Abstract
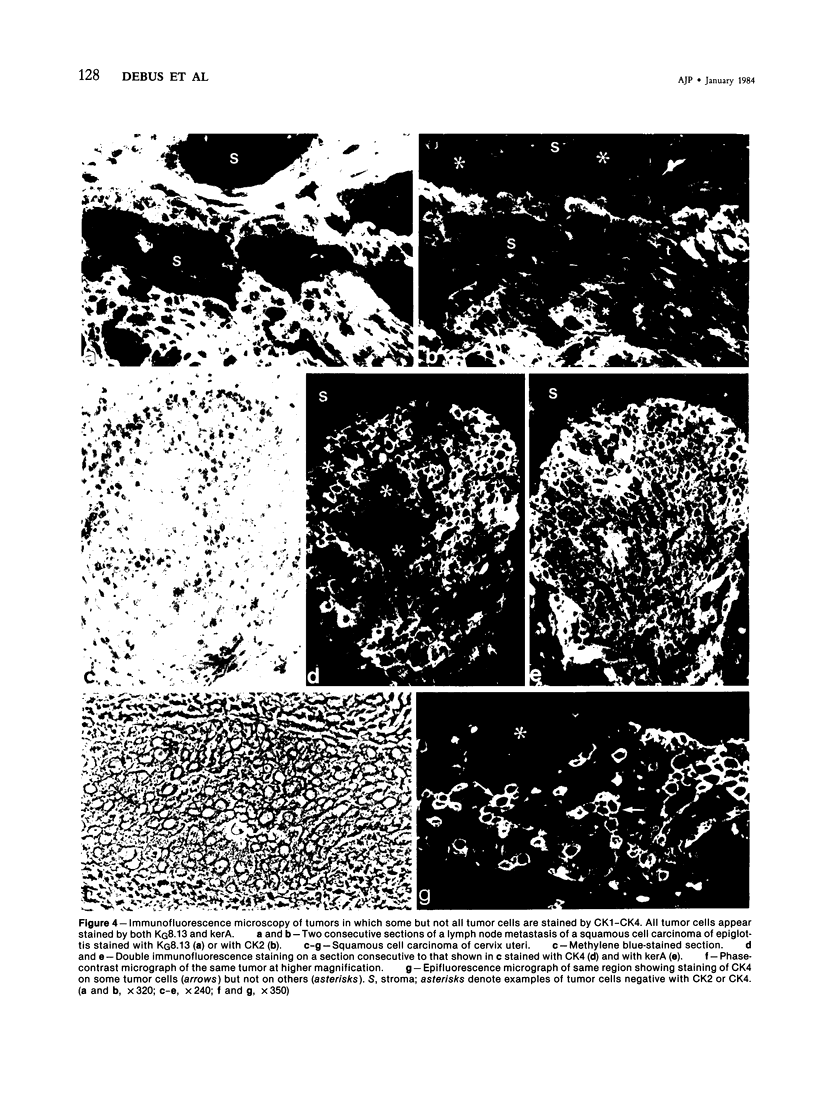
Carcinomas of different origin have been tested in immunofluorescence microscopy with the monoclonal murine antibodies CK1-CK4, which recognize a single cytokeratin polypeptide (human cytokeratin No. 18) present in simple but not in stratified squamous epithelia, and with the monoclonal antibody KG8.13 and guinea pig kerA antibodies, both of which recognize a variety of cytokeratins common to almost all epithelial cell types. Tumors derived from simple epithelia, including adenocarcinomas and some other tumors such as ductal breast carcinomas, were strongly stained by all three antibodies. So was a transitional carcinoma of the bladder. In contrast, basal cell epithelioma, cloacogenic carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma of skin, tongue, and esophagus appeared negative with CK1-CK4 but positive with the other two antibodies. Other squamous cell carcinomas derived from epiglottis and cervix uteri showed a mixture of positive and negative cells when tested with CK1-CK4, although all tumor cells were positive when tested with KG8.13 and with kerA. Thus, use of an appropriate collection of cytokeratin antibodies with different specificities not only allows tumors of epithelial origin to be distinguished from other tumor types but, in addition, allows a further subdivision of carcinomas in relation to their histologic origin.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Weber K. The distribution of keratin type intermediate filaments in human breast cancer. An immunohistological study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;37(3):277–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02892576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Treuner J., Hölscher A., Weber K., Shauer A. Diagnosis of human childhood rhabdomyosarcoma of antibodies to desmin, the structural protein of muscle specific intermediate filaments. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;39(2):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02892848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Weber K., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Osborn M. Antibodies to intermediate filaments as diagnostic tools: human gastrointestinal carcinomas express prekeratin. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal cytokeratin antibodies that distinguish simple from stratified squamous epithelia: characterization on human tissues. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1641–1647. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denk H., Krepler R., Lackinger E., Artlieb U., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunocytochemical analysis of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton in human hepatocellular carcinomas and in hepatic neoplastic nodules of mice. Lab Invest. 1982 Jun;46(6):584–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. I., Vidrich A., Sun T. T. Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of the differentiation of skin, corneal and esophageal epithelial cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Winter S., Grund C., Schmid E., Schiller D. L., Jarasch E. D. Isolation and characterization of desmosome-associated tonofilaments from rat intestinal brush border. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):116–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Kapanci Y., Barazzone P., Franke W. W. Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized filaments in human neoplastic cells. A diagnostic aid for the surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol. 1981 Sep;104(3):206–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Abdulaziz Z., Beverley P., Corvalan J. R., Ford C., Lane E. B., Mota M., Nash J. R., Pulford K., Stein H. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the histopathological diagnosis of human malignancy. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1253–1267. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigi O., Geiger B., Eshhar Z., Moll R., Schmid E., Winter S., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Detection of a cytokeratin determinant common to diverse epithelial cells by a broadly cross-reacting monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1429–1437. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to intermediate filament proteins of human cells: unique and cross-reacting antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):414–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer H., Bennett G. S., Tapscott S. J., Croop J. M., Toyama Y. Intermediate-size filaments: changes in synthesis and distribution in cells of the myogenic and neurogenic lineages. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):317–329. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B. Monoclonal antibodies provide specific intramolecular markers for the study of epithelial tonofilament organization. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):665–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Volc-Platzer B., Krepler R. Different keratin polypeptides in epidermis and other epithelia of human skin: a specific cytokeratin of molecular weight 46,000 in epithelia of the pilosebaceous tract and basal cell epitheliomas. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):285–295. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Altmannsberger M., Shaw G., Schauer A., Weber K. Various sympathetic derived human tumors differ in neurofilament expression. Use in diagnosis of neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):141–156. doi: 10.1007/BF02932859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Geisler N., Shaw G., Sharp G., Weber K. Intermediate filaments. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):413–429. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Haag D., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2618–2622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Kant A., Moesker O., Jap P. H., Vooijs G. P. Use of antibodies to intermediate filaments in the characterization of human tumors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):331–339. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., McLeod J. A., Pinkus G. S. Immunoperoxidase localization of keratin in human neoplasms: a preliminary survey. Am J Pathol. 1980 Oct;101(1):41–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Shih C., Green H. Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock-Mitchell J., Eichner R., Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. Immunolocalization of keratin polypeptides in human epidermis using monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):580–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







