Abstract
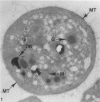
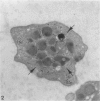
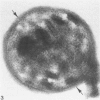
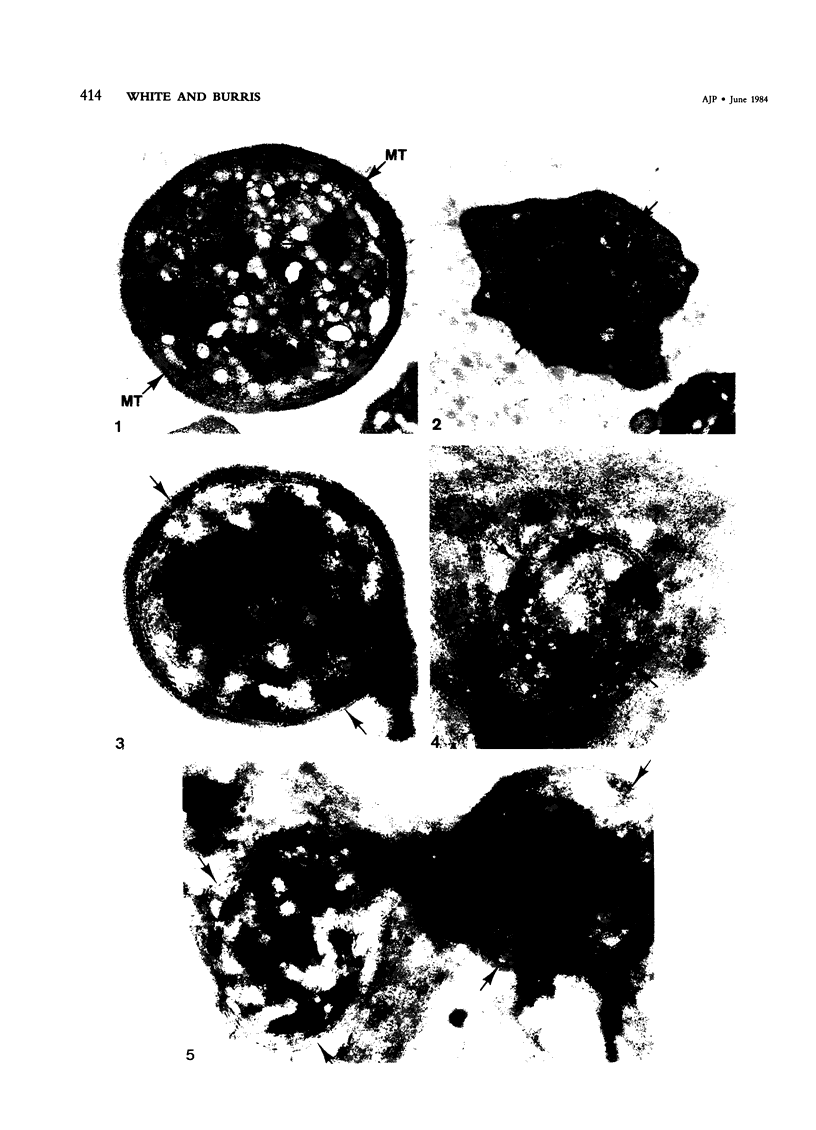
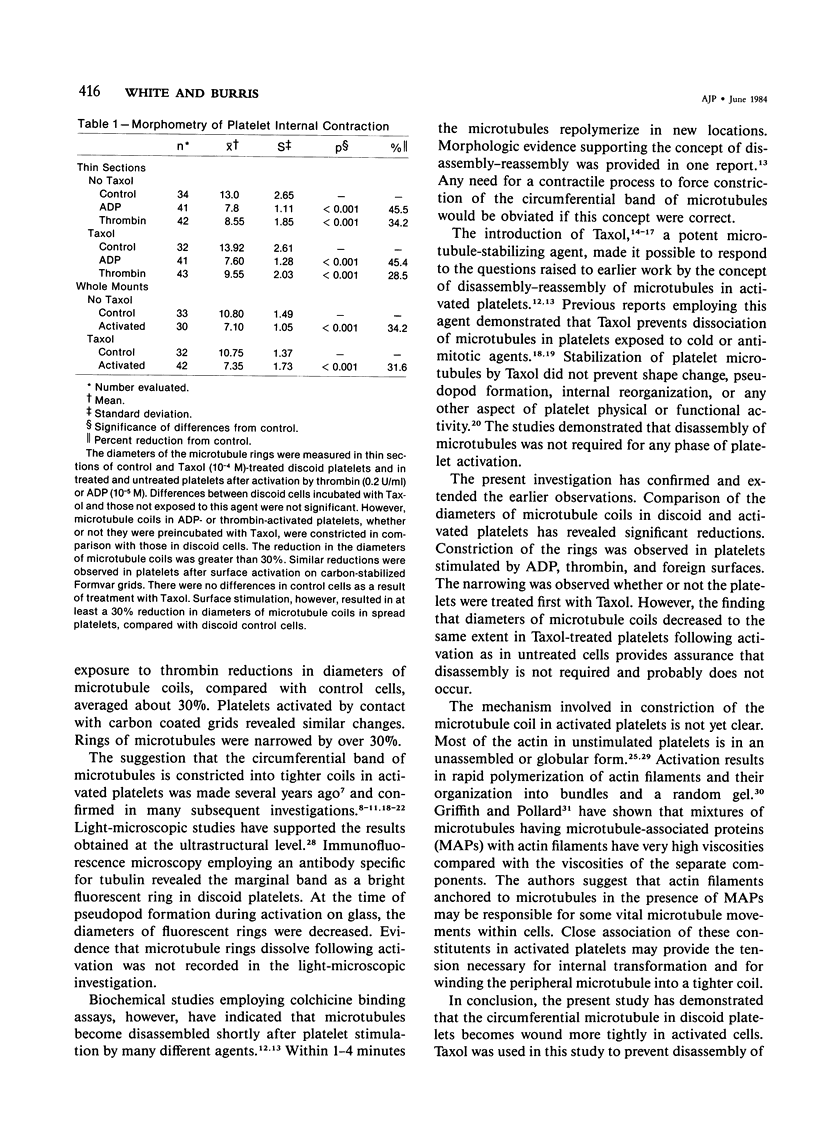
Blood platelets have a characteristic discoid shape supported by a circumferential band of microtubules. Following stimulation by aggregating agents or foreign surfaces, platelets lose their discoid form, extend pseudopods, and undergo a process of internal reorganization. Randomly dispersed cytoplasmic organelles become concentrated in cell centers within rings of microtubules and masses of microfilaments. Questions have been raised about this process and its contractile nature by studies demonstrating that platelet microtubules dissolve within seconds after activation and reassemble several minutes later in new locations. Earlier investigations showed that Taxol, a microtubule-stabilizing agent, did not inhibit platelet shape change, internal transformation, secretion, aggregation, or clot retraction. In the present study the diameters of microtubule coils in discoid platelets treated or not treated with Taxol and in platelets activated by thrombin, ADP, and a foreign surface were measured. The results of the study reveal no significant differences in diameters of microtuble rings in control or Taxol-treated cells. However, after activation by ADP, thrombin, or the grid surface, the diameter of coiled microtubules decreased by 30% or more. The results support the concept that internal transformation is a contractile event.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antin P. B., Forry-Schaudies S., Friedman T. M., Tapscott S. J., Holtzer H. Taxol induces postmitotic myoblasts to assemble interdigitating microtubule-myosin arrays that exclude actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):300–308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Further studies on microtubules. A marginal bundle in human and rat thrombocytes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Dec;13(5):469–477. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O. Microtubules in disk-shaped blood cells. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1970;9:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis M., Breton-Gorius J. Les microtubules et les fibrilles dans les plaquettes étalées. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1965 Jul-Aug;5(4):657–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Zucker M. B. Changes in platelet volume produced by temperature, metabolic inhibitors, and aggregating agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Nov;120(2):296–301. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson C. C., White J. G. Platelet interaction with bacteria. I. Reaction phases and effects of inhibitors. Am J Pathol. 1971 Nov;65(2):367–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Brabander M., Geuens G., Nuydens R., Willebrords R., De Mey J. Taxol induces the assembly of free microtubules in living cells and blocks the organizing capacity of the centrosomes and kinetochores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5608–5612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. The cytoskeleton of blood platelets viewed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;24(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., Phillips D. R., Rao G. H., Plow E. F., Walz D. A., Ross R., Harker L. A., White J. G. Biochemical studies of two patients with the gray platelet syndrome. Selective deficiency of platelet alpha granules. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI109823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnella P. A., Nachmias V. T. Platelet activation and microfilament bundling. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):146–151. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith L. M., Pollard T. D. Evidence for actin filament-microtubule interaction mediated by microtubule-associated proteins. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):958–965. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon G. B., Taylor D. A. Microtubules in hamster platelets. J Cell Biol. 1965 Aug;26(2):673–676. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney D. M., Chao F. C. Ionophore-induced disassembly of blood platelet microtubules: effect of cyclic AMP and indomethacin. J Cell Physiol. 1980 May;103(2):289–298. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., White M. S., Prater T., Taylor R. G., Davis K. S. Ultrastructural analysis of platelets in nonhuman primates. III. Stereo microscopy of microtubules during platelet adhesion and the release reaction. Exp Mol Pathol. 1982 Dec;37(3):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(82)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson J. C., Zuiches C. A. Elucidation of the platelet cytoskeleton. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Cytoskeleton of human platelets at rest and after spreading. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T., Sullender J., Fallon J., Asch A. Observations on the "cytoskeleton" of human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1980 Feb 29;42(5):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Horwitz S. B. Taxol stabilizes microtubules in mouse fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V. Organization of actin in the leading edge of cultured cells: influence of osmium tetroxide and dehydration on the ultrastructure of actin meshworks. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):695–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner M., Ikeda Y. Quantitative assessment of polymerized and depolymerized platelet microtubules. Changes caused by aggregating agents. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):443–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI109321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Gerrard J. M. Interaction of microtubules and microfilaments in platelet contractile physiology. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol. 1979;9:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Influence of taxol on the response of platelets to chilling. Am J Pathol. 1982 Aug;108(2):184–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H. Effects of a microtubule stabilizing agent on the response of platelets to vincristine. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):474–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Rao G. H. Influence of a microtubule stabilizing agent on platelet structural physiology. Am J Pathol. 1983 Aug;112(2):207–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]