha | 1 ng/ml | Activates JNK | 110 |
| Forskolin | 5 μM | Activates adenylate cyclase | 110 |
| Sphingosylphosphorylcholine | 5 μM | Stimulates DNA binding activity of AP-1 | 110 |
| Lipopolysaccharide | 1 μg/ml | Stimulates various immune defense mechanisms | 110 |
| TGF-β1 | 5 ng/ml | Regulates proliferation, differentiation, and other cellular functions | 200 |
| Bisindolylmaleimide II | 25 nM | Inhibits protein kinase C | 100 |
| H-89, dihydrochloride | 100 nM | Inhibits protein kinase A | 90 |
| N-Nitro-l-arginine | 100 μM | Inhibits nitric oxide synthases, bNOS and eNOS | 90 |
| SP600125 | 100 nM | Inhibits JNK | 90 |
| SB203580 | 1 μM | Inhibits p38 MAPK | 90 |
| PD98059 | 20 μM | Inhibits MEK1/2 | 5 |
| U0126 | 10 μM | Inhibits MEK1/2 | 2 |
A measure of the viral activity observed in PDA cultures 4 days post-JCV exposure using ImageJ software (open-source program distributed by the National Institutes of Health) for quantitation of late viral protein (Vp-1) expression determined by intensity of immunoblot banding and represented here as a percentage-based comparison with the control value (no treatment). bNOS, brain nitric acid synthase; eNOS, endothelial nitric acid synthase.
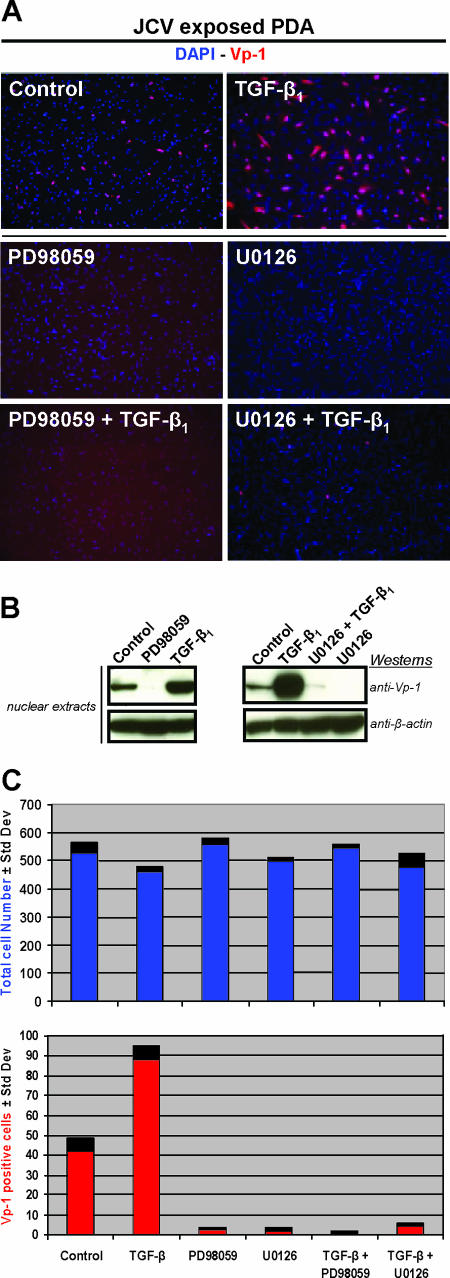
For further confirmation, immunostaining experiments were performed utilizing anti-Vp-1 to assay viral multiplication in JCV-exposed PDA treated with either of the MEK inhibitors PD98059 and U0126, plus both of these conditions with TGF-β1 stimulation (Fig. 1A). The control comparison of PDA not treated with PD98059 or U0126 showed twice as many cells staining for Vp-1 with TGF-β1 stimulation as without TGF-β1 stimulation. Both PD98059 and U0126 blocked nearly all Vp-1 expression in the nonstimulated and TGF-β1-stimulated cultures, confirming inhibition of viral multiplication by MEK inhibitors. PDA nuclear extracts analyzed by Western blotting also showed significant inhibition of TGF-β1 stimulation by PD98059 and U0126 (Fig. 1B). Treatment with MEK1/2 inhibitors was not toxic to PDA as measured by the total cell numbers (Fig. 1C).
FIG. 1.
