Abstract
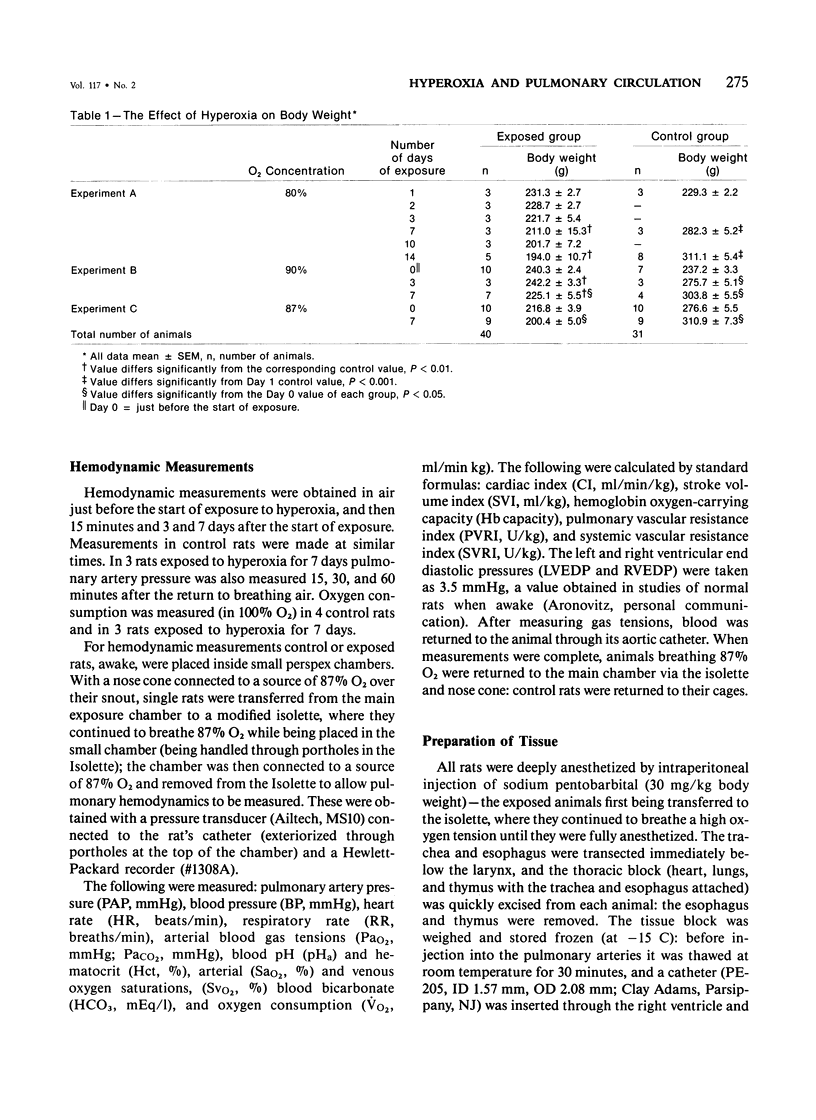
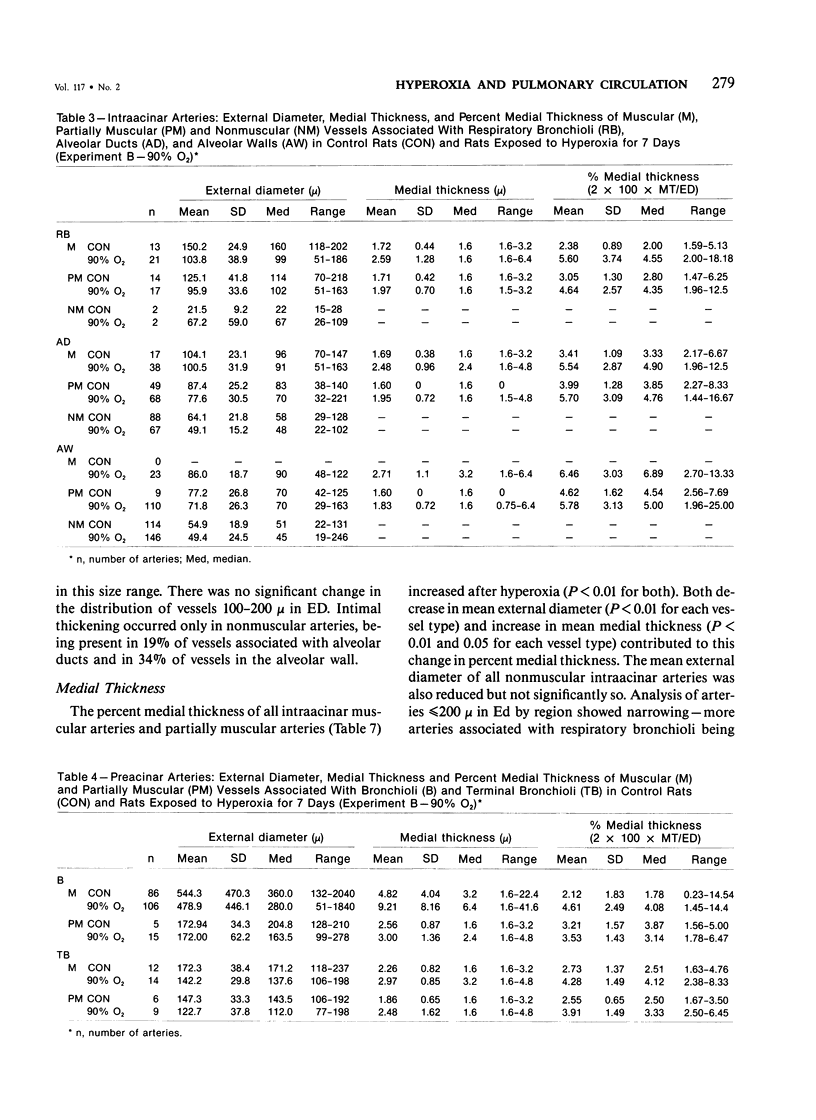
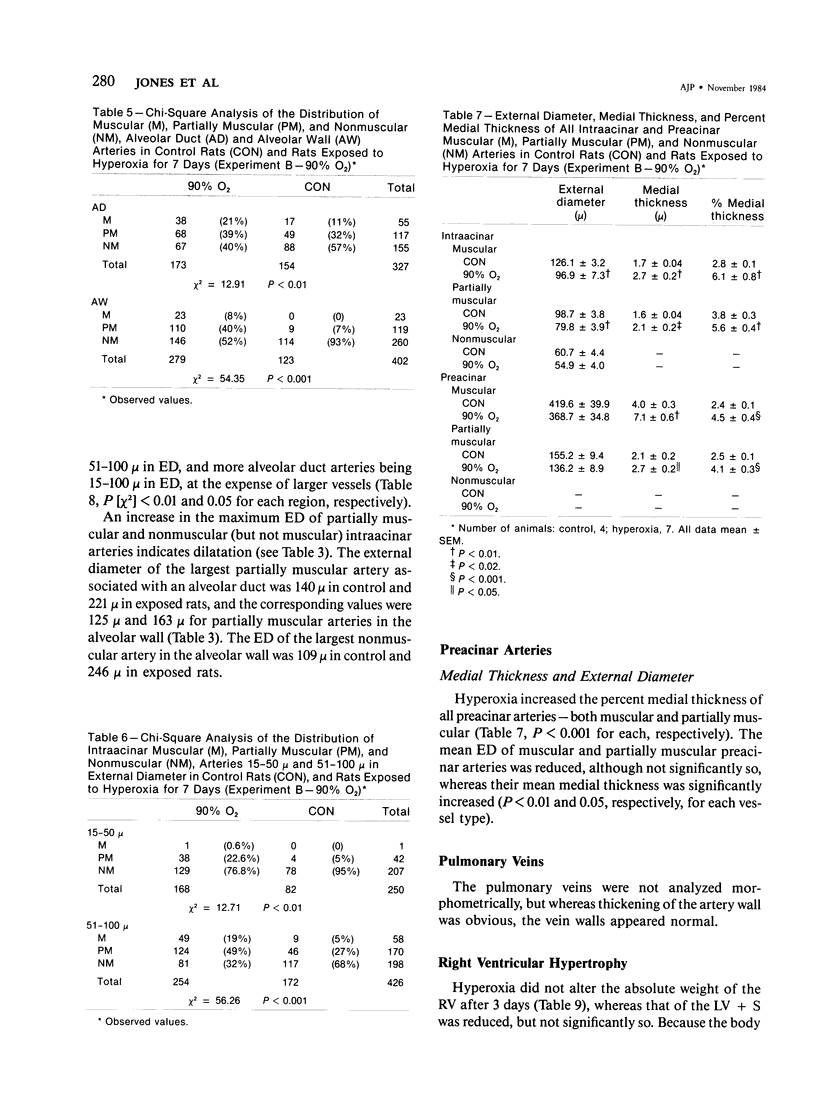
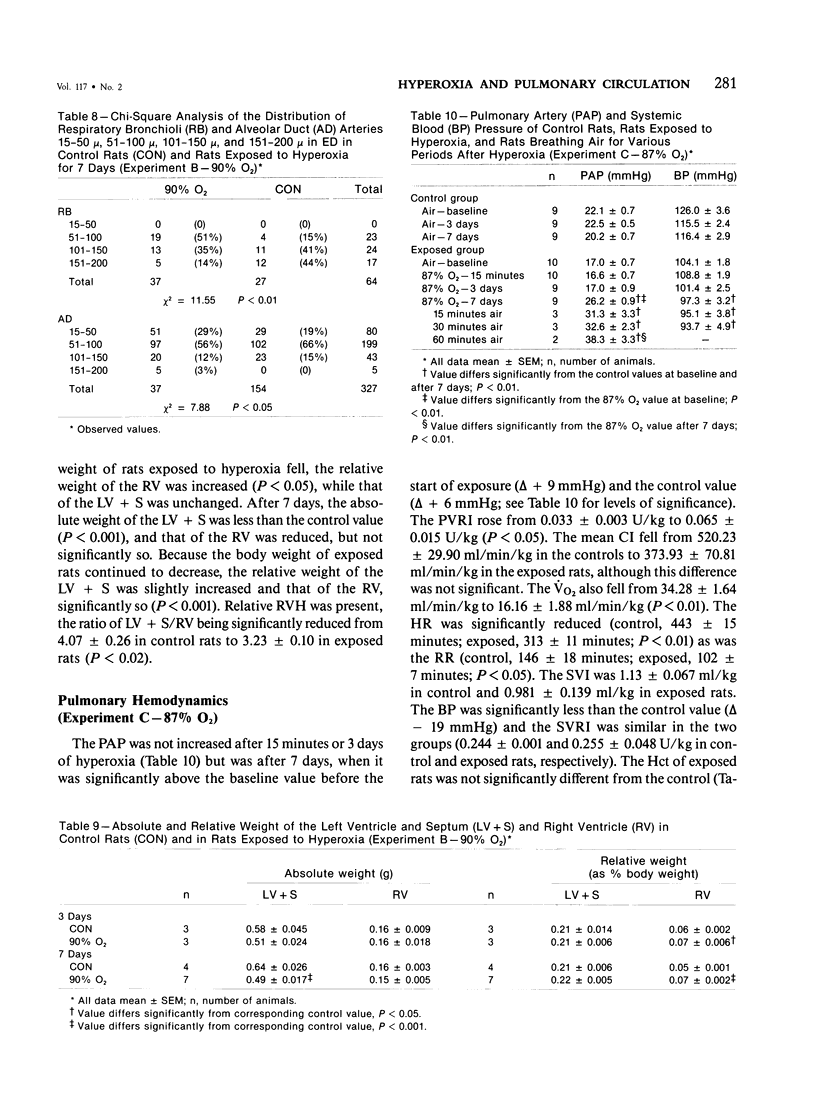
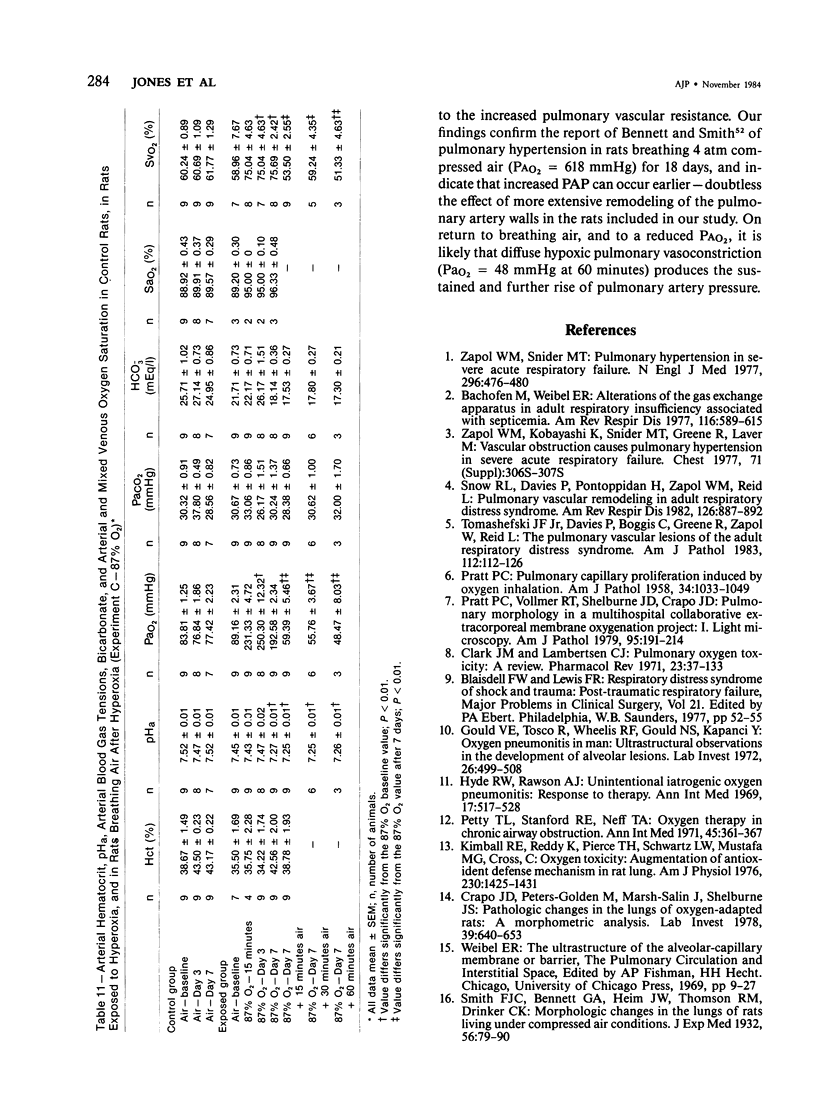
This study shows by morphometric and hemodynamic techniques that exposure to hyperoxia at normobaric pressure causes rapid structural remodeling of rat pulmonary arteries and pulmonary hypertension. After 7 days of 90% O2, pulmonary artery cross-sectional area is reduced