Abstract
The migration of bronchoalveolar macrophages ( BAMs ) into hilar lymph nodes ( HLNs ) was investigated in order to assess their potential importance in pulmonary immune responses. 51Chromium- or 111Indium-labeled broncholaveolar cells ( BACs ) or purified BAMs were inoculated into the tracheas of syngeneic guinea pigs, and the number of cells that reached HLN at 24-72 hours was estimated by 1) measuring the cell-associated radioactivity in HLN and 2) counting the radiolabeled cells in autoradiographic preparations. It was determined that 400-2900 BAM/10(7) inoculated BACs or BAMs reached the HLNs within a 3-day period. From this data, it was calculated that in a normal animal as many as 8700 BAMs might reach HLNs daily. These migratory phagocytes are potentially important in facilitating the systemic spread of macrophage-resistant intracellular organisms from the lung. Furthermore, following phagocytosis and killing of microorganisms in the alveolus, BAMs might migrate to HLNs and present antigen to stimulate a primary immune response.
Full text
PDF




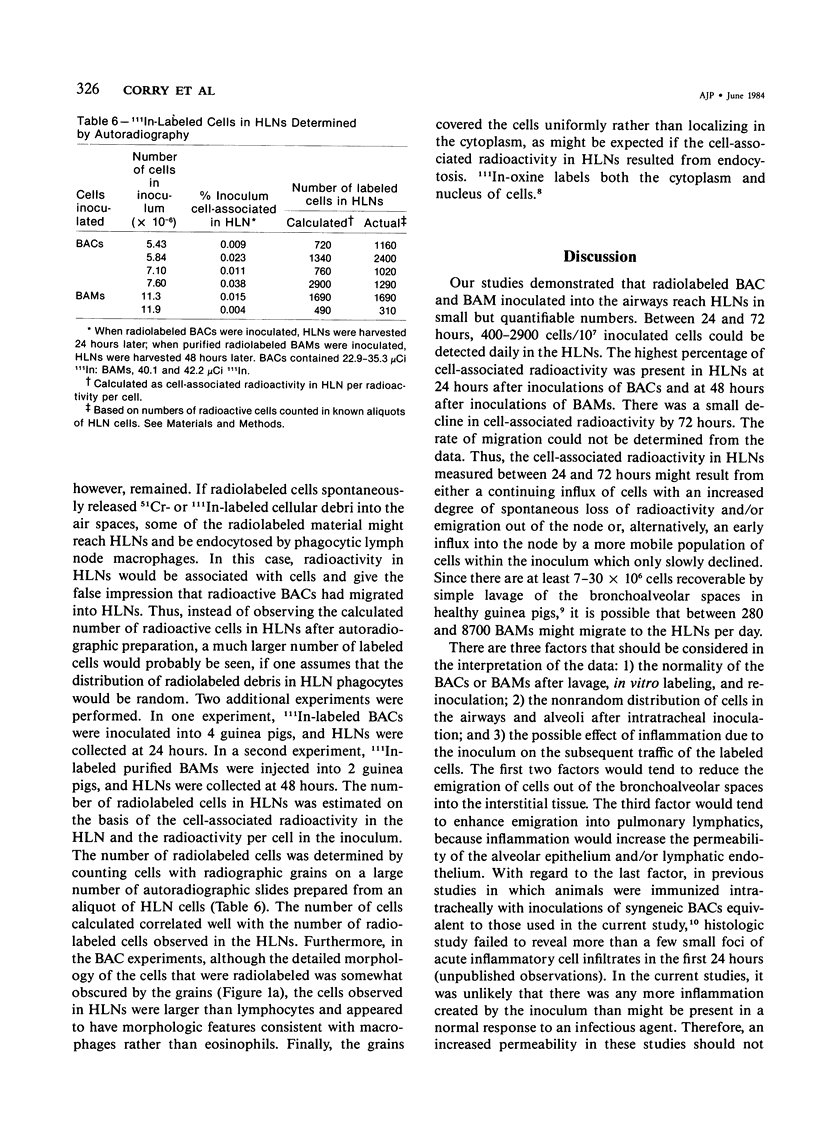
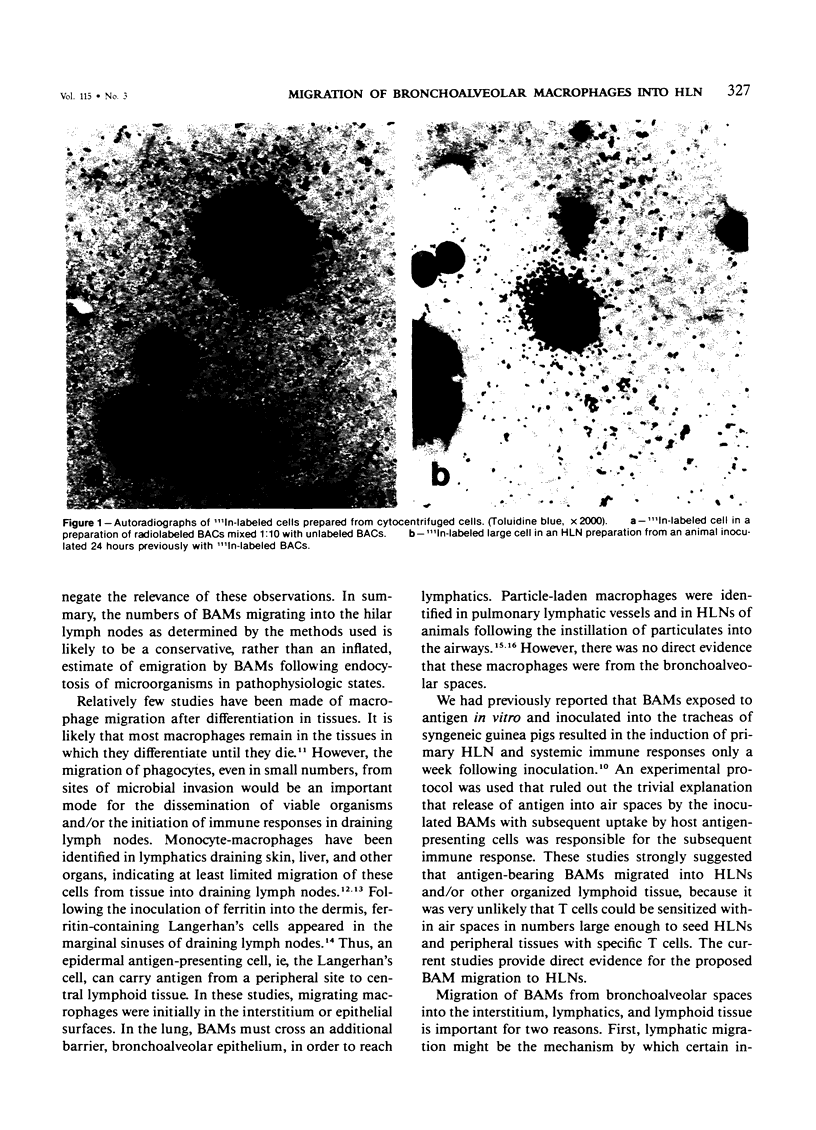

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Role of monocytes and interstitial cells in the generation of alveolar macrophages II. Kinetic studies after carbon loading. Lab Invest. 1980 May;42(5):518–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The structure and function of monocytes and macrophages. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:163–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60443-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. H., 2nd, Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Kuhn C., 3rd 111Indium-labeled human alveolar macrophages and monocytes: function and ultrastructure. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(2):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenberg D. J., Daniele R. P. Characterization of immunocompetent cells recovered from the respiratory tract and tracheobronchial lymph node of normal guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Dec;114(6):1099–1105. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.6.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M. Alveolobronchiolar transport mechanisms. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Jan;131(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. The disposal of inhaled particulate matter; a unifying hypothesis. Am J Pathol. 1963 Feb;42:119–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Balfour B. M., Armstrong J. A., Griffiths S. Functional anatomy of lymph nodes. II. Peripheral lymph-borne mononuclear cells. Anat Rec. 1978 Jan;190(1):5–21. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Toews G. B., Lyons C. R., Uhr J. W. Antigen presentation by guinea pig alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons C. R., Lipscomb M. F. Alveolar macrophages in pulmonary immune responses. I. Role in the initiation of primary immune responses and in the selective recruitment of T lymphocytes to the lung. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1113–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roser B. The origins, kinetics, and fate of macrophage populations. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Aug;8(2):139–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberberg-Sinakin I., Thorbecke G. J., Baer R. L., Rosenthal S. A., Berezowsky V. Antigen-bearing langerhans cells in skin, dermal lymphatics and in lymph nodes. Cell Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., McIntosh G. H., Morris B. The traffic of cells through tissues: a study of peripheral lymph in sheep. J Anat. 1970 Jul;107(Pt 1):87–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van oud Alblas A. B., van Furth R. Origin, Kinetics, and characteristics of pulmonary macrophages in the normal steady state. J Exp Med. 1979 Jun 1;149(6):1504–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