(A) Permissive JCV cell type study. Immunostaining of PDA cultures 4 days post-JCV exposure (control) and also with the addition of either 20 μM of PD98059 or 10 μM of U0126. These same three conditions were also tested in the presence of 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then stained with anti-Vp-1 (red) to determine relative JCV multiplication. Cellular nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Western blot assays, from separate experiments having culture conditions identical to those of the immunostaining, utilized nuclear extracts that were resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Vp-1 and anti-β-actin. β-Actin was a consistent immunoblot loading control for nuclear extracts and whole-cell lysates, as determined by comparative experiments with α/β-tubulin antibodies. (C) Comparative counts of total versus Vp-1-stained cells were determined from images with an ×10 magnification using ImageJ software (an open-source program distributed by the National Institutes of Health at http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/). Results included are representative of three independent experiments.
Effect of stimulants/inhibitors of signaling pathways on JCV multiplication.
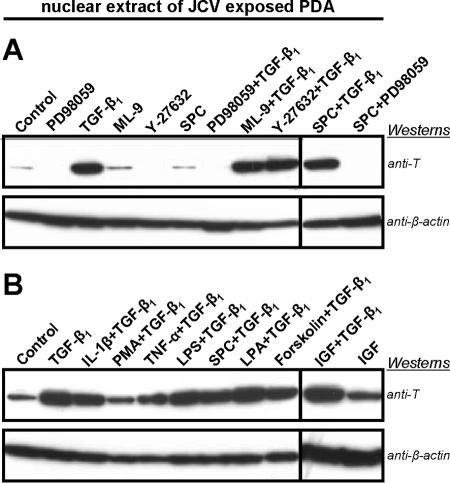
JCV-exposed PDA were treated with various signal transduction pathway stimulators and inhibitors in the presence of TGF-β1. Four days post-JCV exposure, the treated PDA were analyzed for early viral protein expression using anti-T antigen in immunoblotting experiments. Cells were cotreated with TGF-β1 and either interleukin-1β, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate, tumor necrosis factor alpha, lipopolysaccharide, sphingosylphosphorylcholine, lysophosphatidic acid, 7-deacetyl-7-O-N-methylpiperazino-γ-butyryl-dihydrochloride (forskolin), insulin-like growth factor 1, or myosin light chain kinase inhibitor (ML-9). Rho kinase inhibitor (Y-2763) showed inhibition of JCV multiplication; however, no significant inhibitory effect was observed when cells were cotreated with TGF-β1. Only PD98059 significantly reduced the effect of TGF-β1 stimulation (Fig. 2A). The stimulatory effect of TGF-β1 on JCV multiplication in cotreatments with other signaling activators showed no cumulative stimulation (Fig. 2B). This observation suggests that stimulation of JCV multiplication by TGF-β1 occurs through MEK.
FIG. 2.
(A) Western blotting comparison of the effects of various signal transduction pathway stimulators or inhibitors on early viral protein expression in PDA cultures 4 days post-JCV exposure. Blotting assays utilized nuclear extracts that were resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-T antigen (anti-T) and anti-β-actin. The anti-β-actin blot serves as the total protein loading control. (B) Western blot comparison similar to that found above but focusing on the combined effects of TGF-β1 with various signal transduction pathway stimulators on early viral protein expression. Results included are representative of three independent experiments. SPC, sphingosylphosphorylcholine; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; PMA, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; IGF, insulin-like growth factor 1.
The MEK1/2 inhibitors PD98059 and U0126 effectively reduce JCV multiplication.
MEK1/2 are critical members of the MAPK pathway that have been shown to be involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. The first “nonclassical” kinase inhibitors were the MEK inhibitors PD98059 and U0126. PD98059 is a potent and specific cell-permeable inhibitor of MEK1/2 activation. Likewise, U0126 inhibits MEK1/2 activation but also inhibits the active forms of MEK1/2. Blocking MEK1/2 activity inhibits the phosphorylation-based activation cascade of ERK1/2 and ERK1/2 substrates. Because PD98059 and U0126 inhibition is noncompetitive with respect to ATP and ERK1/2, the specific nature of these MEK1/2 inhibitors was employed to investigate possible connections between MAPK signaling pathways and JCV multiplication. While both PD98059 and U0126 were effective in inhibiting JCV multiplication, as measured by the levels of JCV protein expression detected in immunoblotting experiments (Fig. 3), slightly less viral protein expression was observed with U0126 than with identical concentrations of PD98059.
