Abstract
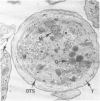
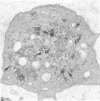
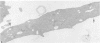
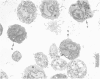
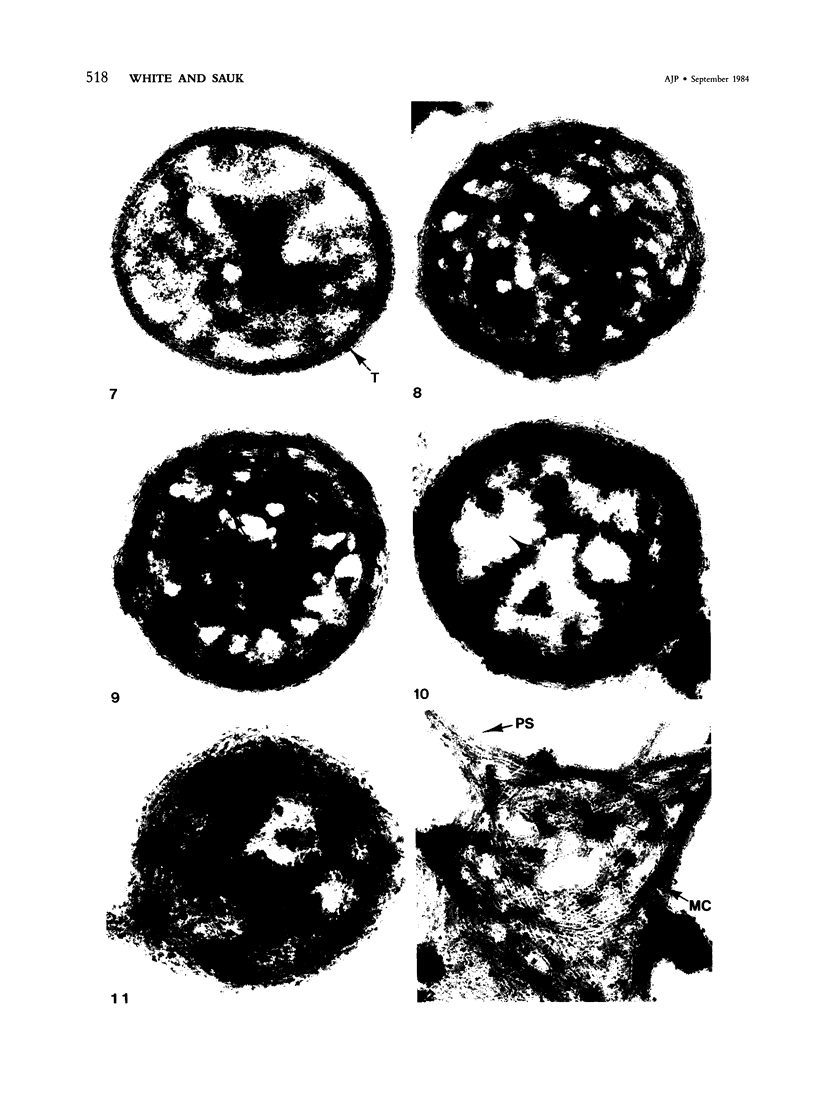
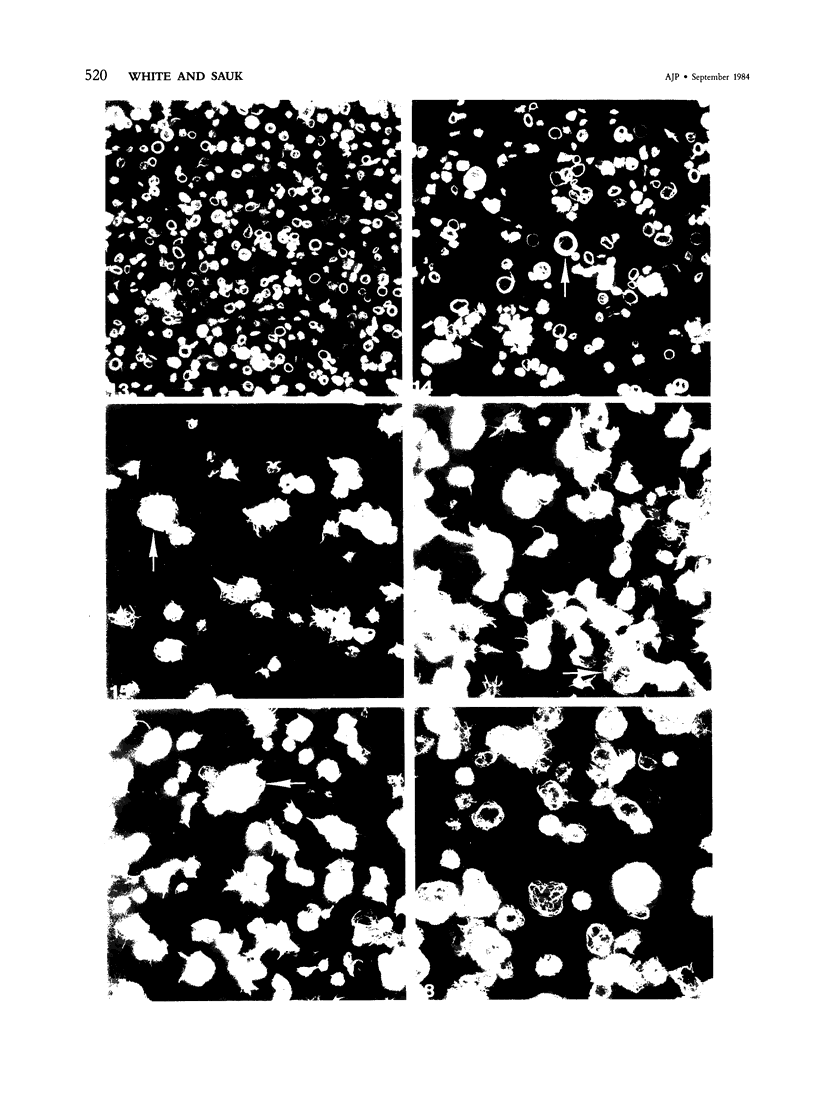
Normal human platelets are characteristically discoid in shape. The lentiform appearance is supported by a circumferential band of microtubules lying just under the cell membrane along its greatest circumference. Some of the cells from patients with giant platelet disorders are also disk-shaped, but the majority of their huge platelets are spherical. In the present study platelets from patients with the Gray platelet syndrome (GPS), May-Hegglin anomaly (MHA), and Epstein's syndrome (ES) were examined in thin sections and negatively stained whole mounts, and by indirect immunofluorescence with a monoclonal antibody to tubulin for determination of the organization of their microtubule systems. Many GPS platelets and some ES and MHA platelets were discoid and contained circumferential bundles of microtubules. The number of coils in the band was increased 10-20-fold. Giant spherical platelets also contained increased numbers of individual microtubules and coils, but they were not organized into circumferential bundles. Immunofluorescence revealed an organization of assembled tubulin in the huge cells, suggestive of balls of yarn. Failure of the microtubules to organize into a circumferential band may explain why the majority of the huge cells have a spherical form.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behnke O. An electron microscope study of the rat megacaryocyte. II. Some aspects of platelet release and microtubules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Microtubules in disk-shaped blood cells. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1970;9:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Zelander T. Substructure in negatively stained microtubules of mammalian blood platelets. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Aug;43(1):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90401-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis M., Breton-Gorius J. Les microtubules et les fibrilles dans les plaquettes étalées. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1965 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. The cytoskeleton of blood platelets viewed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Sahud M. A., Piel C. F., Goodman J. R., Bernfield M. R., Kushner J. H., Ablin A. R. Hereditary macrothrombocytopathia, nephritis and deafness. Am J Med. 1972 Mar;52(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin H. A., Ginsburg A. D. May-Hegglin anomaly: a defect in megakaryocyte fragmentation? Br J Haematol. 1974 Jan;26(1):117–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. W., Shaikh B. S., Ottie J. N., Storch A. E., Saleem A., White J. G. Platelet function, ultrastructure, and survival in the May-Hegglin anomaly. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Nov;74(5):663–668. