Abstract
Based on the finding that Langerhans cells and histiocytosis X cells react with the monoclonal antibody OKT6, raised against a subset of thymocytes, we used this antibody to study the cells collected by bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from 131 patients, including 18 with pulmonary histiocytosis X, 43 with pulmonary sarcoidosis, 67 with miscellaneous pulmonary disorders, and 3 controls. Immunofluorescence studies demonstrated the presence of OKT6-reactive cells in all patients with pulmonary histiocytosis X (mean +/- SEM, 5.29% +/- 1.14% of all cells in BAL fluid). Immunoelectron microscopic studies revealed that the cells labeled in these patients (n = 13) contained Langerhans granules. The number of fluorescent cells in the other 113 patients was significantly smaller (mean +/- SEM, 0.20% +/- 0.04% of all cells; P less than 0.001). In the 3 control patients, in the 43 patients with sarcoidosis, and in 61 of the 67 patients with miscellaneous disorders unrelated to histiocytosis X, no cells or less than 1% of the total were labeled; however, in the 6 remaining patients in this miscellaneous group, 1.3 to 2.8% of all cells in BAL were labeled. In 3 of these 6 patients, immunoelectronmicroscopic examination showed that the cells labeled by OKT6 had the general characteristics of Langerhans cells but lacked Langerhans granules. OKT3, OKT4, and OKT8 monoclonal antibodies did not stain histiocytosis X cells in BAL fluid.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset F., Corrin B., Spencer H., Lacronique J., Roth C., Soler P., Battesti J. P., Georges R., Chrétien J. Pulmonary histiocytosis X. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):811–820. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Soler P., Jaurand M. C., Bignon J. Ultrastructural examination of broncho-alveolar lavage for diagnosis of pulmonary histiocytosis X: Preliminary report on 4 cases. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):303–306. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Soler P., Wyllie L., Abelanet R., Le Charpentier M., Kreis B., Breathnach A. S. Langerhans cells in a bronchiolar-alveolar tumour of lung. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974;362(4):315–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00427080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset F., Soler P., Wyllie L., Mazin F., Turiaf J. Langerhans' cells and lung interstitium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;278:599–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Poppema S., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Location of T cell and major histocompatibility complex antigens in the human thymus. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):771–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach A. S. The cell of Langerhans. Int Rev Cytol. 1965;18:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60550-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet S., Dournovo P., Richard M. S., Soler P., Basset F. Reactivity of histiocytosis X cells with monoclonal anti-T6 antibody. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):685–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubertret L., Breton-Gorius J., Fosse M., Touraine R. Peroxidatic activity in endoplasmic reticulum of normal human Langerhans cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Oct;30(4):313–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Inflammatory and immune processes in the human lung in health and disease: evaluation by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):149–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanami O., Basset F., Ferrans V. J., Soler P., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary Langerhans' cells in patients with fibrotic lung disorders. Lab Invest. 