FIG. 3.
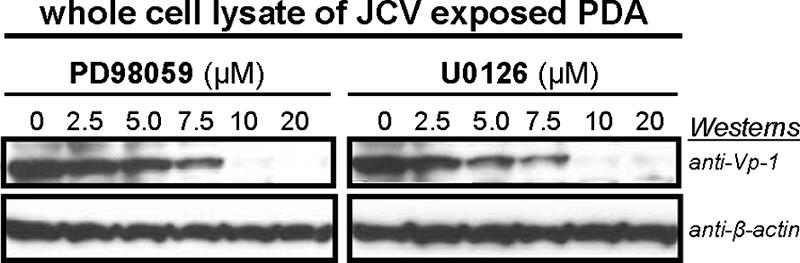
Western blot comparison of the effects of various concentrations of PD98059 and U0126 on late viral protein expression in PDA cultures 4 days post-JCV exposure. Concentrations tested include the accepted effective dosages of PD98059 (20 μM) and U0126 (10 μM) found in the literature for MEK1/2 inhibition in similar cell types. Blot assays utilized whole-cell lysates that were resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Vp-1 and anti-β-actin. The anti-β-actin blot serves as the total protein loading control. Results included are representative of three independent experiments.
TGF-β1 increases JCV multiplication in human neural progenitor cells.
Progenitor cells support only low-level JCV multiplication compared with that supported by PDA (20). To determine if TGF-β1 stimulates JCV multiplication in nonpermissive cell types, JCV-exposed progenitors were treated with TGF-β1. JCV multiplication was then assessed 4 days post-JCV exposure utilizing anti-Vp-1 for immunostaining of fixed-cell cultures and immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates. Statistical analysis of three individual experiments showed no significant difference in cell numbers between untreated and TGF-β1-treated progenitors, but staining for Vp-1 in the TGF-β1-treated progenitors (15%) was significantly increased above that for untreated cells (0.9%). This stimulatory role of TGF-β1 on JCV multiplication was also confirmed by the immunoblotting results (Fig. 4).
FIG. 4.
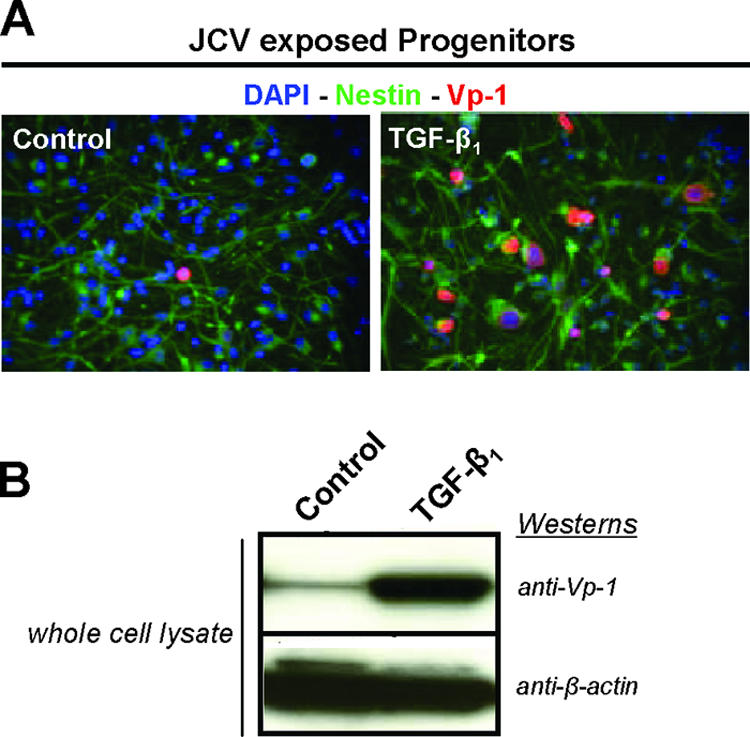
Nonpermissive JCV cell type studies. (A) Immunostaining of human CNS progenitor cell cultures 4 days post-JCV exposure (control) and also with the addition of 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and then stained with anti-human nestin (green), which distinguishes progenitor cells from other CNS cell types, and anti-Vp-1 (red) to determine relative JCV multiplication. Cellular nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Western blots, from separate experiments having culture conditions identical to those for the immunostaining but with cells being infected with JCV for 7 days, utilized whole-cell lysates that were resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Vp-1 and anti-β-actin. The anti-β-actin blot serves as the total protein loading control. Results included are representative of at least three independent experiments.