by a striking loss of intraacinar arteries (control, 13 +/- 1 sq mm; exposed, 8 +/- 1 sq mm; P less than 0.001), the ratio of arteries to alveoli being 4:100 in control rats and 2.5:100 after hyperoxia. The lumen of preacinar and intraacinar arteries is narrowed by a reduction of vessel external diameter (ED) and an increased medial wall thickness (MT). There is a significant reduction in the percent medial thickness [( 2 X 100 X MT]/ED) in both regions. The proportion of muscular and partially muscular intraacinar arteries increases at the expense of nonmuscular ones (P [chi 2] less than 0.01), and fully muscular arteries appear in the alveolar wall where they are not normally found. Intimal thickening occurs in 19% of alveolar duct and 34% of alveolar wall nonmuscular arteries. Right ventricular hypertrophy occurs, the ratio of the left ventricle plus the septum to the right ventricle being significantly reduced (control, 4.07 +/- 0.26; exposed, 3.23 +/- 0.10; P less than 0.02). After 3 days of 87% O2, pulmonary artery pressure is still normal (17.0 +/- 0.9 mmHg) but after 7 days it is significantly increased (26.2 +/- 0.9 mmHg; P less than 0.01), as is pulmonary vascular resistance (control, 0.033 +/- 0.003; exposed, 0.065 +/- 0.015 U/kg; P less than 0.05). Return to air breathing (after 7 days at 87% O2) causes pulmonary vasoconstriction and a further rise of the pulmonary artery pressure (to 38.3 +/- 3.3 mmHg after 60 minutes).