1981 Mar;44(3):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Davis G. S., Giancola M. S. Biochemical analyses of bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of healthy human volunteer smokers and nonsmokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Nov;118(5):863–875. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.5.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Uda H., Yokoyama M. Localization of non-specific esterase and endogenous peroxidase in the murine epidermal Langerhans' cells. Br J Dermatol. 1980 Jul;103(1):61–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1980.tb15838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Sato S., Harrist T. J., Mihm M. C., Jr Characterization of Langerhans cells by the use of monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1981 Nov;45(5):465–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Bhan A. K., Sato S., Mihm M. C., Jr, Harrist T. J. A new immunologic marker for human Langerhans cells. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 26;304(13):791–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103263041320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
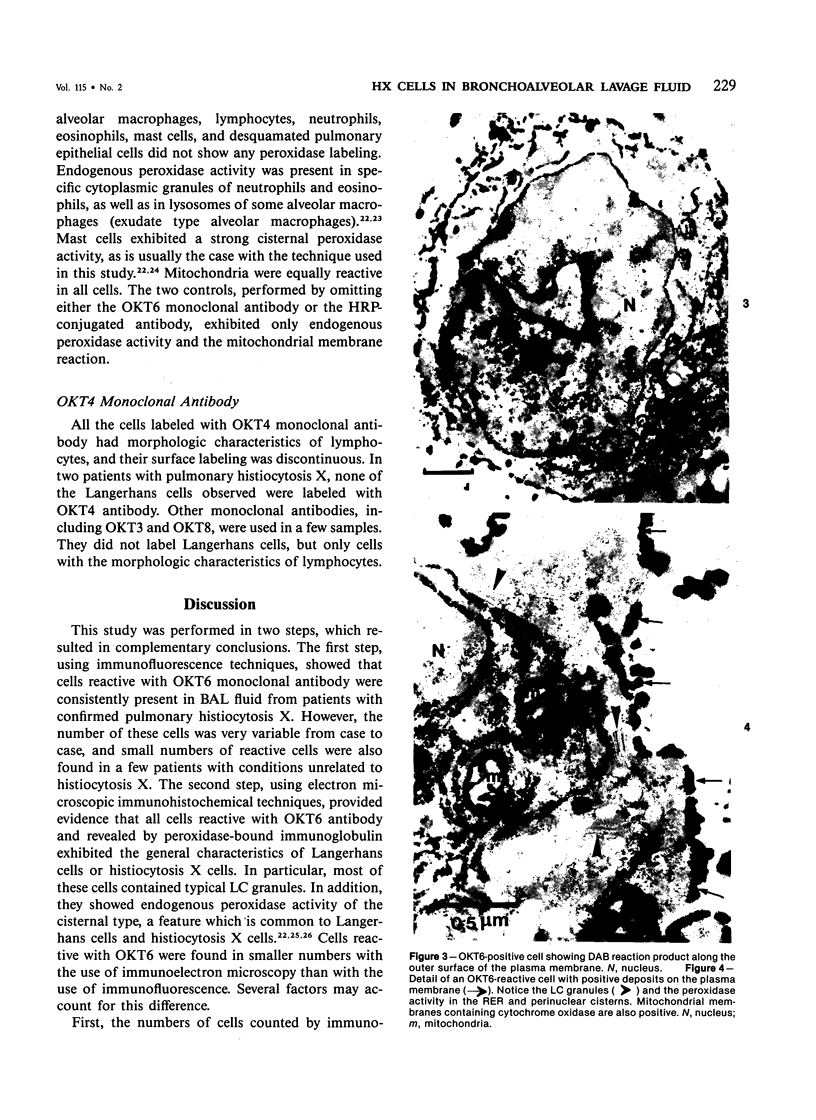
- Murphy G. F., Harrist T. J., Bhan A. K., Mihm M. C., Jr Distribution of cell surface antigens in histiocytosis X cells. Quantitative immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):90–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disease characterized and perpetuated by activated lung T-lymphocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):73–94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Current concepts in immunology: Regulation of the immune response--inducer and suppressor T-lymphocyte subsets in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):370–373. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Kazmierowski J. A., Roberts W. C., Frank M. M., Crystal R. G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D., Fahimi H. D., Cotran R. S. Fine structural cytochemical localization of peroxidase activity in rat peritoneal cells: mononuclear cells, eosinophils and mast cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1971 Sep;19(9):571–575. doi: 10.1177/19.9.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roels F., Wisse E., De Prest B., van der Meulen J. Cytochemical discrimination between catalases and peroxidases using diaminobenzidine. Histochemistry. 1975;41(4):281–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00490073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G. The Langerhans cell. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(2):95–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler P., Basset F., Mazin F., Grandsaigne M., Breton-Gorius J. Peroxidatic activities of human alveolar macrophages in some pulmonary granulomatous disorders. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Jun;31(6):511–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon M. L., Fountain L., Krebs H. M., Horta-Barbosa L., Fuccillo D. A., Sever J. L. Birbeck granules (Langerhans' cell granules) in human lymph nodes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Dec;60(6):771–779. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.6.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K. The langerhans cell. Curr Probl Dermatol. 1972;4:79–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager H., Jr, Zimmet S. M., Schwartz S. L. Pinocytosis by human alveolar macrophages. Comparison of smokers and nonsmokers. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):247–251. doi: 10.1172/JCI107759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]