MEK1 plays a role in regulating JCV multiplication.
To further examine the role of MEK in JCV tropism, in light of the reduction of viral protein expression by MEK1/2 inhibitors, PDA were transfected with either control plasmid or plasmid encoding constitutively active MEK1 (CA-MEK1) and then exposed to JCV. CA-MEK1-transfected PDA showed enhanced Vp-1 production compared to that of PDA transfected with control plasmid (Fig. 5). To assess if overexpression of CA-MEK1 affected ERK phosphorylation levels, total ERK1/2 and phosphorylated ERK1/2 levels were measured. Even though ERK1/2 levels were unaffected, phosphorylated ERK1/2 increased with the overexpression of CA-MEK1, demonstrating the functional activity of CA-MEK1.
FIG. 5.
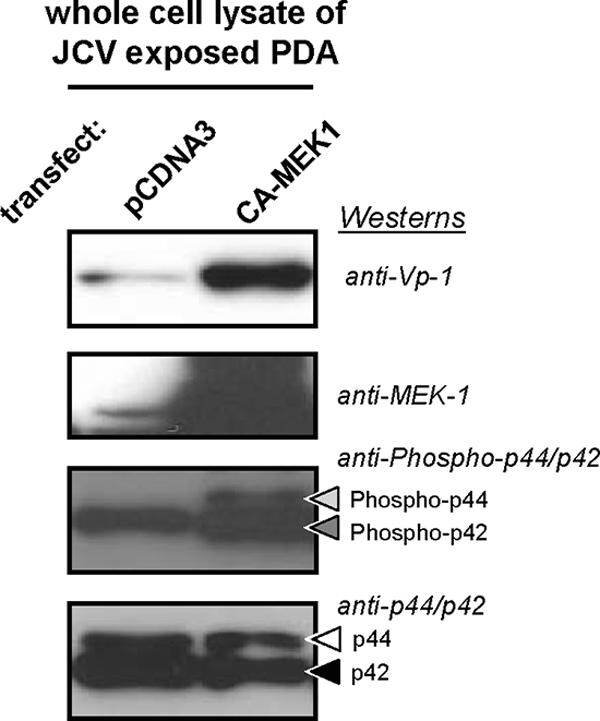
Western blot demonstration of the effects of constitutively active MEK1 (CA-MEK1) protein overexpression on MAPK activation (phosphorylated p44/42 [Phospho-p44/42], also known as phosphorylated or activated ERK1/2) and viral multiplication in PDA cultures 4 days post-exposure to 100 HAU of JCV per 5 × 105 cells. CA-MEK1 overexpression was achieved by transfecting PDA cultures with a plasmid that shares the name of this mutant protein. The control transfection was performed with pCDNA3. Blots utilized whole-cell lysates that were resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Vp-1, anti-MEK1, anti-Ph-p44/p42, and anti-p44/p42. The anti-p44/p42 blot serves as a total protein loading control. Results included are representative of three independent experiments.
TGF-β1 promotes the association of Smads with an active JCV promoter variant.
JCV protein expression is regulated by the association of cellular transcription factors with the viral promoter. Hence, variation of promoter sequence can dictate which transcription factors bind and, thereby, affect viral production. Because of known involvement of Smad proteins in transcriptional regulation and the direct effects of TGF-β1 on Smad pathways, here we examined the ability of TGF-β1 to enhance the association of Smad proteins with variants of JCV promoter sequence.
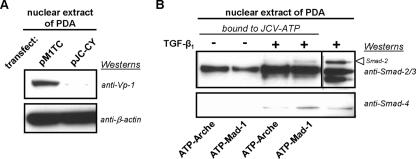
A JCV genomic plasmid with Archetype promoter sequence, which showed low viral protein expression, and a JCV genomic plasmid with Mad-1 promoter sequence, which showed high viral protein expression (Fig. 6A), were used as templates for the amplification of anchored JCV promoter regions. In an approach similar to antibody-based immunoprecipitations, JCV-anchored transcriptional promoters (ATP-Mad-1 and ATP-Arche) were used to test the affinity of DNA binding proteins from nuclear extracts of nontreated, as well as TGF-β1-treated, PDA nuclear extracts. Smad proteins that bound to the JCV-anchored transcriptional promoters were analyzed by Western blotting using Smad2/3 and Smad4 antibodies. As shown in Fig. 6B, Smad2 from nontreated PDA showed no binding to JCV-anchored transcriptional promoters. However, with TGF-β1 treatment, Smad2 was found to associate with ATP-Mad-1. Similarly, Smad4 of nontreated control PDA bound neither ATP-Mad-1 nor ATP-Arche, while Smad4 from TGF-β1-treated PDA associated with ATP-Mad-1 and, to a lesser extent, ATP-Arche. These findings suggest that an increase in Smad association with specific JCV promoter sequences, as the result of TGF-β1 activation, plays a role in increased viral multiplication.
