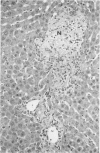
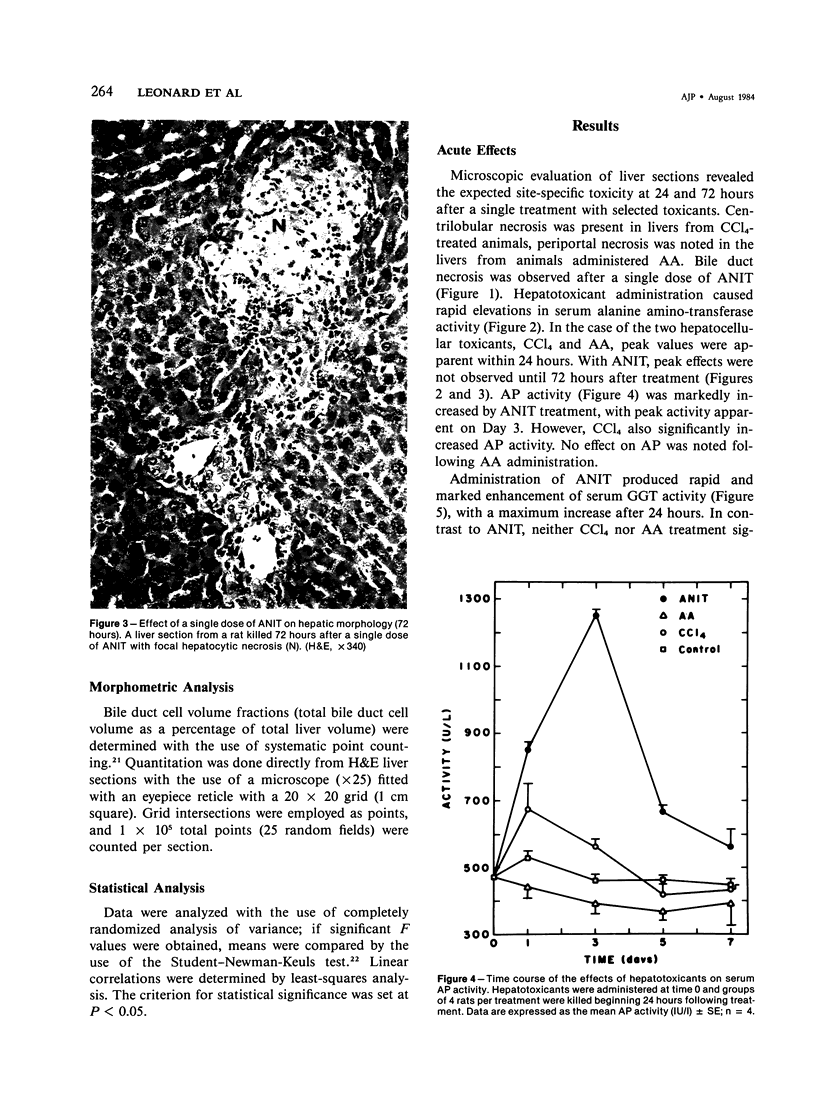
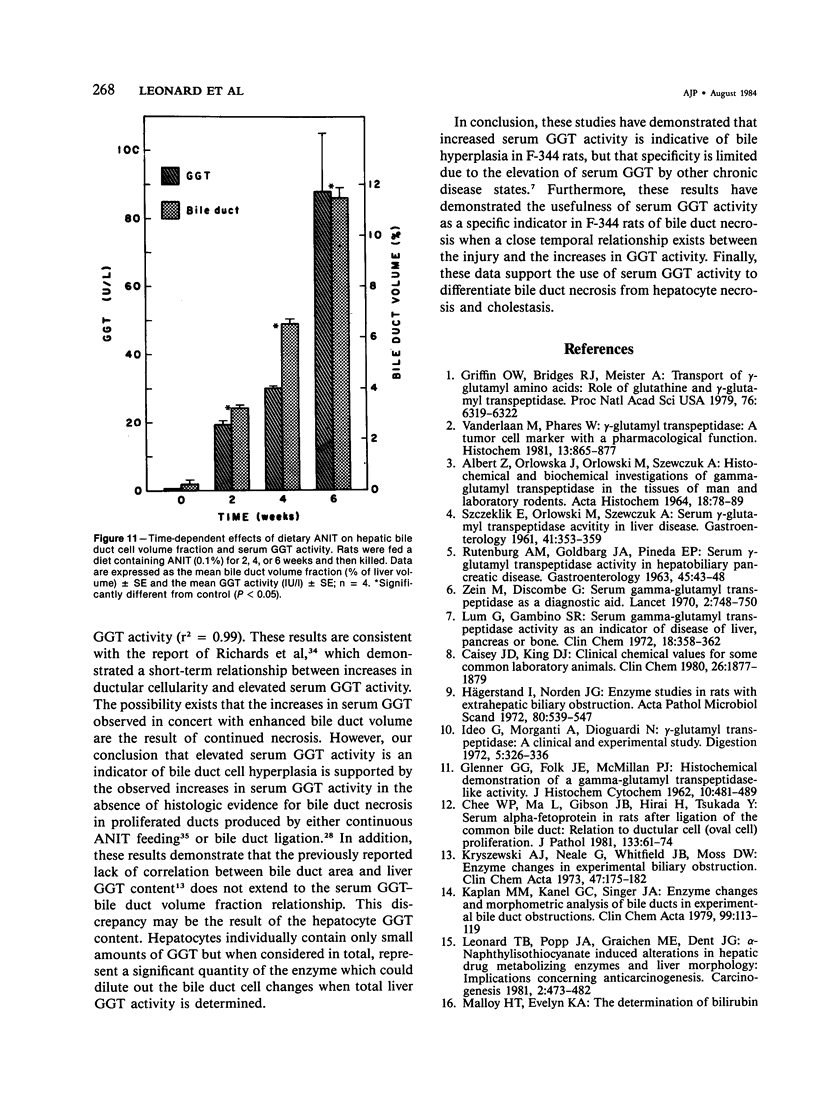
Abstract
Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), a marker of hepatic injury used extensively in humans, has been used rarely in rats because its specificity has not been previously defined. Studies were designed for investigation of the specificity of serum GGT activity with the use of cell type specific hepatotoxicants in Fischer 344 rats. Single necrogenic doses of CCl4, allyl alcohol (AA), and alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) were used to produce cell specific injury in centrilobular hepatocytes, periportal hepatocytes, and bile duct cells, respectively. Administration of CCl4 markedly increased serum activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (AP), and serum bile acid concentrations within 24 hours but had no effect on serum GGT activity. ANIT treatment increased serum GGT and AP activities and bile acid concentration 24 hours following administration. Allyl alcohol administration increased serum ALT activity but had no effect on GGT activity. Administration of ANIT in the diet at 0.01%, 0.022%, 0.047%, and 0.1% for 2, 4, and 6 weeks produced dose- and time-dependent increases in serum GGT activity which strongly correlated with quantitative increases in hepatic bile duct volume, which was determined morphometrically. These observations support the use of serum GGT activity in the rat as diagnostic of bile duct cell necrosis when increases are detected shortly after the insult and as an indicator of possible bile duct hyperplasia.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT Z., ORLOWSKA J., ORLOWSKI M., SZEWCZUK A. HISTOCHEMICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL INVESTIGATIONS OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE IN THE TISSUES OF MAN AND LABORATORY RODENTS. Acta Histochem. 1964 May 30;18:78–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers G. N., Jr, McComb R. B. A continuous spectrophotometric method for measuring the activity of serum alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1966 Feb;12(2):70–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caisey J. D., King D. J. Clinical chemical values for some common laboratory animals. Clin Chem. 1980 Dec;26(13):1877–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmet V. J., Krstulović B., Van Damme B. Histochemical study of rat liver in alpha-naphthyl isothiocyanate (ANIT) induced cholestasis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):401–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath C., Prentice D. E., Street A. E., Crook D. Serum bile acid concentration in some experimental liver lesions of rat. Toxicology. 1980;15(2):113–127. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Bridges R. J., Meister A. Transport of gamma-glutamyl amino acids: role of glutathione and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6319–6322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY R. J., CHIAMORI N., GOLUB O. J., BERKMAN S. Revised spectrophotometric methods for the determination of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase, glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, and lactic acid dehydrogenase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Oct;34:381–398. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.4_ts.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hägerstrand I., Nordén J. G. Enzyme studies in rats with extra-hepatic biliary obstruction. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1972;80(4):539–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idéo G., Morganti A., Dioguardi N. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: a clinical and experimental study. Digestion. 1972;5(6):326–336. doi: 10.1159/000197206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarzabek J. I., Kampa I. S. A correlation of serum bile acid levels with conventional biochemical parameters in the assessment of hepatobiliary dysfunctions. Clin Biochem. 1981 Dec;14(6):309–310. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(81)91052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Kanel G. C., Singer J. A. Enzyme changes and morphometric analysis of bile ducts in experimental bile duct obstruction. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Dec 3;99(2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krstulović B., Van Damme, Desmet V. J. Comparative histochemical study of rat liver in bile-duct ligation and in alpha-napthyl isothiocyanate (ANIT) intoxication. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):423–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszewski A. J., Neale G., Whitfield J. B., Moss D. W. Enzyme changes in experimental biliary obstruction. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Aug 30;47(2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard T. B., Popp J. A., Graichen M. E., Dent J. G. alpha-Naphthylisothiocyanate induced alterations in hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes and liver morphology: implications concerning anticarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(6):473–482. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.6.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnet K., Kelbaek H., Frandsen P. Predictive value of the concentration in serum of total 3 alpha-hydroxy bile acids in the diagnosis of hepatobiliary disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1982 Mar;17(2):263–268. doi: 10.3109/00365528209182050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum G., Gambino S. R. Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity as an indicator of disease of liver, pancreas, or bone. Clin Chem. 1972 Apr;18(4):358–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashige F., Imai K., Osuga T. A simple and sensitive assay of total serum bile acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jul 1;70(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLEAN M. R., REES K. R. Hyperplasia of bile-ducts induced by alpha-naphthyl-iso-thiocyanate: experimental biliary cirrhosis free from biliary obstruction. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):175–188. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaa G. L., Priestly B. G. Intrahepatic cholestasis induced by drugs and chemicals. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Sep;28(3):207–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTTENBURG A. M., GOLDBARG J. A., PINEDA E. P. SERUM GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE ACTIVITY IN HEPATOBILIARY PANCREATIC DISEASE. Gastroenterology. 1963 Jul;45:43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. L., Tsukada Y., Potter V. R. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase and alpha-fetoprotein expression during alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5133–5138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER J. W., CARRUTHERS J. S. Electron microscopy of hyperplastic ductular cells in alpha-naphthyl isothiocyanateinduced cirrhosis. Lab Invest. 1963 Apr;12:471–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaeger R., Haux P., Kattermann R. Studies on the mechanism of the increase in serum alkaline phosphatase activity in cholestasis: significance of the hepatic bile acid concentration for the leakage of alkaline phosphatase from rat liver. Enzyme. 1982;28(1):3–13. doi: 10.1159/000459078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener S., Braun J. P., Rico A. G., Benard P., Burgat-Sacaze V. Urine gamma-glutamyl transferase in rat kidney toxicology: nephropathy by repeated injections of mercuric chloride. Effects of sodium selenite. Toxicology. 1979 Mar-Apr;12(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(79)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. M., Hornbuckle W. Diagnostic use of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase in canine liver disease. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Sep;40(9):1321–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szasz G. A kinetic photometric method for serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Clin Chem. 1969 Feb;15(2):124–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderlaan M., Phares W. gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase: a tumour cell marker with a pharmacological function. Histochem J. 1981 Sep;13(5):865–877. doi: 10.1007/BF01003295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. C., Ma L., Gibson J. B., Hirai H., Tsukada Y. Serum alpha-fetoprotein in rats after ligation of the common bile duct: relation to ductular cell (oval cell) proliferation. J Pathol. 1981 Jan;133(1):61–74. doi: 10.1002/path.1711330107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein M., Discombe G. Serum gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as a diagnostic aid. Lancet. 1970 Oct 10;2(7676):748–750. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]