Abstract
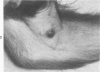
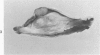
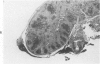
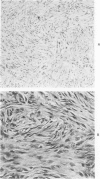
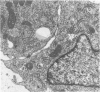
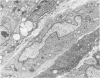
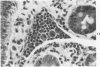
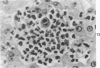
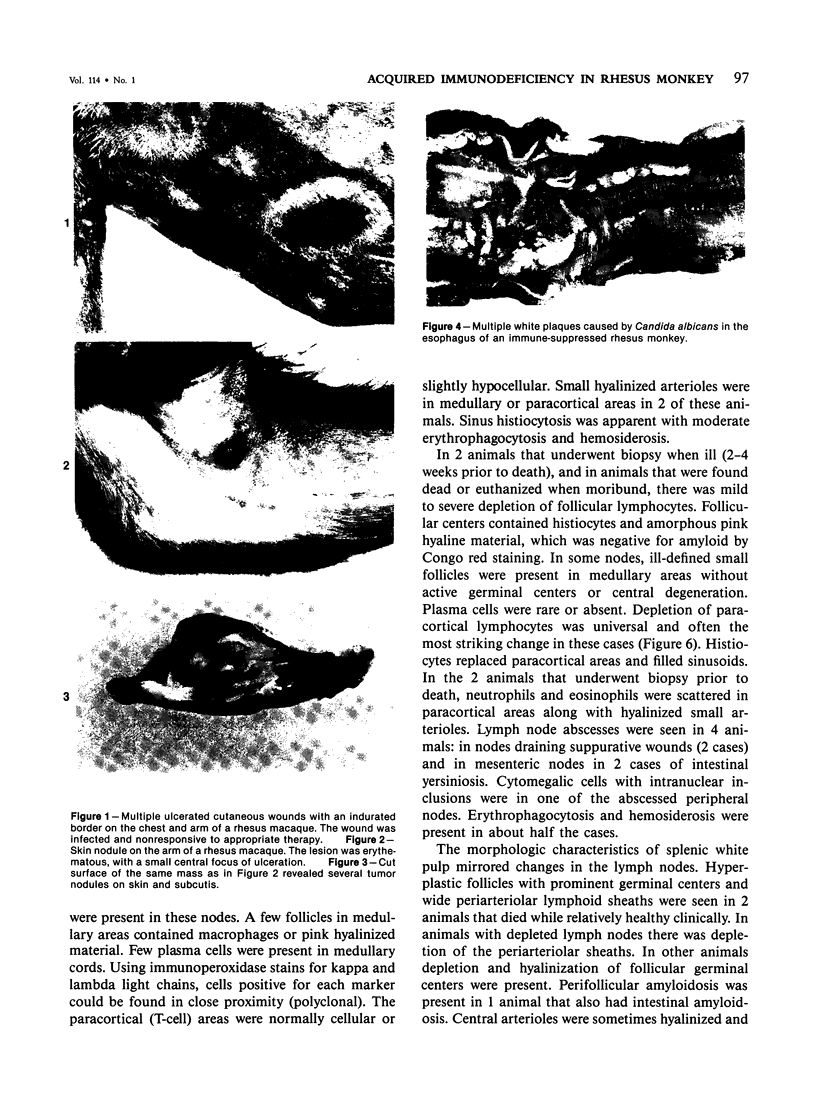
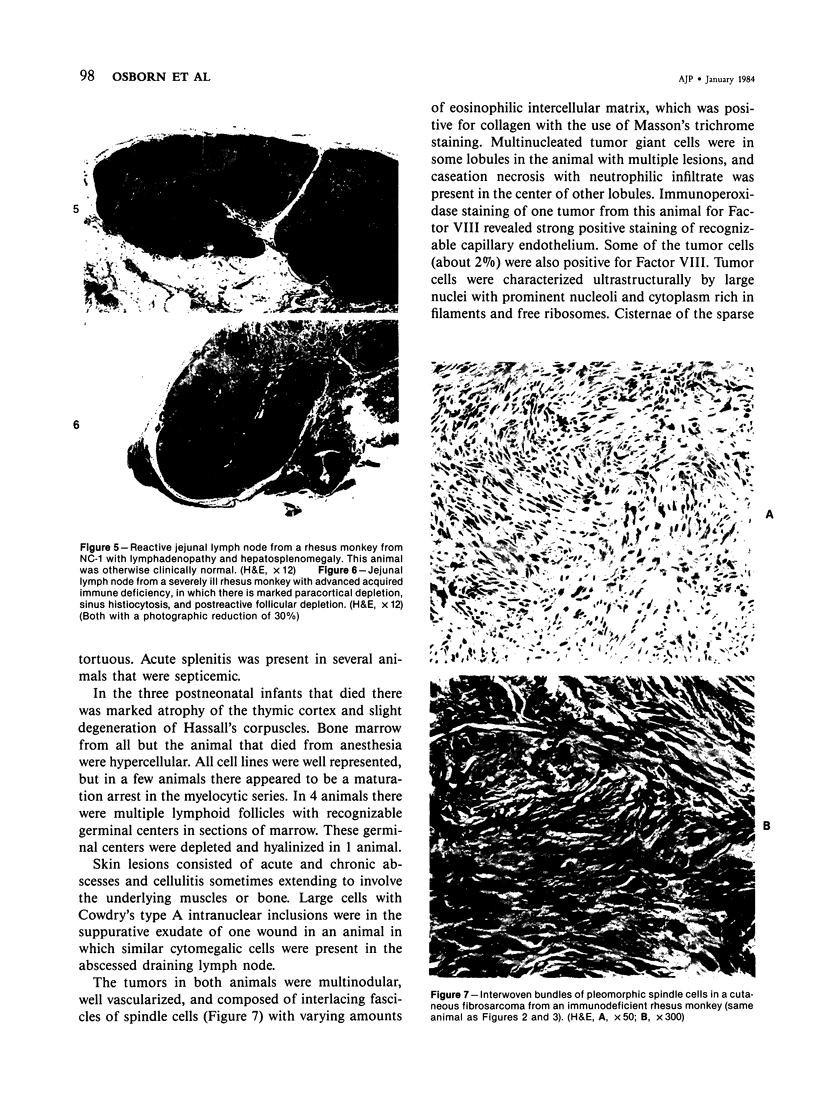
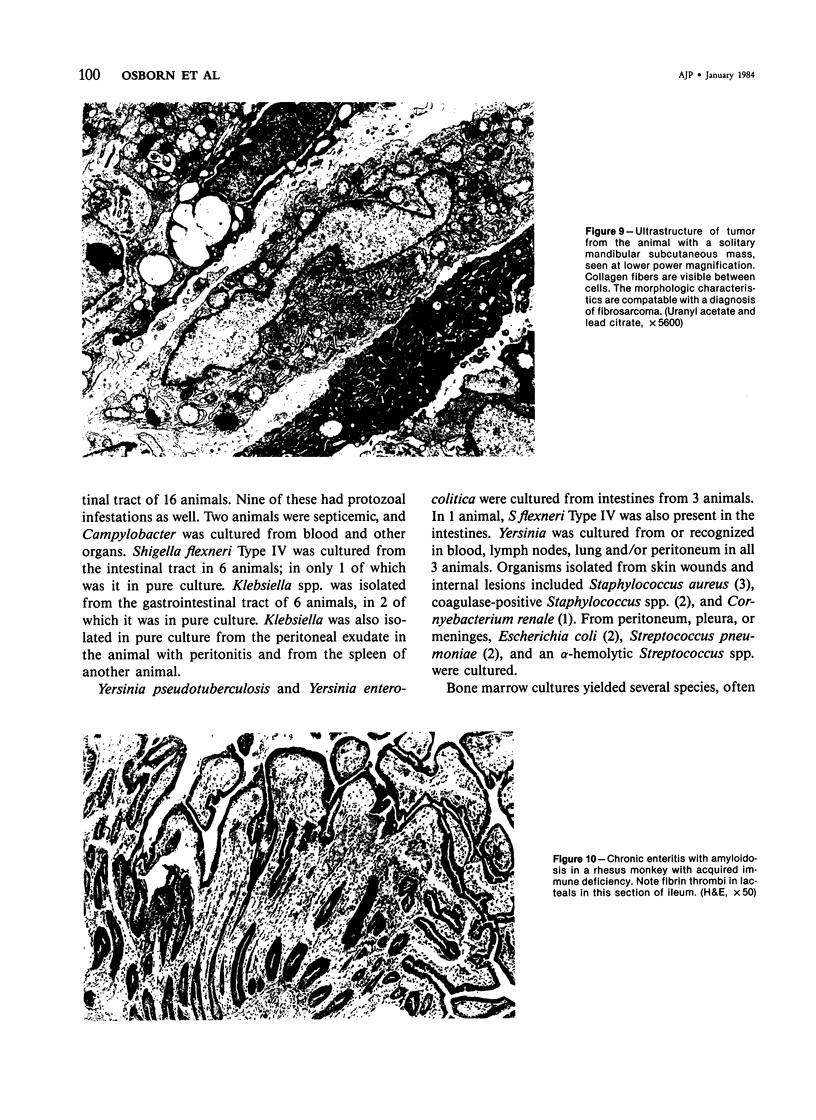
A syndrome of acquired immunodeficiency within a group of outdoor-housed rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) with unusually high mortality has been identified at the California Primate Research Center. The cause of death for most of the affected animals included septicemia and/or chronic diarrhea with wasting, often complicated by other problems. In many cases, multiple or unusual infectious agents were isolated or recognized, including cytomegalovirus, Cryptosporidium spp., and Candida albicans. Septicemias due to usually innocuous agents such as Staphylococcus epidermidis and Alcaligenes faecalis were seen. Two animals developed cutaneous fibrosarcomas. Affected animals had generalized lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly, with depletion of T-cell populations, initially follicular hyperplasia followed by depletion, and absence of plasma cells. This spontaneous disease syndrome in nonhuman primates has similarities to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) in humans, providing an animal model for the study of the complex factors modulating the immune system.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann A. J., Wara D. W. Evaluation of infants and children with recurrent infection. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1975 Sep;5(11):3–47. doi: 10.1016/s0045-9380(75)80005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. J., Jarrett W. F., Jarrett O., Laird H. M. Feline leukemia-virus infection of kittens: mortality associated with atrophy of the thymus and lymphoid depletion. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):807–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell J. A., Frank A. L., Dunnick N. R., Rowe D. S., Conliffe M. A., Parkman P. D., Meyer H. M., Jr Rhesus leukocyte-associated herpesvirus. II. Natural and experimental infection. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):630–637. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson F. L., Martin J. H., Lynn J. A. Formalin fixation for electron microscopy: a re-evaluation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;59(3):365–373. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desforges J. F. AIDS and preventive treatment in hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 13;308(2):94–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301133080209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Nair M., Onoe K., Tanaka T., Floyd R., Good R. A. Impairment of cell-mediated immunity functions by dietary zinc deficiency in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Haas S. M., Luecke R. W. Effect of zinc deficiency on the immune response of the young adult A/J mouse. J Nutr. 1977 Oct;107(10):1889–1895. doi: 10.1093/jn/107.10.1889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank A. L., Bissell J. A., Rowe D. S., Dunnick N. R., Mayner R. E., Hopps H. E., Parkman P. D., Meyer H. M., Jr Rhesus leukocyte-associated herpesvirus. I. Isolation and characterization of a new herpesvirus recovered from rhesus monkey leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(5):618–629. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. J., Ackerman A. B. Kaposi's sarcoma: an extensively disseminated form in young homosexual men. Hum Pathol. 1982 Oct;13(10):882–892. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrickson R. V., Maul D. H., Osborn K. G., Sever J. L., Madden D. L., Ellingsworth L. R., Anderson J. H., Lowenstine L. J., Gardner M. B. Epidemic of acquired immunodeficiency in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1983 Feb 19;1(8321):388–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91503-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;75(5):734–738. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.5.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesan V., Rukmini C., Vijayaraghavan M., Tulpule P. G. Immune studies with T-2 toxin: effect of feeding and withdrawal in monkeys. Food Chem Toxicol. 1982 Feb;20(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(82)80014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr G. R., Allen J. R., Scheffler G., Couture J. Fetal and postnatal growth of rhesus monkeys (M. mulatta). J Med Primatol. 1974;3(4):221–235. doi: 10.1159/000460008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J. A., Tyler W. S. Scanning electron microscopy of the surface morphology of mammalian lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Mar;103(3):313–328. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilen G. H., Gould D., Fowler M., Dungworth D. L. C-type virus in tumor tissue of a woolly monkey (Lagothrix spp.) with fibrosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):881–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Frank E., Spira T. J., Landesman S. H. Acquired immune deficiency in Haitians: opportunistic infections in previously healthy Haitian immigrants. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):125–129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]