FIG. 6.
(A) Western blot comparison of the viral multiplication in PDA cultures of two different strains of JCV. Blots utilized nuclear extracts from PDA cultures that had been transfected with either Mad-1 (pM1TC) or Archetype (pJC-CY) plasmids, resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Vp-1 and anti-β-actin. The anti-β-actin blot serves as the total protein loading control. (B) An ATPA utilizing Western blot comparison of Smad binding profiles derived from either the JCV Mad-1 (ATP-Mad-1) or Archetype (ATP-Arche) promoter nucleotide sequences. This ATPA utilized nuclear extracts from PDA cultures that were either untreated (−) or treated with 5 ng/ml of TGF-β1 (+). Proteins from these nuclear extracts that bound to ATP-Mad-1 or ATP-Arche were eluted by boiling into protein loading buffer, resolved on 4 to 12% gradient gels, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and probed with anti-Smad2 and anti-Smad4. A nuclear extract from TGF-β1-treated PDA that was not subjected to binding was also loaded on the gels as an unbound control. Results included are representative of three independent experiments.
DISCUSSION
In an effort to exploit the cellular signaling pathways used for viral propagation, we screened JCV-exposed PDA cultures via treatments with a number of stimulants and inhibitors of signal transduction pathways. We found that TGF-β1 stimulated JCV multiplication while specific MEK inhibitors decreased it. In cotreatments, MEK inhibitors were the only compounds tested that significantly decreased the TGF-β1 stimulation, identifying MEK as having a central effect on JCV multiplication.
There is evidence that TGF-β1 levels are increased during immunosuppressive conditions, particularly noteworthy in HIV/AIDS (6). Because PML occurs in the context of JCV reactivation during immunosuppression and is most commonly associated with AIDS, our demonstration of JCV stimulation through a TGF-β1/MEK axis suggests the importance of TGF-β1 in pathogenesis.
It has been previously reported that JCV infection leads to the activation of MAPKs, ERK1/2, within the first few hours of viral exposure (25). However, other MAPK stimulants used in this study showed no significant effect on JCV multiplication, either alone or in combination with TGF-β1. Also, the comparison of MEK inhibitor treatments, 4 hours before or 4 hours after JCV exposure, revealed that the effects are at the intracellular level, possibly in the nucleus.
The significance of host activation of MAPK in other models of viral infection has been reported. In the HIV-1 model, activation of MAPK is beneficial for viral replication, where inhibition leads to reduced viral replication (11). In addition, involvement of ERK in activity of adenovirus type 7 (1), Borna disease virus (23), influenza A virus (24), and hepatitis C virus (10) suggests a general strategy for enhanced viral replication (17). In our studies here, despite MEK being a specific downstream component of the MAPK pathway and a point of cross talk with other signaling pathways, activation of the MAPK, p38, JNK, or protein kinase A pathway showed no significant increase in JCV multiplication. Even though TGF-β1 alone was sufficient to increase JCV multiplication, this stimulatory effect was significantly diminished by inhibitors that specifically block MEK1/2 activation and/or activity, demonstrating that TGF-β1 stimulation is transduced through MEK. Additionally, the stimulation by overexpression of constitutively active MEK1 points to the central role that MEK activity plays in JCV multiplication.
The site of latency and the molecular events leading to reactivation are critical features of the pathogenesis of CNS diseases associated with latent and/or persistent viruses (18, 22). The transcriptional regulation of JCV expression is the limiting factor governing the range of cell types that can serve as sites of JCV latency and reactivation (18). The understanding that increased TGF-β1 levels occur in the context of immunosuppressive conditions prompted us to test if TGF-β1 addition would increase JCV multiplication in nonsusceptible cell types. Interestingly, TGF-β1 stimulated JCV multiplication in progenitor cells (which normally support only low-level viral multiplication). These results highlight the possibility that even though specific cellular receptors are important for JCV internalization, other factors which act at the level of transcription and replication are crucial for JCV regulation.