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.5.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon G. B., Taylor D. A. Microtubules in hamster platelets. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):673–676. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund A. S., Karlsson R., Arro E., Fredriksson B. A., Lindberg U. Visualization of the peripheral weave of microfilaments in glia cells. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Jun;1(2):127–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00711795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leven R. M., Nachmias V. T. Cultured megakaryocytes: changes in the cytoskeleton after ADP-induced spreading. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):313–323. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusher J. M., Schneider J., Mizukami I., Evans R. K. The May-Hegglin anomaly: platelet function, ultrastructure and chromosome studies. Blood. 1968 Dec;32(6):950–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Cytoskeleton of human platelets at rest and after spreading. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Dupuis D., Kunicki T. J., Caen J. P. Analysis of the glycoprotein and protein composition of Bernard-Soulier platelets by single and two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1431–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI110172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penington D. G., Streatfield K., Roxburgh A. E. Megakaryocytes and the heterogeneity of circulating platelets. Br J Haematol. 1976 Dec;34(4):639–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raccuglia G. Gray platelet syndrome. A variety of qualitative platelet disorder. Am J Med. 1971 Dec;51(6):818–828. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90311-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scurfield G., Radley J. M. Aspects of platelet formation and release. Am J Hematol. 1981;10(3):285–296. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V. Organization of actin in the leading edge of cultured cells: influence of osmium tetroxide and dehydration on the ultrastructure of actin meshworks. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):695–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Effects of colchicine and Vinca alkaloids on human platelets. I. Influence on platelet microtubules and contractile function. Am J Pathol. 1968 Aug;53(2):281–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. The ultrastructure of defective human platelets. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Nov 1;21(2):109–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00240281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Krivit W. An ultrastructural basis for the shape changes induced in platelets by chilling. Blood. 1967 Nov;30(5):625–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Ultrastructural studies of the gray platelet syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):445–462. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]