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):589–615. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooksby G. A., Dennis R. L., Datnow B., Clark D. Experimental emphysema. Histologic changes and alterations in pulmonary circulation. Calif Med. 1967 Nov;107(5):391–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büsing C. M., Bleyl U. Oxygen induced pulmonary hyaline membranes (PHM) and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974;363(2):113–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01201314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Lambertsen C. J. Pulmonary oxygen toxicity: a review. Pharmacol Rev. 1971 Jun;23(2):37–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. B. Potential adverse effects of lung macrophages and neutrophils. Fed Proc. 1979 Nov;38(12):2644–2647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Moskowitz M. A., Antoniades H. N., Levine L. Serotonin receptor-mediated stimulation of bovine smooth muscle cell prostacyclin synthesis and its modulation by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7134–7138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Barry B. E., Foscue H. A., Shelburne J. Structural and biochemical changes in rat lungs occurring during exposures to lethal and adaptive doses of oxygen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jul;122(1):123–143. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Peters-Golden M., Marsh-Salin J., Shelburne J. S. Pathologic changes in the lungs of oxygen-adapted rats: a morphometric analysis. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):640–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Tierney D. F. Superoxide dismutase and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON R. M., HUTCHINSON E. C., JONES A. M. Ventricular weight in cardiac hypertrophy. Br Heart J. 1952 Jul;14(3):413–420. doi: 10.1136/hrt.14.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. B., Hoidal J. R., Brown D. M., Repine J. E. Pulmonary inflammation due to oxygen toxicity: involvement of chemotactic factors and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 May;123(5):521–523. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.5.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):412–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Tosco R., Wheelis R. F., Gould N. S., Kapanci Y. Oxygen pneumonitis in man. Ultrastructural observations on the development of alveolar lesions. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Karnovsky M. J. Smooth muscle cell proliferation in the occluded rat carotid artery: lack of requirement for luminal platelets. Am J Pathol. 1979 Mar;94(3):585–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde R. W., Rawson A. J. Unintentional iatrogenic oxygen pneumonitis--response to therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Sep;71(3):517–531. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Zapol W. M., Reid L. Pulmonary arterial wall injury and remodelling by hyperoxia. Chest. 1983 May;83(5 Suppl):40S–42S. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.5_supplement.40s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball R. E., Reddy K., Peirce T. H., Schwartz L. W., Mustafa M. G., Cross C. E. Oxygen toxicity: augmentation of antioxidant defense mechanisms in rat lung. Am J Physiol. 1976 May;230(5):1425–1431. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.5.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kydd G. H. Lung changes resulting from prolonged exposure to 100 per cent oxygen at 550 mm. Hg. Aerosp Med. 1967 Sep;38(9):918–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb D. Rat lung pathology and quality of laboratory animals: the user's view. Lab Anim. 1975 Jan;9(1):1–8. doi: 10.1258/002367775780994781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. A macrophage-dependent factor that stimulates the proliferation of fibroblasts in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1976 Sep;84(3):501–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. The effect of continued hypoxia on rat pulmonary arterial circulation. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):188–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Ultrastructural features of the distended pulmonary arteries of the normal rat. Anat Rec. 1979 Jan;193(1):71–97. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091930106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. J. An elastin stain. Med Lab Technol. 1971 Apr;28(2):148–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRATT P. C. Pulmonary capillary proliferation induced by oxygen inhalation. Am J Pathol. 1958 Nov-Dec;34(6):1033–1049. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Stanford R. E., Neff T. A. Continuous oxygen therapy in chronic airway obstruction. Observations on possible oxygen toxicity and survival. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Sep;75(3):361–367. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt P. C., Vollmer R. T., Shelburne J. D., Crapo J. D. Pulmonary morphology in a multihospital collaborative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation project. I. Light microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1979 Apr;95(1):191–214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner F., Felig P., Trachtenberg E. Structure of rat lung after protracted oxygen breathing. Arch Pathol. 1967 Jan;83(1):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. L., Davies P., Pontoppidan H., Zapol W. M., Reid L. Pulmonary vascular remodeling in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):887–892. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. G., Kilo C., Williamson J. R., Murch D. W. Differences in pericyte contractile function in rat cardiac and skeletal muscle microvasculatures. Microvasc Res. 1979 Nov;18(3):336–352. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(79)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomashefski J. F., Jr, Davies P., Boggis C., Greene R., Zapol W. M., Reid L. M. The pulmonary vascular lesions of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jul;112(1):112–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapol W. M., Snider M. T. Pulmonary hypertension in severe acute respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 3;296(9):476–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703032960903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]