A series of reports indicate that several MAPKs can be rapidly activated by TGF-β1 in a manner dependent on cell type and condition (19). The biochemical link between the TGF-β1 and MAPK pathways has been elusive due to the paucity of supportive evidence. Smad proteins are the only known TGF-β1 receptor substrates capable of signal transduction. TGF-β1 conveys a signal by translocating Smads into the nucleus. Translocated Smads are then regulated in the ability to affect gene expression by forming complexes with DNA binding cofactors and transcriptional coactivators/corepressors.
The level of JCV multiplication depends upon the nucleotide sequence of the viral regulatory region and the interaction of this promoter sequence with host cell transcription factors (18, 26, 28). Nucleotide sequences that act as transcriptional promoters are located between the early and late protein coding regions and contain the origin of DNA replication (8, 18). These sequences also contain TATA boxes, as well as binding sites for Sp1, YB1, sup2, pur-α, c-Jun, and NF-1. The increased viral multiplication in PDA stimulated by TGF-β1 treatment revealed concurrent increases of Smad2/4 association with JCV-Mad-1 promoter sequence (a highly active JCV regulatory region variant), compared to JCV Archetype promoter sequence (a much less active regulatory region variant). Because TGF-β1 is involved in activating Smads, which can translocate to the nucleus, Smads may associate with highly active JCV promoter sequences as transcriptional coactivators of JCV gene expression. Our findings support the notion that binding of Smads to highly active JCV promoters is, in part, responsible for fostering JCV propagation and therefore suggest the role that TGF-β1 plays in stimulating JCV multiplication. In line with other published reports (19), our results raise the possibility that TGF-β1 may simultaneously activate Smad and MAPK pathways which then physically converge on the target, in this case the JCV promoter.
Currently, we are studying Smad cofactor binding to JCV promoters and examining if Smad association requires MEK activity. We are also testing MEK1/2 inhibition on the activity of a closely related polyomavirus, BK virus, which is also activated during immunosuppressive conditions.
In conclusion, we have demonstrated that a TGF-β1/MEK axis is involved in JCV multiplication. We have shown that TGF-β1 promotes association of Smads with a highly active variant of JCV promoter sequence and that JCV multiplication in human glial cultures can be significantly reduced by the administration of MEK1/2 inhibitors. Therefore, greater understanding of the MEK1/2 signaling pathway may lead to novel antiviral therapies.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health.
We thank Harish Pant for supplying the CA-MEK1 plasmid. We also thank M. C. G. Monaco-Kushner, L. Schwartz, M. Gravell, and H. Pant (NINDS/NIH) and J. D. Weissman (EIB/NCI/NIH) for their constructive criticisms.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 4 April 2007.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alcorn, M. J., J. L. Booth, K. M. Coggeshall, and J. P. Metcalf. 2001. Adenovirus type 7 induces interleukin-8 production via activation of extracellular regulated kinase 1/2. J. Virol. 75:6450-6459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blenis, J. 1993. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:5889-5892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen, Y. G., A. Hata, R. S. Lo, D. Wotton, Y. Shi, N. Pavletich, and J. Massague. 1998. Determinants of specificity in TGF-beta signal transduction. Genes Dev. 12:2144-2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crews, C. M., and R. L. Erikson. 1993. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell 74:215-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Davis, R. J. 2000. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dhar, A., J. Gardner, K. Borgmann, L. Wu, and A. Ghorpade. 2006. Novel role of TGF-beta in differential astrocyte-TIMP-1 regulation: implications for HIV-1-dementia and neuroinflammation. J. Neurosci. Res. 83:1271-1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Enam, S., T. M. Sweet, S. Amini, K. Khalili, and L. Del Valle. 2004. Evidence for involvement of transforming growth factor beta1 signaling pathway in activation of JC virus in human immunodeficiency virus 1-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 128:282-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frisque, R. J., G. L. Bream, and M. T. Cannella. 1984. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J. Virol. 51:458-469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garrington, T. P., and G. L. Johnson. 1999. Organization and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11:211-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Giambartolomei, S., F. Covone, M. Levrero, and C. Balsano. 2001. Sustained activation of the Raf/MEK/Erk pathway in response to EGF in stable cell lines expressing the hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein. Oncogene 20:2606-2610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jacque, J. M., A. Mann, H. Enslen, N. Sharova, B. Brichacek, R. J. Davis, and M. Stevenson. 1998. Modulation of HIV-1 infectivity by MAPK, a virion-associated kinase. EMBO J. 17:2607-2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jensen, P. N., and E. O. Major. 2001. A classification scheme for human polyomavirus JCV variants based on the nucleotide sequence of the noncoding regulatory region. J. Neurovirol. 7:280-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Johnson, R. A., X. L. Ma, A. D. Yurochko, and E. S. Huang. 2001. The role of MKK1/2 kinase activity in human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 82:493-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lange-Carter, C. A., C. M. Pleiman, A. M. Gardner, K. J. Blumer, and G. L. Johnson. 1993. A divergence in the MAP kinase regulatory network defined by MEK kinase and Raf. Science 260:315-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lewis, T. S., P. S. Shapiro, and N. G. Ahn. 1998. Signal transduction through MAP kinase cascades. Adv. Cancer Res. 74:49-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lopez-Casillas, F., J. L. Wrana, and J. Massague. 1993. Betaglycan presents ligand to the TGF beta signaling receptor. Cell 73:1435-1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Luo, H., B. Yanagawa, J. Zhang, Z. Luo, M. Zhang, M. Esfandiarei, C. Carthy, J. E. Wilson, D. Yang, and B. M. McManus. 2002. Coxsackievirus B3 replication is reduced by inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway. J. Virol. 76:3365-3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Major, E. O. 2001. Human polyomaviruses, p. 2175-2196. In D. M. Knipe, P. M. Howley, D. E. Griffin, R. A. Lamb, M. A. Martin, B. Roizman, and S. E. Straus (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
- 19.Massague, J., S. W. Blain, and R. S. Lo. 2000. TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell 103:295-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Messam, C. A., J. Hou, R. M. Gronostajski, and E. O. Major. 2003. Lineage pathway of human brain progenitor cells identified by JC virus susceptibility. Ann. Neurol. 53:636-646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Messam, C. A., and E. O. Major. 2000. Stages of restricted HIV-1 infection in astrocyte cultures derived from human fetal brain tissue. J. Neurovirol. 6(Suppl. 1):S90-S94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nathanson, N., R. Ahmed, F. Gonzalez-Scarano, D. E. Griffin, K. Holmes, F. Murphy, and H. Robinson. 2003. Viral pathogenesis. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
- 23.Planz, O., S. Pleschka, and S. Ludwig. 2001. MEK-specific inhibitor U0126 blocks spread of Borna disease virus in cultured cells. J. Virol. 75:4871-4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pleschka, S., T. Wolff, C. Ehrhardt, G. Hobom, O. Planz, U. R. Rapp, and S. Ludwig. 2001. Influenza virus propagation is impaired by inhibition of the Raf/MEK/ERK signalling cascade. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:301-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Querbes, W., A. Benmerah, D. Tosoni, P. P. Di Fiore, and W. J. Atwood. 2004. A JC virus-induced signal is required for infection of glial cells by a clathrin- and eps15-dependent pathway. J. Virol. 78:250-256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Raj, G. V., and K. Khalili. 1995. Transcriptional regulation: lessons from the human neurotropic polyomavirus, JCV. Virology 213:283-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ravichandran, V., B. F. Sabath, P. N. Jensen, S. A. Houff, and E. O. Major. 2006. Interactions between c-Jun, nuclear factor 1, and JC virus promoter sequences: implications for viral tropism. J. Virol. 80:10506-10513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Seth, P., F. Diaz, and E. O. Major. 2003. Advances in the biology of JC virus and induction of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neurovirol. 9:236-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sontag, E., S. Fedorov, C. Kamibayashi, D. Robbins, M. Cobb, and M. Mumby. 1993. The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell 75:887-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wick, W., U. Naumann, and M. Weller. 2006. Transforming growth factor-beta: a molecular target for the future therapy of glioblastoma. Curr. Pharm. Des. 12:341-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yang, X., and D. Gabuzda. 1999. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infectivity by the ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Virol. 73:3460-3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yogo, Y., T. Kitamura, C. Sugimoto, T. Ueki, Y. Aso, K. Hara, and F. Taguchi. 1990. Isolation of a possible archetypal JC virus DNA sequence from nonimmunocompromised individuals. J. Virol. 64:3139-3143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]